GemGIS - Spatial Data Processing for Geomodeling
GemGIS - Spatial Data Processing for Geomodeling - Published in JOSS (2022)
Science Score: 98.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 21 DOI reference(s) in README and JOSS metadata -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: joss.theoj.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
5 of 16 committers (31.3%) from academic institutions -
✓Institutional organization owner
Organization cgre-aachen has institutional domain (www.cgre.rwth-aachen.de) -
✓JOSS paper metadata
Published in Journal of Open Source Software
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Repository
Spatial data processing for geomodeling
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: cgre-aachen
- License: lgpl-3.0
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://gemgis.readthedocs.io/en/latest
- Size: 903 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 278
- Watchers: 17
- Forks: 43
- Open Issues: 31
- Releases: 32
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
GemGIS - Spatial data and information processing for geomodeling and subsurface data
 [](https://www.python.org/downloads/)



[](https://www.repostatus.org/#active)

[](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03709)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/)



[](https://www.repostatus.org/#active)

[](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03709)
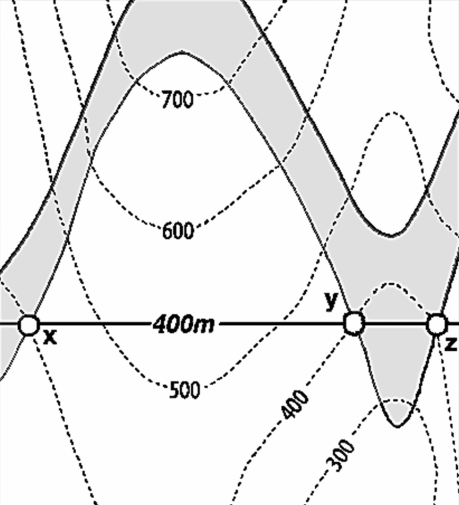
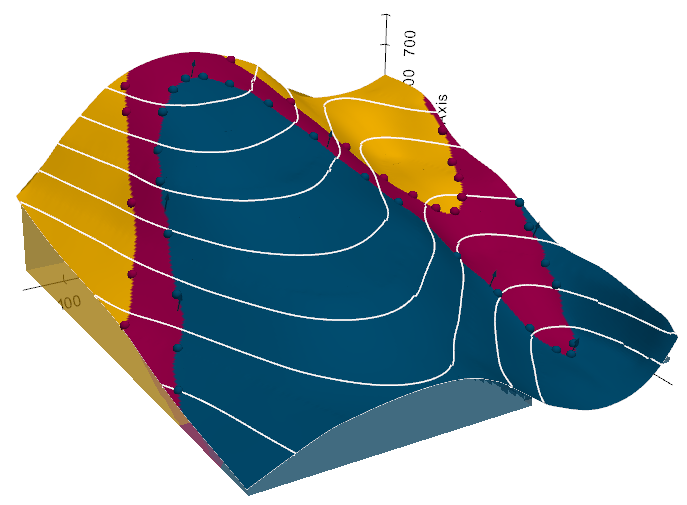
Overview
We attempt to simplify the access to open-source spatial data processing for geological modeling and for subsurface data (wells, seismic, etc.) with the development of GemGIS, a Python-based open-source library.
GemGIS wraps and extends the functionality of packages known to the geo-community such as GeoPandas, rasterio, OWSLib, Shapely, PyVista, Pandas, NumPy and the geomodeling package GemPy. GemGIS works with the latest release of Gempy (2025.2.0).
The aim of GemGIS, as indicated by the name, is to become a bridge between conventional geoinformation systems (GIS) such as ArcGIS and QGIS, and geomodeling tools such as GemPy, allowing simpler and more automated workflows from one environment to the other. This also includes making it simpler to visualize the results obtained from GemGIS and GemPy with PyVista or Blender. Further, subsurface data processing workflows are implemented for integrated data analyses.
