Dynamax
Dynamax: A Python package for probabilistic state space modeling with JAX - Published in JOSS (2025)
Science Score: 100.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 5 DOI reference(s) in README and JOSS metadata -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: joss.theoj.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
7 of 34 committers (20.6%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
✓JOSS paper metadata
Published in Journal of Open Source Software
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Scientific Fields
Repository
A Python package for probabilistic state space modeling with JAX
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: probml
- License: mit
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://probml.github.io/dynamax/
- Size: 245 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 864
- Watchers: 25
- Forks: 100
- Open Issues: 68
- Releases: 13
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
Welcome to DYNAMAX!
Dynamax is a library for probabilistic state space models (SSMs) written in JAX. It has code for inference (state estimation) and learning (parameter estimation) in a variety of SSMs, including:
- Hidden Markov Models (HMMs)
- Linear Gaussian State Space Models (aka Linear Dynamical Systems)
- Nonlinear Gaussian State Space Models
- Generalized Gaussian State Space Models (with non-Gaussian emission models)
The library consists of a set of core, functionally pure, low-level inference algorithms, as well as a set of model classes which provide a more user-friendly, object-oriented interface. It is compatible with other libraries in the JAX ecosystem, such as optax (used for estimating parameters using stochastic gradient descent), and Blackjax (used for computing the parameter posterior using Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) or sequential Monte Carlo (SMC)).
Documentation
For a highlevel summary, see this JOSS 2024 article.
For tutorials and API documentation, see: https://probml.github.io/dynamax/.
For an extension of dynamax that supports structural time series models, see https://github.com/probml/sts-jax.
For an illustration of how to use dynamax inside of bayeux to perform Bayesian inference for the parameters of an SSM, see https://jax-ml.github.io/bayeux/examples/dynamaxandbayeux/.
Installation and Testing
To install the latest releast of dynamax from PyPi:
{.console}
pip install dynamax # Install dynamax and core dependencies, or
pip install dynamax[notebooks] # Install with demo notebook dependencies
To install the latest development branch:
{.console}
pip install git+https://github.com/probml/dynamax.git
Finally, if you\'re a developer, you can install dynamax along with the test and documentation dependencies with:
{.console}
git clone git@github.com:probml/dynamax.git
cd dynamax
pip install -e '.[dev]'
To run the tests:
{.console}
pytest dynamax # Run all tests
pytest dynamax/hmm/inference_test.py # Run a specific test
pytest -k lgssm # Run tests with lgssm in the name
What are state space models?
A state space model or SSM is a partially observed Markov model, in which the hidden state, $zt$, evolves over time according to a Markov process, possibly conditional on external inputs / controls / covariates, $ut$, and generates an observation, $y_t$. This is illustrated in the graphical model below.
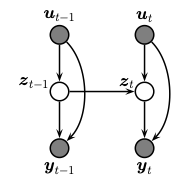
The corresponding joint distribution has the following form (in dynamax, we restrict attention to discrete time systems):
$$p(y{1:T}, z{1:T} \mid u{1:T}) = p(z1 \mid u1) \prod{t=2}^T p(zt \mid z{t-1}, ut) \prod{t=1}^T p(yt \mid zt, u_t)$$
Here $p(zt | z{t-1}, ut)$ is called the transition or dynamics model, and $p(yt | z{t}, ut)$ is called the observation or emission model. In both cases, the inputs $ut$ are optional; furthermore, the observation model may have auto-regressive dependencies, in which case we write $p(yt | z{t}, ut, y_{1:t-1})$.
We assume that we see the observations $y{1:T}$, and want to infer the hidden states, either using online filtering (i.e., computing $p(zt|y{1:t})$ ) or offline smoothing (i.e., computing $p(zt|y{1:T})$ ). We may also be interested in predicting future states, $p(z{t+h}|y{1:t})$, or future observations, $p(y{t+h}|y_{1:t})$, where h is the forecast horizon. (Note that by using a hidden state to represent the past observations, the model can have \"infinite\" memory, unlike a standard auto-regressive model.) All of these computations can be done efficiently using our library, as we discuss below. In addition, we can estimate the parameters of the transition and emission models, as we discuss below.
