profit
Probabilistic Response mOdel Fitting with Interactive Tools
Science Score: 54.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
✓Academic publication links
Links to: zenodo.org -
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (17.3%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Repository
Probabilistic Response mOdel Fitting with Interactive Tools
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: redmod-team
- License: mit
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: master
- Homepage: https://profit.readthedocs.io
- Size: 3.71 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 15
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 10
- Open Issues: 28
- Releases: 8
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md

Probabilistic Response Model Fitting with Interactive Tools
This is a collection of tools for studying parametric dependencies of black-box simulation codes or experiments and construction of reduced order response models over input parameter space.
proFit can be fed with a number of data points consisting of different input parameter combinations and the resulting output of the simulation under investigation. It then fits a response-surface through the point cloud using Gaussian process regression (GPR) models. This probabilistic response model allows to predict ("interpolate") the output at yet unexplored parameter combinations including uncertainty estimates. It can also tell you where to put more training points to gain maximum new information (experimental design) and automatically generate and start new simulation runs locally or on a cluster. Results can be explored and checked visually in a web frontend.
Telling proFit how to interact with your existing simulations is easy and requires no changes in your existing code. Current functionality covers starting simulations locally or on a cluster via Slurm, subsequent surrogate modelling using GPy, scikit-learn, as well as an active learning algorithm to iteratively sample at interesting points and a Markov-Chain-Monte-Carlo (MCMC) algorithm. The web frontend to interactively explore the point cloud and surrogate is based on plotly/dash.
Features
- Compute evaluation points (e.g. from a random distribution) to run simulation
- Template replacement and automatic generation of run directories
- Starting parallel runs locally or on the cluster (SLURM)
- Collection of result output and postprocessing
- Response-model fitting using Gaussian Process Regression and Linear Regression
- Active learning to reduce number of samples needed
- MCMC to find a posterior parameter distribution (similar to active learning)
- Graphical user interface to explore the results
Installation
Currently, the code is under heavy development, so it should be cloned from GitHub via Git and pulled regularly.
Requirements
bash
sudo apt install python3-dev build-essential
To enable compilation of the fortran modules the following is needed:
bash
sudo apt install gfortran
Dependencies
- numpy, scipy, matplotlib, sympy, pandas
- ChaosPy
- GPy
- scikit-learn
- h5py
- plotly/dash - for the UI
- ZeroMQ - for messaging
- sphinx - for documentation, only needed when
docsis specified - torch, GPyTorch - only needed when
gpuis specified
All dependencies are configured in setup.cfg and should be installed automatically when using pip.
Automatic tests use pytest.
Windows 10
To install proFit under Windows 10 we recommend using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2) with the Ubuntu 20.04 LTS distribution (install guide).
After the installation of WSL2 execute the following steps in your Linux terminal (when asked press y to continue):
Make sure you have the right version of Python installed and the basic developer toolset available
bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip python3-dev build-essential
To install proFit from Git (see below), make sure that the project is located in the Linux file system not the Windows system.
To configure the Python interpreter available in your Linux distribution in pycharm (tested with professional edition) follow this guide.
Installation from PyPI
To install the latest stable version of proFit, use
bash
pip install profit
For the latest pre-release, use
bash
pip install --pre profit
Installation from Git
To install proFit for the current user (--user) in development-mode (-e) use:
bash
git clone https://github.com/redmod-team/profit.git
cd profit
pip install -e . --user
Fortran
Certain surrogates require a compiled Fortran backend. To enable compilation of the fortran modules during install:
USE_FORTRAN=1 pip install .
Troubleshooting installation problems
Make sure you have all the requirements mentioned above installed.
If
pipis not recognized try the following:bash python3 -m pip install -e . --userIf pip warns you about PATH or proFit is not found close and reopen the terminal and type
profit --helpto check if the installation was successful.
Documentation using Sphinx
Install requirements for building the documentation using sphinx
pip install .[docs]
Additionally pandoc is required on a system level:
sudo apt install pandoc
HowTo
Examples for different model codes are available under examples/:
* fit: Simple fit via python interface.