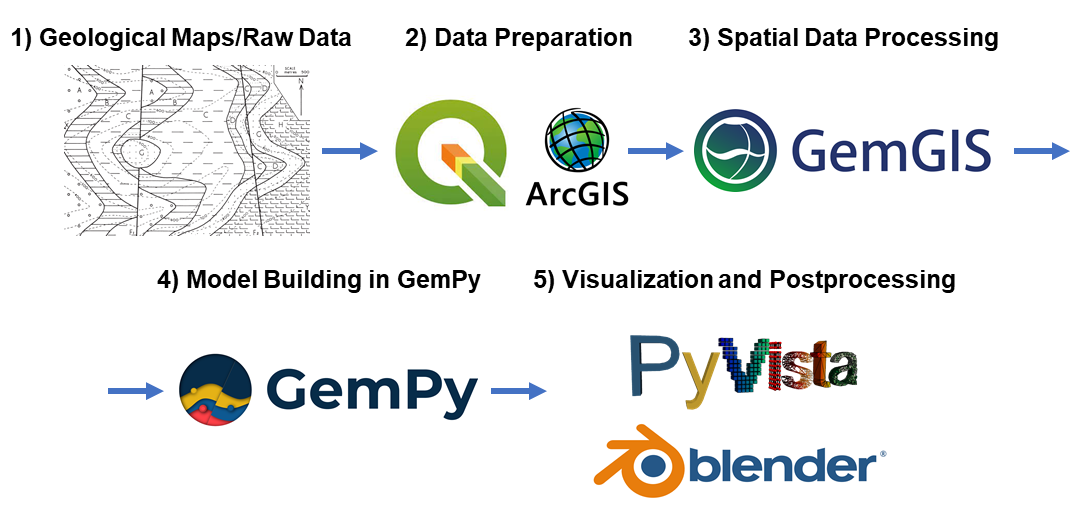
Resources
Find the documentation of GemGIS here. It includes introductions to the main libraries used and to introductory topics like "What is vector data?" or "What is raster data?".
In addition, tutorial notebooks provide an overview of the different features of GemGIS. The notebooks can also be downloaded directly from here. Furthermore, many example models showcase a variety of geological structures that can be modeled with GemGIS and GemPy. The API Reference provides an overview of the implemented functions in GemGIS and how to use them.
Installation
It is recommended to use GemGIS with python">=3.11" in a separated environment. The main packages and its dependencies can be installed via the conda-forge channel. GemGIS is then available through PyPi or Conda.
1) conda install -c conda-forge geopandas">=1.1.1" rasterio">=1.4.3"
2) conda install -c conda-forge pyvista">=0.46.3"
3) pip install gemgis / conda install -c conda-forge gemgis
Check out the Installation Page for more detailed instructions.
If you are an open-source software developer, please install GemGIS and its dependencies, also for building the documentation, using the development YML file.
Contribution Guidelines
The Contribution Guidelines for GemGIS can be found here: Contribution Guidelines
We welcome issue reports, questions, ideas for new features and pull-requests to fix issues or even add new features to the software. Once a pull-request is opened, we will guide through the review process.
Citation
If you use GemGIS for any published work, please cite it using the reference below:
Jstel, A., Endlein Correira, A., Pischke, M., de la Varga, M., Wellmann, F.: GemGIS - Spatial Data Processing for Geomodeling. Journal of Open Source Software, 7(73), 3709, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03709, 2022.
@article{Jstel2022,
doi = {10.21105/joss.03709},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03709},
year = {2022},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
volume = {7},
number = {73},
pages = {3709},
author = {Alexander Jstel and Arthur Endlein Correira and Marius Pischke and Miguel de la Varga and Florian Wellmann},
title = {GemGIS - Spatial Data Processing for Geomodeling},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software}
}
References and published articles utilizing GemGIS
- Jstel, A. et al.: 3D structural and probabilistic modelling of geothermal reservoir horizons in the Northern Eifel and its foreland. Zeitschrift der Deutschen Gesellschaft fr Geowissenschaften, 176 (1), 115-146, https://doi.org/10.1127/zdgg/2025/0436, 2025
- Marquetto, L. et al.: Developing a 3D hydrostratigraphical model of the emerged part of the Pelotas Basin along the northern coast of Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil. Environmental Earth Sciences, 83, 10, 329, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-024-11609-y, 2024
- Jstel, A. et al.: From Maps to Models - Tutorials for structural geological modeling using GemPy and GemGIS. Journal of Open Source Education, 6(66), 185, https://doi.org/10.21105/jose.00185, 2023.
- Jstel, A. et al.: GemGIS - Spatial Data Processing for Geomodeling. Journal of Open Source Software, 7(73), 3709, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03709, 2022.
- Jstel, A., Endlein Correira, A., Wellmann, F. and Pischke, M.: GemGIS GemPy Geographic: Open-Source Spatial Data Processing for Geological Modeling. EGU General Assembly 2021, https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu21-4613, 2021.
- Jstel, A.: 3D Probabilistic Modeling and Data Analysis of the Aachen-Weisweiler Area: Implications for Deep Geothermal Energy Exploration, unpublished Master Thesis at RWTH Aachen University, 2020.
- de la Varga, M., Schaaf, A., and Wellmann, F.: GemPy 1.0: open-source stochastic geological modeling and inversion, Geosci. Model Dev., 12, 1-32, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-1-2019, 2019.
