KeepDelta
KeepDelta: A Python Library for Human-Readable Data Differencing - Published in JOSS (2025)
Science Score: 93.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 6 DOI reference(s) in README and JOSS metadata -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: joss.theoj.org -
○Academic email domains
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
✓JOSS paper metadata
Published in Journal of Open Source Software
Keywords
Repository
A Python Library for Human-Readable Data Differencing
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: aslan-ng
- License: mit
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://pypi.org/project/keepdelta/
- Size: 15.4 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 0
- Releases: 11
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
KeepDelta
A Python Library for Human-Readable Data Differencing
[](https://joss.theoj.org/papers/fe9cc7429528b344b4b6561fdf674f45)
KeepDelta is a lightweight Python library designed to efficiently track and manage changes (deltas) between Python built-in types. It is applicable to various scenarios that require dynamic data management, especially when incremental numerical changes are present, such as simulations and sensing. While many alternative tools operate at the binary level, KeepDelta emphasizes human-readable delta encoding, facilitating debugging and analysis for Python developers and researchers across multiple domains.
What is Delta Encoding?
In many computational scenarios, efficiently managing evolving data is crucial. Traditional methods, that rely on full-state encoding — which means storing and/or transmitting complete snapshots at each step — can be inefficient due to the large size of the snapshots. Delta encoding addresses this challenge by capturing and applying only the changes (deltas) between successive states of data structures, resulting in significantly smaller and more manageable data.
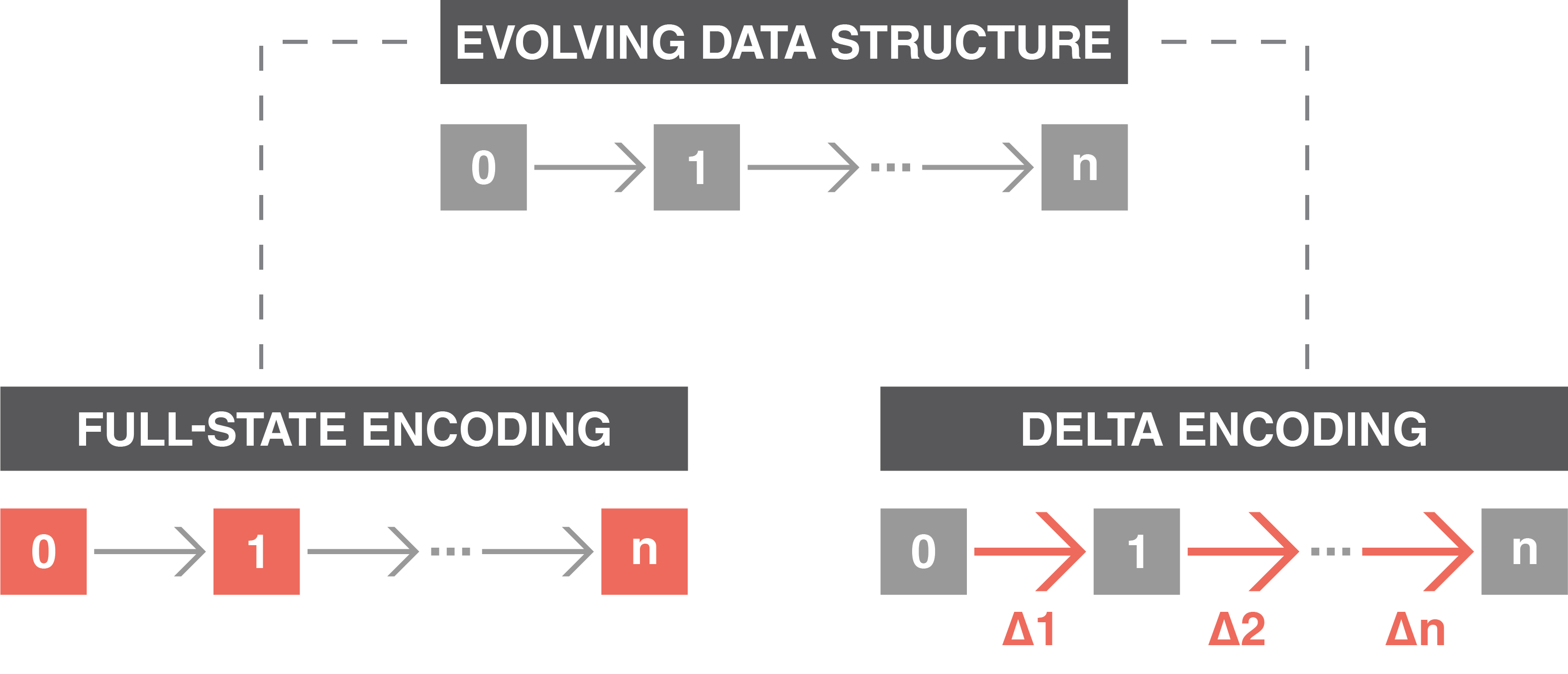
Managing evolving data structures: full-state encoding (left) stores the entire system state at each timestep, represented by colored blocks. In contrast, delta encoding (right) records only the differences between states, highlighted by colored arrows and identified by Δ, providing a more efficient solution for storage and/or transmission.