* mockup: Simple model called by console command based on template directory.
Also, the integration tests under tests/integration_tests/ may be informative examples:
* active_learning:
* 1D: One dimensional mockup with active learning
* 2D: Two dimensional mockup with active learning
* Log: Active learning with logarithmic search space
* MCMC: Markov-Chain-Monte-Carlo application to mockup experimental data
* mockup:
* 1D
* 2D
* Custom postprocessor: Instead of the prebuilt postprocessor, a user-built class is used.
* Custom worker: A user-built worker function is used.
* Independent: Output with an independent (linear) variable additional to input parameters: f(t; u, v).
* KarhunenLoeve: Multi output surrogate model with Karhunen-Loeve encoder.
* Multi output: Multi output surrogate with two different output variables.
Steps
Create and enter a directory (e.g.
study) containingprofit.yamlfor your run. If your code is based on text configuration files for each run, copy the according directory totemplateand replace values of parameters to be varied within UQ/surrogate models by placeholders{param}.Running the simulations:
bash profit runto start simulations at all the points. Per default the generated input variables are written toinput.txtand the output data is collected inoutput.txt.
For each run of the simulation, proFit creates a run directory, fills the templates with the generated input data and collects the results. Each step can be customized with the configuration file.
To fit the model:
bash profit fitCustomization can be done withprofit.yamlagain.Explore data graphically:
