bwsample
bwsample: Processing Best-Worst Scaling data - Published in JOSS (2021)
Science Score: 59.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 33 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: joss.theoj.org, zenodo.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
1 of 3 committers (33.3%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (12.1%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Scientific Fields
Repository
Sampling algorithm for best-worst scaling sets.
Basic Info
Statistics
- Stars: 7
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 12
- Releases: 11
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
bwsample: Sampling and Evaluation of Best-Worst Scaling sets
Sampling algorithm for best-worst scaling (BWS) sets, extracting pairs from evaluated BWS sets, count in dictionary of keys sparse matrix, and compute scores based on it.
The package bwsample addresses three areas:
Installation
The bwsample git repo is available as PyPi package
sh
pip install "bwsample>=0.7.0"
Overview
The bwsample can be deployed at different stages to prepare BWS example sets and post-process evaluated BWS sets.
An Active Learning experiment using an Web App with BWS user interface to judge sentence examples is shown in the diagram below. The bwsample would be implemented in a (python based) REST API. The App requests new BWS example sets, and bwsample.sample generates these. After the App posts the evaluation results to the API, bwsample.count extract new pairwise data from evaluated BWS sets. The pairwise comparision matrix can be used by bwsample.rank to compute scores for a new updated training set.
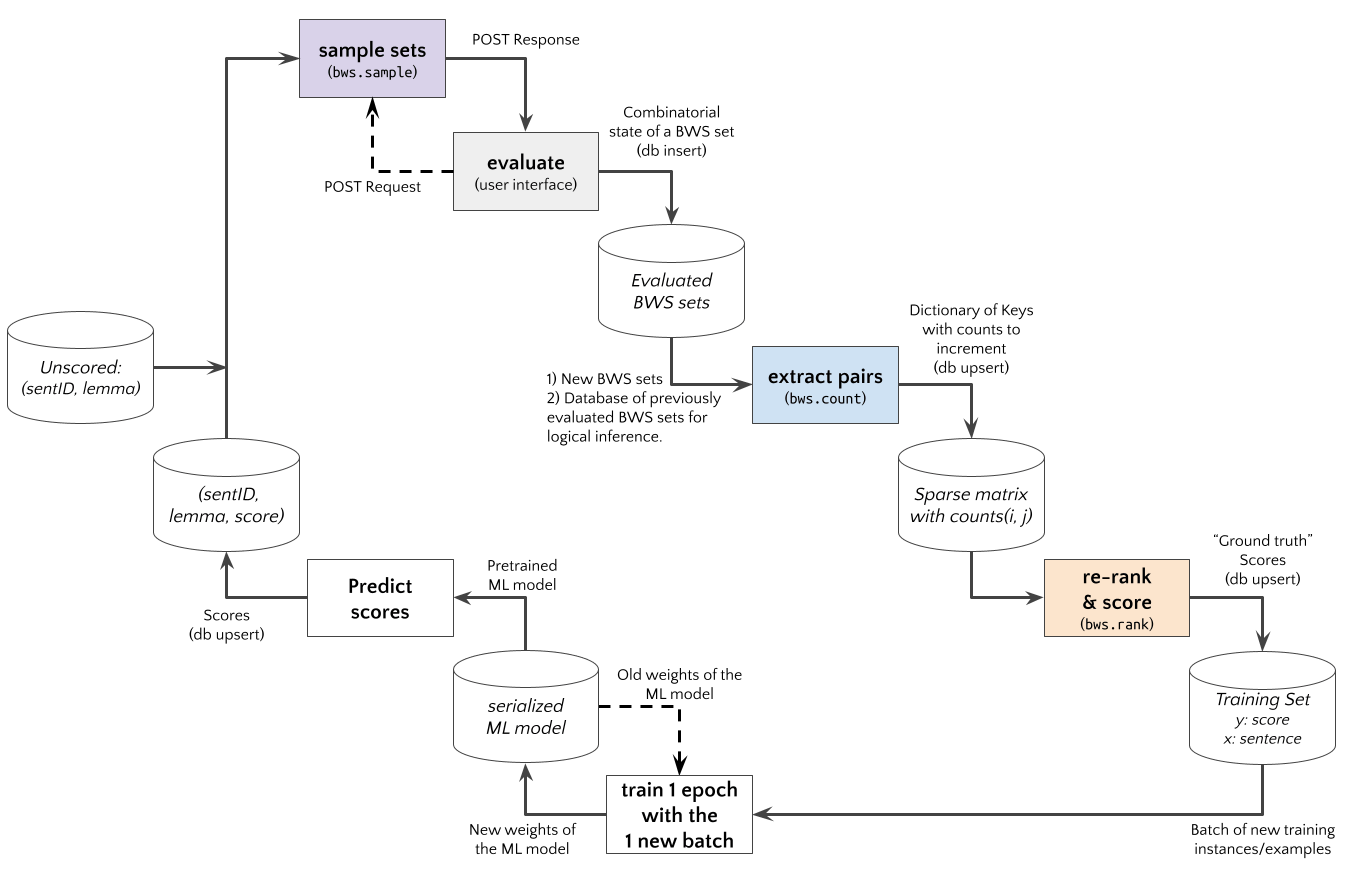
Sampling
Input Data:
The input data examples for bwsample.sample should be a List[anything].