Features
- Generates compact and human-readable differences between two Python variables.
- Applies delta to a variable to reconstruct the updated version.
- Supports common Python built-in data types.
- Handles deeply nested and mixed data structures efficiently.
- Requires no external dependencies.
Installation
Install the package using pip:
sh
pip install keepdelta
Usage
There are two core methods corresponding to the creation and application of delta encodings:
1. create(old, new):
The create function compares the old and new variables to generate delta that captures the differences between two data structures. It produces a compact data structure containing only these differences, and its high human readability greatly aids debugging during development.
Example:
```python
import keepdelta as kd
Initial data
old = { ... "name": "Alice", ... "age": 20, ... "is_student": True ... }
Updated data
new = { ... "name": "Alice", ... "age": 25, ... "is_student": False ... }
Create delta
delta = kd.create(old, new) print(delta) { "age": 5, "is_student": False } ```
2. apply(old, delta):
The apply function takes the old variable and the delta, then applies the delta to recreate the updated, new variable.
Example:
```python
import keepdelta as kd
Initial data
old = { ... "name": "Alice", ... "age": 20, ... "is_student": True ... }
Delta
delta = { ... "age": 5, ... "is_student": False ... }
Apply delta
new = kd.apply(old, delta) print(new) { "name": "Alice", "age": 25, "is_student": False } ```
For more usage examples, refer to the examples folder in the project repository, or continue to the next section, "Supported Data Types & Behaviors”, for a detailed look at how each structure is handled.
Supported Data Types & Behaviors
KeepDelta supports common native Python data structures, ensuring compatibility and flexibility when working with a wide variety of data types. The currently supported structures are listed below. Click any item to see how it’s handled and view a quick example:
🔸 Primitive Types:
Boolean (bool)
Since booleans have only two states, the delta is simply the new state (True or False). #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = False >>> # Updated data >>> new = True >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) True ```
String (str)
The delta for strings is simply the new string value. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = "hello" >>> # Updated data >>> new = "bye" >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) bye ```
Integer (int)
For integers, the delta is computed as subtraction of values, yielding the offset to apply during reconstruction. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = 42 >>> # Updated data >>> new = 45 >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) 3 ```
Float (float)
For floats, the delta is computed as subtraction of values, yielding the offset to apply during reconstruction. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = 3.13 >>> # Updated data >>> new = 3.14 >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) 0.01 ```
Complex (complex)
For complex numbers, the delta is computed as subtraction of values, yielding the offset to apply during reconstruction. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = 3+4j >>> # Updated data >>> new = 1+5j >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) (-2+1j) ```
NoneType (None)
Since KeepDelta supports type change, it is possible to track the changes from `None` to other types or vise versa. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = 1.62 >>> # Updated data >>> new = None >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) None ```
🔸 Collections:
Dictionary (dict)
When diffing dictionaries, key-value pairs in the inputs are compared. The key removal is marked with the special token `__delete__`. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = { ... "location": "earth", ... "age": 20, ... "snacks": ["chocolate", "bananas"], ... "student": True, ... } >>> # Updated data >>> new = { ... "location": "mars", ... "age": 30, ... "snacks": ["chocolate", "bananas"], ... "happy": True, ... } >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) { "location": "mars", # Location changed from "earth" → "mars" "age": 10, # Age increased by 10 "student": "__delete__", # The removed key "happy": True # The newly added key } ```
List (list)
The delta for a list is a dictionary where each key is a list index and each value describes the change applied at that position; including a numerical offset (to adjust the original element) or `__delete__` (to remove it). #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = [2, 3, 5, 7] >>> # Updated data >>> new = [2, 3, 4] >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) { 2: -1, # Third element has been decreased by 1 3: "__delete__" # Fourth element has been deleted } ```
Tuple (tuple)
The delta for a tuple is a dictionary where each key is a list index and each value describes the change applied at that position; including a numerical offset (to adjust the original element) or `__delete__` (to remove it). #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = (2, 3, 5, 7) >>> # Updated data >>> new = (2, 3, 4) >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) { 2: -1, # Third element has been decreased by 1 3: "__delete__" # Fourth element has been deleted } ```
