https://github.com/cvs-health/uqlm
UQLM: Uncertainty Quantification for Language Models, is a Python package for UQ-based LLM hallucination detection
Science Score: 36.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org, nature.com -
○Academic email domains
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (12.7%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
UQLM: Uncertainty Quantification for Language Models, is a Python package for UQ-based LLM hallucination detection
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: cvs-health
- License: apache-2.0
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://cvs-health.github.io/uqlm/latest/index.html
- Size: 13.5 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 995
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 98
- Open Issues: 18
- Releases: 18
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md

uqlm: Uncertainty Quantification for Language Models
UQLM is a Python library for Large Language Model (LLM) hallucination detection using state-of-the-art uncertainty quantification techniques.
Installation
The latest version can be installed from PyPI:
bash
pip install uqlm
Hallucination Detection
UQLM provides a suite of response-level scorers for quantifying the uncertainty of Large Language Model (LLM) outputs. Each scorer returns a confidence score between 0 and 1, where higher scores indicate a lower likelihood of errors or hallucinations. We categorize these scorers into four main types:
| Scorer Type | Added Latency | Added Cost | Compatibility | Off-the-Shelf / Effort | |------------------------|----------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------| | Black-Box Scorers | ⏱️ Medium-High (multiple generations & comparisons) | 💸 High (multiple LLM calls) | 🌍 Universal (works with any LLM) | ✅ Off-the-shelf | | White-Box Scorers | ⚡ Minimal (token probabilities already returned) | ✔️ None (no extra LLM calls) | 🔒 Limited (requires access to token probabilities) | ✅ Off-the-shelf | | LLM-as-a-Judge Scorers | ⏳ Low-Medium (additional judge calls add latency) | 💵 Low-High (depends on number of judges)| 🌍 Universal (any LLM can serve as judge) |✅ Off-the-shelf | | Ensemble Scorers | 🔀 Flexible (combines various scorers) | 🔀 Flexible (combines various scorers) | 🔀 Flexible (combines various scorers) | ✅ Off-the-shelf (beginner-friendly); 🛠️ Can be tuned (best for advanced users) |
Below we provide illustrative code snippets and details about available scorers for each type.
Black-Box Scorers (Consistency-Based)
These scorers assess uncertainty by measuring the consistency of multiple responses generated from the same prompt. They are compatible with any LLM, intuitive to use, and don't require access to internal model states or token probabilities.

Example Usage:
Below is a sample of code illustrating how to use the BlackBoxUQ class to conduct hallucination detection.
```python from langchaingooglevertexai import ChatVertexAI llm = ChatVertexAI(model='gemini-pro')
from uqlm import BlackBoxUQ bbuq = BlackBoxUQ(llm=llm, scorers=["semanticnegentropy"], usebest=True)
results = await bbuq.generateandscore(prompts=prompts, numresponses=5) results.todf() ```
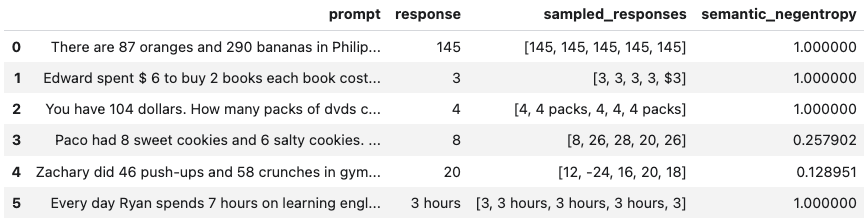
Above, use_best=True implements mitigation so that the uncertainty-minimized responses is selected. Note that although we use ChatVertexAI in this example, any LangChain Chat Model may be used. For a more detailed demo, refer to our Black-Box UQ Demo.