For example, List[Dict[ID,DATA]] with identifiers using the key "id" and the associated data using the key "data", e.g.
python
examples = [
{"id": "id1", "data": "data..."},
{"id": "id2", "data": ["other", "data"]},
{"id": "id3", "data": {"key", "value"}},
{"id": "id4", "data": "lorem"},
{"id": "id5", "data": "ipsum"},
{"id": "id6", "data": "blind"},
{"id": "id7", "data": "text"}
]
Call the function:
The number of items per BWS set n_items (M) must be specified, e.g. n_items=4 if your App displays four items.
The 'overlap' algorithm assigns every i*(M-1)+1-th example to two consecutive BWS sets, so that 1/(M-1) of examples are evaluated two times.
The 'twice' algorithm connects the remaining (M-2)/(M-1) non-overlapping from 'overlapping' so that all examples occur twice.
The total number of sampled BWS sets might differ accordingly.
python
import bwsample as bws
samples = bws.sample(examples, n_items=4, method='overlap')
Output Data: The output has the following structure
[
[{'id': 'id1', 'data': 'data...'}, {'id': 'id2', 'data': ['other', 'data']}, {'id': 'id3', 'data': {'key', 'value'}}, {'id': 'id4', 'data': 'lorem'}],
[{'id': 'id1', 'data': 'data...'}, {'id': 'id4', 'data': 'lorem'}, {'id': 'id5', 'data': 'ipsum'}, {'id': 'id6', 'data': 'blind'}]
]
Warning: len(examples) must be a multiple of (n_items - 1)
References:
- Section 5 (page 4) in: Hamster, U. A. (2021, March 9). Extracting Pairwise Comparisons Data from Best-Worst Scaling Surveys by Logical Inference. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/qkxej
Counting
Input Data:
The input dataevaluations for bwsample.count should structured as List[Tuple[List[ItemState], List[ItemID]]].
The labelling/annotation application should produce a list of item states List[ItemState] with the states BEST:1, WORST:2 and NOT:0 for each item.
And the corresponding list of IDs List[ItemID] for each item or resp. example.
python
evaluations = (
([0, 0, 2, 1], ['id1', 'id2', 'id3', 'id4']),
([0, 1, 0, 2], ['id4', 'id5', 'id6', 'id7']),
([1, 2, 0, 0], ['id7', 'id8', 'id9', 'id1'])
)
Call the function:
python
import bwsample as bws
agg_dok, direct_dok, direct_detail, logical_dok, logical_detail = bws.count(evaluations)
Output Data:
The function bwsample.count outputs Dictionary of Keys (DOK) with the data structure Dict[Tuple[ItemID, ItemID], int], e.g. agg_dok, direct_dok, direct_detail["bw"], etc., what contain variants which pairs where counted:
agg_dokdirect_dokdirect_detail["bw"]--BEST>WORSTdirect_detail["bn"]--BEST>NOTdirect_detail["nw"]--NOT>WORST
logical_doklogical_detail["nn"]--D>E>F vs X>E>Zlogical_detail["nb"]--D>E>F vs E>Y>Zlogical_detail["nw"]--D>E>F vs X>Y>Elogical_detail["bn"]--D>E>F vs X>D>Zlogical_detail["bw"]--D>E>F vs X>Y>Dlogical_detail["wn"]--D>E>F vs X>F>Zlogical_detail["wb"]--D>E>F vs F>Y>Z
Limit the Database Size:
Logical Inference has quadratic complexity, and it might be beneficial to limit the database what can be done by the logical_database parameter.
python
import bwsample as bws
agg_dok, direct_dok, direct_detail, logical_dok, logical_detail = bws.count(
evaluations, logical_database=evaluations[:1])
Update Frequencies:
The function bwsample.count is an update function, i.e. you can provide previous count or resp. frequency data (e.g. logical_dok) or start from scratch (e.g. agg_dok=None).
```python import bwsample as bws
evaluations = [...] directdok = {...} directdetail = {...} logicaldok = {...} logicaldetail = {...} database = [...]
aggdok, directdok, directdetail, logicaldok, logicaldetail = bws.count( evaluations, directdok=directdok, directdetail=directdetail, logicaldok=logicaldok, logicaldetail=logicaldetail, logicaldatabase=database) ```
References:
- Section 3-4 in: Hamster, U. A. (2021, March 9). Extracting Pairwise Comparisons Data from Best-Worst Scaling Surveys by Logical Inference. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/qkxej
Ranking
Input Data:
The input data is a Dictionary of Keys (DoK) object produced by bwsample.count.