bash profit uistarts a Dash-based browser UI
The figure below gives a graphical representation of the typical profit workflow described above. The boxes in red describe user actions while the boxes in blue are conducted by profit.
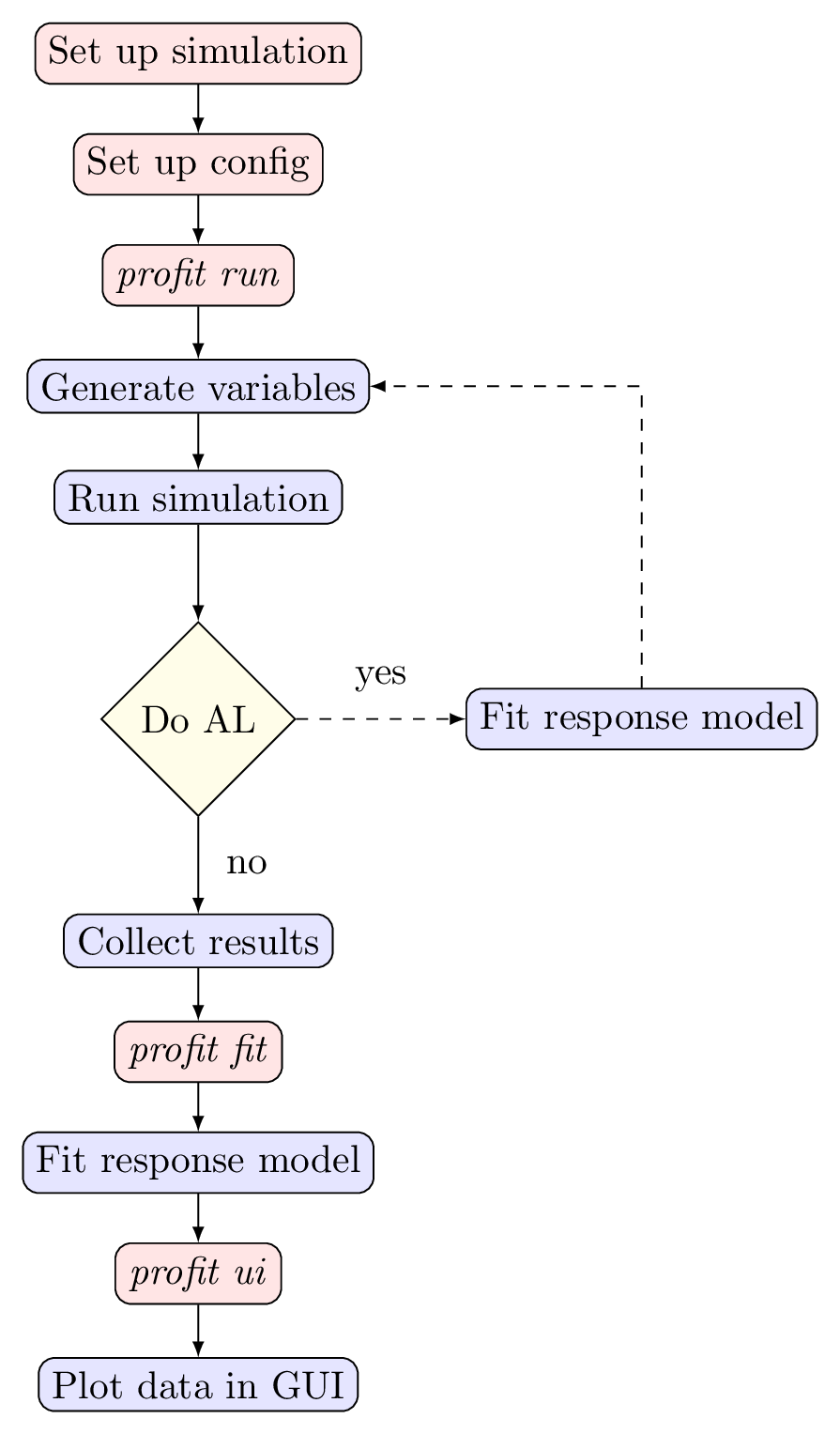
Cluster
proFit supports scheduling the runs on a cluster using slurm. This is done entirely via the configuration files and the usage doesn't change.
profit ui starts a dash server and it is possible to remotely connect to it (e.g. via ssh port forwarding)
User-supplied files
a configuration file: (default:
profit.yaml)- Add parameters and their distributions via
variables - Set paths and filenames
- Configure the run backend (how to interact with the simulation)
- Configure the fit / surrogate model
- Add parameters and their distributions via
the
templatedirectory- containing everything a simulation run needs (scripts, links to executables, input files, etc)
- input files use a template format where
{variable_name}is substituted with the generated values
a custom Postprocessor (optional)
- if the default postprocessors don't work with the simulation a custom one can be specified using the
includeparameter in the configuration.
- if the default postprocessors don't work with the simulation a custom one can be specified using the
Example directory structure:
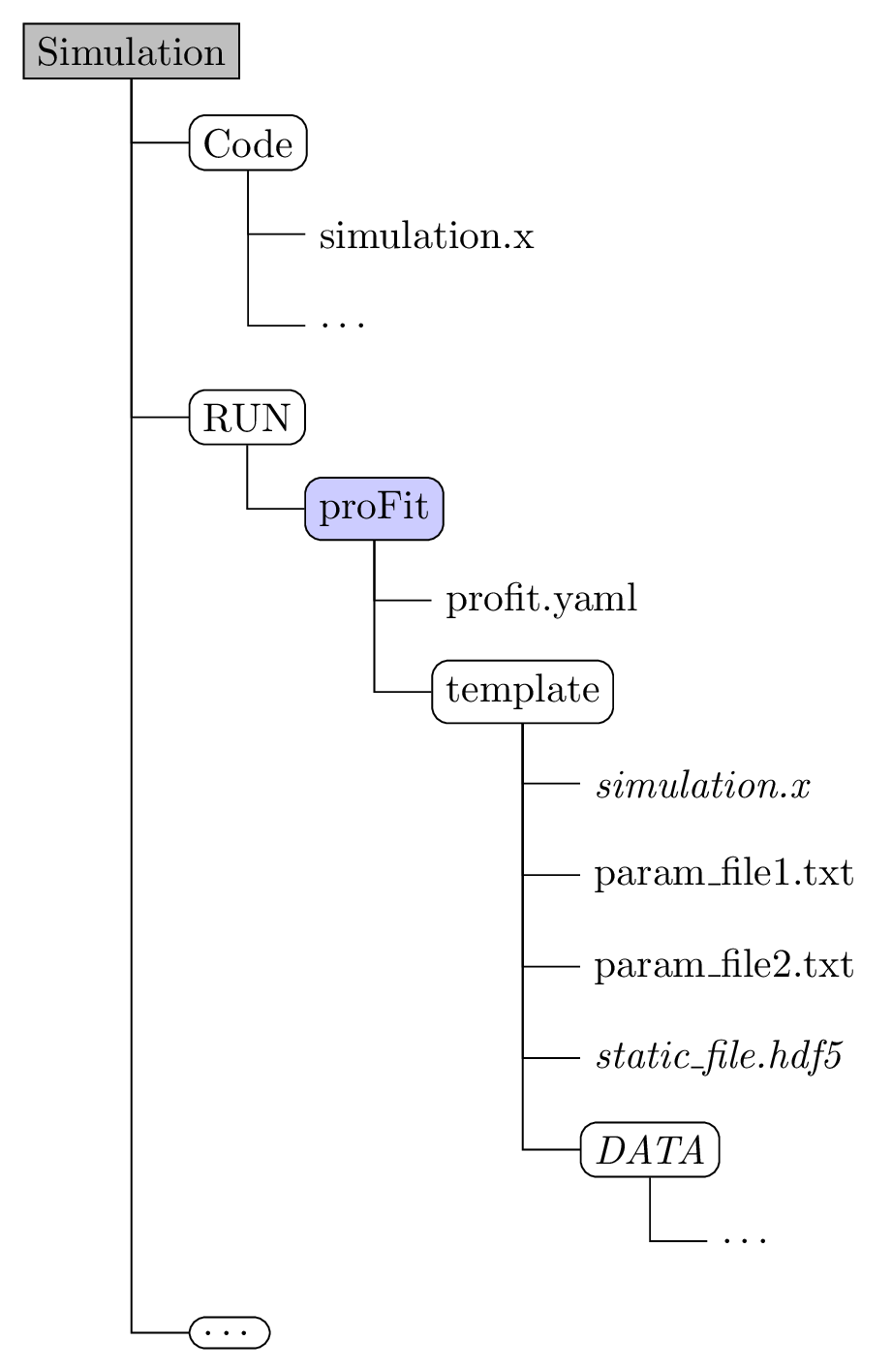
Owner
- Name: RedMod Team
- Login: redmod-team
- Kind: organization
- Repositories: 2
- Profile: https://github.com/redmod-team
Citation (CITATION.cff)