- Powell, D.: Interpretation of Geological Structures Through Maps: An Introductory Practical Manual, Longman, pp. 192, 1992.
- Bennison, G.M.: An Introduction to Geological Structures and Maps, Hodder Education Publication, pp. 78, 1990.
Owner
- Name: Computational Geoscience and Reservoir Engineering @RWTH Aachen
- Login: cgre-aachen
- Kind: organization
- Email: florian.wellmann@cgre.rwth-aachen.de
- Location: Aachen, Germany
- Website: https://www.cgre.rwth-aachen.de
- Repositories: 36
- Profile: https://github.com/cgre-aachen
We investigate novel methods to integrate geoscientific data and knowledge in process simulations of subsurface flow and transport problems.
JOSS Publication
GemGIS - Spatial Data Processing for Geomodeling
Authors

RWTH Aachen University , Computational Geoscience and Reservoir Engineering, Wüllnerstraße 2, 52062 Aachen, Germany, Fraunhofer IEG, Fraunhofer Research Institution for Energy Infrastructures and Geothermal Systems IEG, Kockerellstraße 17, 52062 Aachen, Germany
Geovariances LATAM, Av. Do Contorno, 7218 Sala 1201, 30110–048 Belo Horizonte, Brazil
RWTH Aachen University , Computational Geoscience and Reservoir Engineering, Wüllnerstraße 2, 52062 Aachen, Germany
Terranigma Solutions GmbH, Laurentiusstraße 59, 52072 Aachen
Tags
geology geographic structural geology GIS spatial dataGitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 7
- Watch event: 17
- Issue comment event: 3
- Push event: 9
- Fork event: 1
Last Year
- Issues event: 13
- Watch event: 17
- Issue comment event: 3
- Push event: 9
- Pull request event: 1
- Fork event: 1
- Create event: 1
Committers
Last synced: 10 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Alexander Jüstel | a****l@g****m | 746 |
| alexander.juestel | a****l@r****e | 110 |
| Richard Scott | R****t@o****m | 95 |
| Jüstel | a****l@i****e | 54 |
| AlexanderJuestel | a****l@g****m | 17 |
| Wagner | j****r@i****e | 11 |
| J. Hariharan | j****n@u****u | 10 |
| Florian Wellmann | f****c@g****m | 7 |
| Miguel de la Varga | m****l@t****m | 6 |
| Blue Tyson | b****n | 4 |
| Arthur Endlein | e****r@g****m | 3 |
| Jana Decker | J****a@D****n | 3 |
| Japhiolite | j****u@r****e | 2 |
| Jonathan Pelham | j****n@g****m | 2 |
| Bane Sullivan | b****n@g****m | 1 |
| NilsChudalla | 6****a | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 123
- Total pull requests: 51
- Average time to close issues: 5 months
- Average time to close pull requests: 13 days
- Total issue authors: 28
- Total pull request authors: 4
- Average comments per issue: 2.49
- Average comments per pull request: 0.55
- Merged pull requests: 46
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 10
- Pull requests: 1
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: less than a minute
- Issue authors: 4
- Pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0.1
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 1
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- AlexanderJuestel (77)
- JanWagner1312 (6)
- kanishkan91 (6)
- ada-hou (5)
- Esras (2)
- KetMic (2)
- Magio94 (2)
- spasquet (2)
- ccastelblanco (2)
- jc-barreto (1)
- rvg1986 (1)
- SpongeGirl (1)
- CTomsu (1)
- mluck (1)
- brbr520 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- AlexanderJuestel (40)
- JanWagner1312 (9)
- banesullivan (1)
- obadakhalili (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 3
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 324 last-month
- Total docker downloads: 147
-
Total dependent packages: 2
(may contain duplicates) -
Total dependent repositories: 7
(may contain duplicates) - Total versions: 68
- Total maintainers: 2
proxy.golang.org: github.com/cgre-aachen/gemgis
- Documentation: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/cgre-aachen/gemgis#section-documentation
- License: lgpl-3.0
-
Latest release: v1.1.8
published about 2 years ago
Rankings
pypi.org: gemgis
Spatial data processing for geomodeling
- Homepage: https://gemgis.readthedocs.io/
- Documentation: https://gemgis.readthedocs.io/
- License: GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE Version 3, 29 June 2007 Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc. <http://fsf.org/> Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this license document, but changing it is not allowed. This version of the GNU Lesser General Public License incorporates the terms and conditions of version 3 of the GNU General Public License, supplemented by the additional permissions listed below. 0. Additional Definitions. As used herein, "this License" refers to version 3 of the GNU Lesser General Public License, and the "GNU GPL" refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License. "The Library" refers to a covered work governed by this License, other than an Application or a Combined Work as defined below. An "Application" is any work that makes use of an interface provided by the Library, but which is not otherwise based on the Library. Defining a subclass of a class defined by the Library is deemed a mode of using an interface provided by the Library. A "Combined Work" is a work produced by combining or linking an Application with the Library. The particular version of the Library with which the Combined Work was made is also called the "Linked Version". The "Minimal Corresponding Source" for a Combined Work means the Corresponding Source for the Combined Work, excluding any source code for portions of the Combined Work that, considered in isolation, are based on the Application, and not on the Linked Version. The "Corresponding Application Code" for a Combined Work means the object code and/or source code for the Application, including any data and utility programs needed for reproducing the Combined Work from the Application, but excluding the System Libraries of the Combined Work. 1. Exception to Section 3 of the GNU GPL. You may convey a covered work under sections 3 and 4 of this License without being bound