Set (set)
For sets, the delta is a dict with two special keys: `__add__` for items to add and `__remove__` for items to drop. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = {1, 2, 3} >>> # Updated data >>> new = {2, 3, 5, 7} >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) { "__add__": {5, 7}, # Numbers added "__remove__": {1} # Numbers removed } ```
Nested & Composite Structures
KeepDelta supports deeply nested combinations of variables, enabling structures like dictionaries of dictionaries, lists of sets, and other complex, interwoven data types. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = { ... "name": "Alice", ... "age": 20, ... "is_student": True, ... "grades": [85.5, 90.0, 78], ... "preferences": { ... "drink": "soda", ... "sports": {"football", "tennis"}, ... }, ... } >>> # Updated data >>> new = { ... "name": "Alice", ... "age": 25, ... "is_student": False, ... "grades": [87, 90.0, 78, 92], ... "preferences": { ... "drink": "coffee", ... "sports": {"football", "bodybuilding"}, ... }, ... } >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) { "is_student": False, # Changed from True → False "grades": { 0: 87, # Updated from 85.5 → 87 3: 92 # New grade appended }, "preferences": { "drink": "coffee", # Switched from “soda” → "coffee" "sports": { "__add__": {"bodybuilding"}, # Sport added "__remove__": {"tennis"} # Sport removed } }, "age": 5 # Increased by 5 } ```
🔸 Special Cases:
Type Conversion
KeepDelta supports changing variables types. In that case, the delta is simply the new value. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = "hello" >>> # Updated data >>> new = 3.14 >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) 3.14 # Type changed from string to float ```
No‑Change Cases
If no differences are found between the two inputs, KeepDelta returns the special token `__nothing__`, indicating that no changes are needed. #### Example: ```python >>> import keepdelta as kd >>> # Initial data >>> old = "hello" >>> # Updated data >>> new = "hello" >>> # Create delta >>> delta = kd.create(old, new) >>> print(delta) "__nothing__" # Both inputs are identical ```
Supported Python Versions
KeepDelta has been tested and verified to work with Python versions 3.7 to 3.13. While it is expected to work with older versions, they have not been tested and are not officially supported.
Citing KeepDelta
If you use KeepDelta in your work, please cite our paper.
You can either:
- Click the “Cite this repository” button at the top of the GitHub page and copy the generated APA or BibTeX.
Or
- Copy one of the entries below:
BibTeX:
bibtex
@article{Noorghasemi_KeepDelta_A_Python_2025,
author = {Noorghasemi, Aslan and McComb, Christopher},
doi = {10.21105/joss.08075},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software},
month = jun,
number = {110},
pages = {8075},
title = {{KeepDelta: A Python Library for Human-Readable Data Differencing}},
url = {https://joss.theoj.org/papers/10.21105/joss.08075},
volume = {10},
year = {2025}
}
APA:
Noorghasemi, A., & McComb, C. (2025). KeepDelta: A Python Library for Human-Readable Data Differencing. Journal of Open Source Software, 10(110), 8075. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.08075
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Feel free to: * Report issues. * Submit feature requests. * Create pull requests.
License
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE.txt for more information.
Owner
- Name: Aslan Noorghasemi
- Login: aslan-ng
- Kind: user
- Location: Earth
- Twitter: Aslan_NGH
- Repositories: 1
- Profile: https://github.com/aslan-ng
Trying to write my own version of "Hello World"
JOSS Publication
KeepDelta: A Python Library for Human-Readable Data Differencing
Authors
Tags
python simulation sensing data structures data differencing delta encoding delta compression differential compression change tracking human-readableGitHub Events
Total
- Release event: 9
- Watch event: 5
- Delete event: 4
- Push event: 133
- Pull request event: 2
- Fork event: 1
- Create event: 13
Last Year
- Release event: 9
- Watch event: 5
- Delete event: 4
- Push event: 133
- Pull request event: 2
- Fork event: 1
- Create event: 13
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 0
- Total pull requests: 2
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: about 23 hours
- Total issue authors: 0
- Total pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 2
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 0
- Pull requests: 2
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: about 23 hours
- Issue authors: 0
- Pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 2
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
Pull Request Authors
- cmccomb (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 81 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 11
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: keepdelta
A Python Library for Human-Readable Data Differencing
- Documentation: https://keepdelta.readthedocs.io/
- License: MIT
-
Latest release: 0.2.0
published 8 months ago