# This CITATION.cff file was generated with cffinit.
# Visit https://bit.ly/cffinit to generate yours today!
cff-version: 1.2.0
title: >-
proFit: Probabilistic Response Model Fitting with
Interactive Tools
message: >-
If you use this software, please cite it using the
metadata from this file. To cite a specific version of
DESC, please cite the correct version from Zenodo at
https://zenodo.org/search?page=1&size=20&q=conceptrecid:%223580488%22&sort=-version&all_versions=True
type: software
license: MIT
authors:
- given-names: Christopher
family-names: ' Albert'
affiliation: Technische Universität Graz
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4773-416X'
email: albert@tugraz.at
- given-names: Maximilian
family-names: Kendler
affiliation: Technische Universität Graz
- given-names: Robert
family-names: Babin
affiliation: Technische Universität Graz
- given-names: Michael
family-names: Hadwiger
affiliation: Technische Universität Graz
- given-names: Richard
family-names: Hofmeister
affiliation: Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht
- given-names: Manal
family-names: Khallaayoune
affiliation: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik
- given-names: Francesco
family-names: Kramp
affiliation: Technische Universität Graz
- given-names: Katharina
family-names: Rath
affiliation: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4962-5656'
- given-names: Baptiste
family-names: Rubino-Moyner
affiliation: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik
identifiers:
- type: doi
value: 10.5281/zenodo.3580488
description: >-
Main DOI, represents all versions and resolves to the
latest one.