Available Scorers:
- Non-Contradiction Probability (Chen & Mueller, 2023; Lin et al., 2024; Manakul et al., 2023)
- Discrete Semantic Entropy (Farquhar et al., 2024; Bouchard & Chauhan, 2025)
- Exact Match (Cole et al., 2023; Chen & Mueller, 2023)
- BERT-score (Manakul et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2020)
- Cosine Similarity (Shorinwa et al., 2024; HuggingFace)
- BLUERT (Sellam et al., 2020; Deprecated as of
v0.2.0)
White-Box Scorers (Token-Probability-Based)
These scorers leverage token probabilities to estimate uncertainty. They are significantly faster and cheaper than black-box methods, but require access to the LLM's internal probabilities, meaning they are not necessarily compatible with all LLMs/APIs.

Example Usage:
Below is a sample of code illustrating how to use the WhiteBoxUQ class to conduct hallucination detection.
```python from langchaingooglevertexai import ChatVertexAI llm = ChatVertexAI(model='gemini-pro')
from uqlm import WhiteBoxUQ wbuq = WhiteBoxUQ(llm=llm, scorers=["min_probability"])
results = await wbuq.generateandscore(prompts=prompts)
results.todf()
```
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cvs-health/uqlm/develop/assets/images/white
Again, any LangChain Chat Model may be used in place of ChatVertexAI. For a more detailed demo, refer to our White-Box UQ Demo.
Available Scorers:
- Minimum token probability (Manakul et al., 2023)
- Length-Normalized Joint Token Probability (Malinin & Gales, 2021)
LLM-as-a-Judge Scorers
These scorers use one or more LLMs to evaluate the reliability of the original LLM's response. They offer high customizability through prompt engineering and the choice of judge LLM(s).

Example Usage:
Below is a sample of code illustrating how to use the LLMPanel class to conduct hallucination detection using a panel of LLM judges.
```python from langchaingooglevertexai import ChatVertexAI llm1 = ChatVertexAI(model='gemini-1.0-pro') llm2 = ChatVertexAI(model='gemini-1.5-flash-001') llm3 = ChatVertexAI(model='gemini-1.5-pro-001')
from uqlm import LLMPanel panel = LLMPanel(llm=llm1, judges=[llm1, llm2, llm3])
results = await panel.generateandscore(prompts=prompts)
results.todf()
```
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cvs-health/uqlm/develop/assets/images/panel
Note that although we use ChatVertexAI in this example, we can use any LangChain Chat Model as judges. For a more detailed demo illustrating how to customize a panel of LLM judges, refer to our LLM-as-a-Judge Demo.
Available Scorers:
- Categorical LLM-as-a-Judge (Manakul et al., 2023; Chen & Mueller, 2023; Luo et al., 2023)
- Continuous LLM-as-a-Judge (Xiong et al., 2024)
- Panel of LLM Judges (Verga et al., 2024)
- Likert Scale Scoring (Bai et al., 2023)
Ensemble Scorers
These scorers leverage a weighted average of multiple individual scorers to provide a more robust uncertainty/confidence estimate. They offer high flexibility and customizability, allowing you to tailor the ensemble to specific use cases.

Example Usage:
Below is a sample of code illustrating how to use the UQEnsemble class to conduct hallucination detection.
```python from langchaingooglevertexai import ChatVertexAI llm = ChatVertexAI(model='gemini-pro')
from uqlm import UQEnsemble
---Option 1: Off-the-Shelf Ensemble---
uqe = UQEnsemble(llm=llm)
results = await uqe.generateandscore(prompts=prompts, num_responses=5)
---Option 2: Tuned Ensemble---
scorers = [ # specify which scorers to include "exactmatch", "noncontradiction", # black-box scorers "minprobability", # white-box scorer llm # use same LLM as a judge ] uqe = UQEnsemble(llm=llm, scorers=scorers)
Tune on tuning prompts with provided ground truth answers
tuneresults = await uqe.tune( prompts=tuningprompts, groundtruthanswers=groundtruthanswers )
ensemble is now tuned - generate responses on new prompts
results = await uqe.generateandscore(prompts=prompts)
results.todf()
```
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cvs-health/uqlm/develop/assets/images/uqensemble
As with the other examples, any LangChain Chat Model may be used in place of ChatVertexAI. For more detailed demos, refer to our Off-the-Shelf Ensemble Demo (quick start) or our Ensemble Tuning Demo (advanced).