Call the function:
The function bwsample.rank computes a python index variable with a proposed ordering (ranked), and ordered list of example IDs (ordids), scores (scores) and further information depending on the selected method.
python
import bwsample as bws
ranked, ordids, metrics, scores, info = bws.rank(dok, method='ratio', adjust='quantile')
Available methods: Computed from extracted pairs:
'ratio'-- Simple ratios for each pair, and sum ratios for each item.'approx'-- Chi-Squared based p-value (Hoaglin Approximation) for each pair, and sum 1-pval for each item (Beh et al, 2018)'btl'-- Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model estimated with MM algorithm (Hunter, 2004).'eigen'-- Eigenvectors of the reciprocal pairwise comparison matrix (Saaty, 2003).'trans'-- Estimate transition probability of the next item to be better.
The implementations ratio, pvalue, 'btl', 'eigen', and 'trans' are fully based on sparse matrix operations and scipy.sparse algorithms, and avoid accidental conversions to dense matrices.
References: - Hoaglin Approximation for p-values: Beh, E., 2018. Exploring How to Simply Approximate the P-value of a Chi-squared Statistic. AJS 47, 63–75. https://doi.org/10.17713/ajs.v47i3.757 - Eigenvector solution in: Saaty, T. L. (2003). Decision-making with the AHP: Why is the principal eigenvector nec- essary. European Journal of Operational Research, 145(1), 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(02)00227-8 - Estimating the BTL model in: Hunter, D. R. (2004). MM algorithms for generalized Bradley-Terry models. The Annals of Statistics, 32(1), 384–406. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1079120141 - MaxDiff score in: Orme, B. (2009). MaxDiff Analysis: Simple Counting, Individual-Level Logit, and HB. https://sawtoothsoftware.com/uploads/sawtoothsoftware/originals/f89a6537-1cae-4fb5-afad-9d325c2a3143.pdf - Hamster, U. A. (2021, April 1). Pairwise comparison based ranking and scoring algorithms. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ev7fw
Appendix
Install a virtual environment
In order to run the Jupyter notebooks or want to work on this project (e.g. unit tests, syntax checks) you should install a Python virtual environment.
sh
python3.7 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt --no-cache-dir
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt --no-cache-dir
pip install -r requirements-demo.txt --no-cache-dir
(If your git repo is stored in a folder with whitespaces, then don't use the subfolder .venv. Use an absolute path without whitespaces.)
Python commands
- Jupyter for the examples:
jupyter lab - Check syntax:
flake8 --ignore=F401 --exclude=$(grep -v '^#' .gitignore | xargs | sed -e 's/ /,/g') - Run Unit Tests:
pytest
Publish
```sh
pandoc README.md --from markdown --to rst -s -o README.rst
python setup.py sdist twine check dist/* twine upload -r pypi dist/* ```
Clean up
sh
find . -type f -name "*.pyc" | xargs rm
find . -type d -name "__pycache__" | xargs rm -r
rm -r .pytest_cache
rm -r .venv
Support
Please open an issue for support.
Contributing
Please contribute using Github Flow. Create a branch, add commits, and open a pull request.
Acknowledgements
The "Evidence" project was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) - 433249742 (GU 798/27-1; GE 1119/11-1).
Maintenance
- till 31.Aug.2023 (v0.7.0) the code repository was maintained within the DFG project 433249742
- since 01.Sep.2023 (v0.8.0) the code repository is maintained by @ulf1.
Citation
Please cite the peer-reviewed JOSS paper when using this software for any purpose.
@article{Hamster2021,
author = {Ulf A. Hamster},
title = {`bwsample`: Processing Best-Worst Scaling data},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software},
year = {2021},
volume = {6},
number = {64},
pages = {3324},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
doi = {10.21105/joss.03324},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03324},
}
Owner
- Name: Ulf Hamster
- Login: ulf1
- Kind: user
- Repositories: 45
- Profile: https://github.com/ulf1
1x developer
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 1
Last Year
- Issues event: 1
Committers
Last synced: 7 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| UH | 5****6@g****m | 184 |
| snyk-bot | s****t@s****o | 3 |
| Daniel S. Katz | d****z@i****g | 1 |
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 0
- Total pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Total issue authors: 0
- Total pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 0
- Pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 0
- Pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- haukelicht (1)
Pull Request Authors
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 68 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 1
- Total versions: 22
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: bwsample
Sampling algorithm for best-worst scaling sets.
- Homepage: http://github.com/ulf1/bwsample
- Documentation: https://bwsample.readthedocs.io/
- License: Apache License 2.0
-
Latest release: 0.7.0
published about 3 years ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- jupyterlab >=3.0.5
- matplotlib >=1.15.0
- mistune >=2.0.3
- pandas >=1.1.5
- flake8 >=3.8.4 development
- pypandoc >=1.5 development
- pytest >=6.2.1 development
- setuptools >=56.0.0 development
- twine ==3.3.0 development
- wheel >=0.31.0 development
- numpy >=1.19.5,<2
- scikit-learn >=0.24.1,<1
- scipy >=1.5.4,<2
- numpy >=1.19.5,<2
- scikit-learn >=0.24.1,<1
- scipy >=1.5.4,<2
- actions/checkout v1 composite
- actions/setup-python v1 composite