repository-code: 'https://github.com/redmod-team/profit'
url: 'https://profit.readthedocs.io/'
keywords:
- Parameter Study
- Gaussian Process
- Regression
- HPC
- Active Learning
abstract: >-
<p>proFit is a collection of tools for studying parametric
dependencies of black-box simulation codes or experiments
and construction of reduced order response models over
input parameter space.</p><p>proFit can be fed with a
number of data points consisting of different input
parameter combinations and the resulting output of the
simulation under investigation. It then fits a
response-surface through the point cloud using Gaussian
process regression (GPR) models. This probabilistic
response model allows to predict (interpolate) the output
at yet unexplored parameter combinations including
uncertainty estimates. It can also tell you where to put
more training points to gain maximum new information
(experimental design) and automatically generate and start
new simulation runs locally or on a cluster. Results can
be explored and checked visually in a web
frontend.</p><p>Telling proFit how to interact with your
existing simulations is easy and requires no changes in
your existing code. Current functionality covers starting
simulations locally or on a cluster via <a
href=\"https://slurm.schedmd.com\">Slurm</a>, subsequent
surrogate modelling using <a
href=\"https://github.com/SheffieldML/GPy\">GPy</a>, <a
href=\"https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn\">scikit-learn</a>,
as well as an active learning algorithm to iteratively
sample at interesting points and a
Markov-Chain-Monte-Carlo (MCMC) algorithm. The web
frontend to interactively explore the point cloud and
surrogate is based on <a
href=\"https://github.com/plotly/dash\">plotly/dash</a>.</p><p>Features
include: <ul><li>Compute evaluation points (e.g. from a
random distribution) to run simulation</li><li>Template
replacement and automatic generation of run
directories</li><li>Starting parallel runs locally or on
the cluster (SLURM)</li><li>Collection of result output
and postprocessing</li><li>Response-model fitting using
Gaussian Process Regression and Linear
Regression</li><li>Active learning to reduce number of
samples needed</li><li>MCMC to find a posterior parameter
distribution (similar to active
learning)</li><li>Graphical user interface to explore the
results</li></ul></p>",
GitHub Events
Total
- Watch event: 1
- Push event: 4
- Pull request review event: 1
- Pull request event: 2
- Fork event: 1
Last Year
- Watch event: 1
- Push event: 4
- Pull request review event: 1
- Pull request event: 2
- Fork event: 1
Committers
Last synced: over 2 years ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Christopher Albert | a****t@a****t | 269 |
| Robert Babin | p****h@x****t | 123 |
| Manal Khallaayoune | 6****4 | 99 |
| Maximilian Kendler | m****r@s****t | 91 |
| Michael Hadwiger | m****r@s****t | 45 |
| Richard Hofmeister | r****r@h****e | 17 |
| Francesco Kramp | f****p@s****t | 16 |
| Baptiste Rubino-Moyner | b****r@i****r | 8 |
| Katharina Rath | k****h@g****t | 3 |
| pre-commit-ci[bot] | 6****] | 3 |
| Robert Babin | r****n@s****t | 2 |
| pre-commit & black | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 65
- Total pull requests: 37
- Average time to close issues: 5 months
- Average time to close pull requests: about 2 months
- Total issue authors: 6
- Total pull request authors: 6
- Average comments per issue: 0.63
- Average comments per pull request: 0.73
- Merged pull requests: 34
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 3
Past Year
- Issues: 0
- Pull requests: 1
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: 1 day
- Issue authors: 0
- Pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 1
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- krystophny (35)
- Rykath (25)
- mkendler (2)
- manal44 (1)
- Squadula (1)
- KathiRath (1)
Pull Request Authors
- Rykath (15)
- mkendler (7)
- michad1111 (6)
- Squadula (4)
- krystophny (3)
- pre-commit-ci[bot] (3)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 71 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 4
- Total versions: 6
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: profit
Probabilistic response model fitting with interactive tools
- Homepage: https://github.com/redmod-team/profit
- Documentation: https://profit.readthedocs.io/en/latest
- License: MIT
-
Latest release: 0.0.1
published over 6 years ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/setup-python v2 composite
- coverallsapp/github-action 1.1.3 composite
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/setup-python v2 composite
- pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish release/v1 composite