Available Scorers:
- BS Detector (Chen & Mueller, 2023)
- Generalized UQ Ensemble (Bouchard & Chauhan, 2025)
Documentation
Check out our documentation site for detailed instructions on using this package, including API reference and more.
Example notebooks
Explore the following demo notebooks to see how to use UQLM for various hallucination detection methods:
- Black-Box Uncertainty Quantification: A notebook demonstrating hallucination detection with black-box (consistency) scorers.
- White-Box Uncertainty Quantification: A notebook demonstrating hallucination detection with white-box (token probability-based) scorers.
- LLM-as-a-Judge: A notebook demonstrating hallucination detection with LLM-as-a-Judge.
- Tunable UQ Ensemble: A notebook demonstrating hallucination detection with a tunable ensemble of UQ scorers (Bouchard & Chauhan, 2025).
- Off-the-Shelf UQ Ensemble: A notebook demonstrating hallucination detection using BS Detector (Chen & Mueller, 2023) off-the-shelf ensemble.
- Semantic Entropy: A notebook demonstrating token-probability-based semantic entropy (Farquhar et al., 2024; Kuhn et al., 2023), which combines elements of black-box UQ and white-box UQ to compute confidence scores.
Associated Research
A technical description of the uqlm scorers and extensive experiment results are contained in this this paper. If you use our framework or toolkit, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
bibtex
@misc{bouchard2025uncertaintyquantificationlanguagemodels,
title={Uncertainty Quantification for Language Models: A Suite of Black-Box, White-Box, LLM Judge, and Ensemble Scorers},
author={Dylan Bouchard and Mohit Singh Chauhan},
year={2025},
eprint={2504.19254},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.19254},
}
Owner
- Name: CVS Health
- Login: cvs-health
- Kind: organization
- Repositories: 3
- Profile: https://github.com/cvs-health
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 26
- Total pull requests: 164
- Average time to close issues: 22 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 2 days
- Total issue authors: 6
- Total pull request authors: 14
- Average comments per issue: 0.38
- Average comments per pull request: 0.48
- Merged pull requests: 99
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 8
Past Year
- Issues: 26
- Pull requests: 164
- Average time to close issues: 22 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 2 days
- Issue authors: 6
- Pull request authors: 14
- Average comments per issue: 0.38
- Average comments per pull request: 0.48
- Merged pull requests: 99
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 8
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- dylanbouchard (19)
- dskarbrevik (3)
- nobodyPerfecZ (1)
- orannahum-qualifire (1)
- dimtsap (1)
- eithannak29 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- dylanbouchard (82)
- mohitcek (23)
- zeya30 (13)
- doyajii1 (9)
- dependabot[bot] (8)
- mehtajinesh (5)
- vaifai (4)
- dimtsap (4)
- Mihir3 (4)
- virenbajaj (4)
- dskarbrevik (2)
- adrian24t (2)
- trumant (2)
- NamrataWalanj7 (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 2
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 1,724 last-month
-
Total dependent packages: 0
(may contain duplicates) -
Total dependent repositories: 0
(may contain duplicates) - Total versions: 51
- Total maintainers: 1
proxy.golang.org: github.com/cvs-health/uqlm
- Documentation: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/cvs-health/uqlm#section-documentation
- License: apache-2.0
-
Latest release: v0.2.6
published 6 months ago
Rankings
pypi.org: uqlm
UQLM (Uncertainty Quantification for Language Models) is a Python package for UQ-based LLM hallucination detection.
- Homepage: https://github.com/cvs-health/uqlm
- Documentation: https://cvs-health.github.io/uqlm/latest/index.html
- License: Apache-2.0
-
Latest release: 0.2.6
published 6 months ago