by section 3 of the GNU GPL. 2. Conveying Modified Versions. If you modify a copy of the Library, and, in your modifications, a facility refers to a function or data to be supplied by an Application that uses the facility (other than as an argument passed when the facility is invoked), then you may convey a copy of the modified version: a) under this License, provided that you make a good faith effort to ensure that, in the event an Application does not supply the function or data, the facility still operates, and performs whatever part of its purpose remains meaningful, or b) under the GNU GPL, with none of the additional permissions of this License applicable to that copy. 3. Object Code Incorporating Material from Library Header Files. The object code form of an Application may incorporate material from a header file that is part of the Library. You may convey such object code under terms of your choice, provided that, if the incorporated material is not limited to numerical parameters, data structure layouts and accessors, or small macros, inline functions and templates (ten or fewer lines in length), you do both of the following: a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the object code that the Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are covered by this License. b) Accompany the object code with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license document. 4. Combined Works. You may convey a Combined Work under terms of your choice that, taken together, effectively do not restrict modification of the portions of the Library contained in the Combined Work and reverse engineering for debugging such modifications, if you also do each of the following: a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the Combined Work that the Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are covered by this License. b) Accompany the Combined Work with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license document. c) For a Combined Work that displays copyright notices during execution, include the copyright notice for the Library among these notices, as well as a reference directing the user to the copies of the GNU GPL and this license document. d) Do one of the following: 0) Convey the Minimal Corresponding Source under the terms of this License, and the Corresponding Application Code in a form suitable for, and under terms that permit, the user to recombine or relink the Application with a modified version of the Linked Version to produce a modified Combined Work, in the manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL for conveying Corresponding Source. 1) Use a suitable shared library mechanism for linking with the Library. A suitable mechanism is one that (a) uses at run time a copy of the Library already present on the user's computer system, and (b) will operate properly with a modified version of the Library that is interface-compatible with the Linked Version. e) Provide Installation Information, but only if you would otherwise be required to provide such information under section 6 of the GNU GPL, and only to the extent that such information is necessary to install and execute a modified version of the Combined Work produced by recombining or relinking the Application with a modified version of the Linked Version. (If you use option 4d0, the Installation Information must accompany the Minimal Corresponding Source and Corresponding Application Code. If you use option 4d1, you must provide the Installation Information in the manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL for conveying Corresponding Source.) 5. Combined Libraries. You may place library facilities that are a work based on the Library side by side in a single library together with other library facilities that are not Applications and are not covered by this License, and convey such a combined library under terms of your choice, if you do both of the following: a) Accompany the combined library with a copy of the same work based on the Library, uncombined with any other library facilities, conveyed under the terms of this License. b) Give prominent notice with the combined library that part of it is a work based on the Library, and explaining where to find the accompanying uncombined form of the same work. 6. Revised Versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License. The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to address new problems or concerns. Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Library as you received it specifies that a certain numbered version of the GNU Lesser General Public License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and conditions either of that published version or of any later version published by the Free Software Foundation. If the Library as you received it does not specify a version number of the GNU Lesser General Public License, you may choose any version of the GNU Lesser General Public License ever published by the Free Software Foundation. If the Library as you received it specifies that a proxy can decide whether future versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License shall apply, that proxy's public statement of acceptance of any version is permanent authorization for you to choose that version for the Library.
-
Latest release: 1.1.8
published about 2 years ago
Rankings
Maintainers (2)
conda-forge.org: gemgis
- Homepage: https://github.com/cgre-aachen/gemgis
- License: LGPL-3.0-only
-
Latest release: 1.0.0
published almost 4 years ago
Rankings
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/upload-artifact v1 composite
- openjournals/openjournals-draft-action master composite
- actions/first-interaction v1 composite
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/setup-python v2 composite
- actions/stale v7 composite
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- conda-incubator/setup-miniconda v2 composite