More information can be found in these books:
- \"Machine Learning: Advanced Topics\", K. Murphy, MIT Press 2023. Available at https://probml.github.io/pml-book/book2.html.
- \"Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing, Second Edition\", S. Särkkä and L. Svensson, Cambridge University Press, 2023. Available at http://users.aalto.fi/~ssarkka/pub/bfs_book_2023_online.pdf
Example usage
Dynamax includes classes for many kinds of SSM. You can use these models to simulate data, and you can fit the models using standard learning algorithms like expectation-maximization (EM) and stochastic gradient descent (SGD). Below we illustrate the high level (object-oriented) API for the case of an HMM with Gaussian emissions. (See this notebook for a runnable version of this code.)
```python import jax.numpy as jnp import jax.random as jr import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from dynamax.hiddenmarkovmodel import GaussianHMM
key1, key2, key3 = jr.split(jr.PRNGKey(0), 3) numstates = 3 emissiondim = 2 num_timesteps = 1000
Make a Gaussian HMM and sample data from it
hmm = GaussianHMM(numstates, emissiondim) trueparams, _ = hmm.initialize(key1) truestates, emissions = hmm.sample(trueparams, key2, numtimesteps)
Make a new Gaussian HMM and fit it with EM
params, props = hmm.initialize(key3, method="kmeans", emissions=emissions) params, lls = hmm.fitem(params, props, emissions, numiters=20)
Plot the marginal log probs across EM iterations
plt.plot(lls) plt.xlabel("EM iterations") plt.ylabel("marginal log prob.")
Use fitted model for posterior inference
post = hmm.smoother(params, emissions) print(post.smoothed_probs.shape) # (1000, 3) ```
JAX allows you to easily vectorize these operations with vmap.
For example, you can sample and fit to a batch of emissions as shown below.
```python from functools import partial from jax import vmap
numseq = 200 batchtruestates, batchemissions = \ vmap(partial(hmm.sample, trueparams, numtimesteps=numtimesteps))( jr.split(key2, numseq)) print(batchtruestates.shape, batch_emissions.shape) # (200,1000) and (200,1000,2)
Make a new Gaussian HMM and fit it with EM
params, props = hmm.initialize(key3, method="kmeans", emissions=batchemissions) params, lls = hmm.fitem(params, props, batchemissions, numiters=20) ```
These examples demonstrate the dynamax models, but we can also call the low-level inference code directly.
Contributing
Please see this page for details on how to contribute.
About
Core team: Peter Chang, Giles Harper-Donnelly, Aleyna Kara, Xinglong Li, Scott Linderman, Kevin Murphy.
Other contributors: Adrien Corenflos, Elizabeth DuPre, Gerardo Duran-Martin, Colin Schlager, Libby Zhang and other people listed here
MIT License. 2022
Owner
- Name: Probabilistic machine learning
- Login: probml
- Kind: organization
- Email: murphyk@gmail.com
- Website: probml.ai
- Twitter: sirbayes
- Repositories: 31
- Profile: https://github.com/probml
Material to accompany my book series "Probabilistic Machine Learning" (Software, Data, Exercises, Figures, etc)
JOSS Publication
Dynamax: A Python package for probabilistic state space modeling with JAX
Authors

Department of Statistics and Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute, Stanford University, USA
CSAIL, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA
Cambridge University, England, UK
Computer Science Department, Technical University of Munich Garching, Germany
Statistics Department, University of British Columbia, Canada
Queen Mary University of London, England, UK
Google DeepMind, USA
Tags
State space models dynamics JAXCitation (CITATION.cff)
cff-version: "1.2.0"
authors:
- family-names: Linderman
given-names: Scott W.
orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3878-9073"
- family-names: Chang
given-names: Peter
- family-names: Harper-Donnelly
given-names: Giles
- family-names: Kara
given-names: Aleyna
- family-names: Li
given-names: Xinglong
- family-names: Duran-Martin
given-names: Gerardo
- family-names: Murphy
given-names: Kevin
contact:
- family-names: Linderman
given-names: Scott W.
orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3878-9073"
- family-names: Murphy
given-names: Kevin
doi: 10.6084/m9.figshare.28665131
message: If you use this software, please cite our article in the
Journal of Open Source Software.
preferred-citation:
authors:
- family-names: Linderman
given-names: Scott W.
orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3878-9073"
- family-names: Chang
given-names: Peter
- family-names: Harper-Donnelly
given-names: Giles
- family-names: Kara
given-names: Aleyna
- family-names: Li
given-names: Xinglong
- family-names: Duran-Martin
given-names: Gerardo
- family-names: Murphy
given-names: Kevin
date-published: 2025-04-03
doi: 10.21105/joss.07069
issn: 2475-9066
issue: 108
journal: Journal of Open Source Software
publisher:
name: Open Journals
start: 7069
title: "Dynamax: A Python package for probabilistic state space
modeling with JAX"
type: article
url: "https://joss.theoj.org/papers/10.21105/joss.07069"
volume: 10
title: "Dynamax: A Python package for probabilistic state space modeling
with JAX"
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 15
- Release event: 9
- Issues event: 34
- Watch event: 177
- Delete event: 6
- Issue comment event: 50
- Push event: 91
- Pull request event: 39
- Fork event: 20
Last Year
- Create event: 15
- Release event: 9
- Issues event: 34
- Watch event: 178
- Delete event: 6
- Issue comment event: 50
- Push event: 91
- Pull request event: 39
- Fork event: 21
Committers
Last synced: 7 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Scott Linderman | s****n@g****m | 419 |
| Peter G. Chang | p****4@g****m | 248 |
| xinglong | x****i@s****a | 149 |
| Kevin P Murphy | m****k@g****m | 142 |
| gileshd | g****d@g****m | 110 |
| karalleyna | a****8@g****m | 86 |
| Gerardo Duran-Martin | g****n@m****m | 69 |
| Caleb Weinreb | c****w@g****m | 24 |
| libby | e****4@g****m | 18 |
| kostastsa | k****s@g****m | 14 |
| Scott Linderman | s****n@g****m | 10 |
| Elizabeth DuPre | e****2@c****u | 10 |
| patel-zeel | p****l@i****n | 8 |
| Ravin Kumar | 7****9 | 6 |
| andrewwarrington | a****g@s****u | 6 |
| davidzoltowski | d****i | 6 |
| Thomas Pinder | t****r@l****k | 4 |
| Hylke Donker | h****r@u****l | 4 |
| partev | p****n@g****m | 3 |
| Eric Denovellis | e****o@b****u | 3 |
| Dominik Straub | d****b@m****g | 2 |
| Yixiu Zhao | z****7@g****m | 2 |
| Caleb Weinreb | c****b@c****m | 2 |
| Arfon Smith | a****n | 1 |
| Xinglong Li | x****i@d****a | 1 |
| Xinglong | x****i@s****n | 1 |
| Collin Schlager | s****n@g****m | 1 |
| DanielTrivino | d****1@g****m | 1 |
| Jake VanderPlas | j****p@g****m | 1 |
| Jason Davies | j****n@j****m | 1 |
| and 4 more... | ||
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 126
- Total pull requests: 104
- Average time to close issues: 2 months
- Average time to close pull requests: about 2 months
- Total issue authors: 43
- Total pull request authors: 34
- Average comments per issue: 1.07
- Average comments per pull request: 1.2
- Merged pull requests: 76
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 28
- Pull requests: 42
- Average time to close issues: about 2 months
- Average time to close pull requests: 27 days
- Issue authors: 13
- Pull request authors: 11
- Average comments per issue: 0.86
- Average comments per pull request: 0.55
- Merged pull requests: 32
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- murphyk (35)
- slinderman (12)
- petergchang (9)
- karalleyna (8)
- hylkedonker (7)
- calebweinreb (6)
- gdalle (4)
- lockwo (3)
- mcusi (2)
- canyon289 (2)
- ghuckins (2)
- gorold (2)
- umeshksingla (2)
- xinglong-li (2)
- gergogomori (1)
Pull Request Authors
- slinderman (19)
- gileshd (14)
- hylkedonker (12)
- calebweinreb (8)
- thomaspinder (6)
- partev (5)
- canyon289 (5)
- emdupre (5)
- edeno (4)
- petergchang (3)
- kstoneriv3 (2)
- QBatista (2)
- murphyk (2)
- anuj-sp (2)
- Umar-Azam (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 2,036 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 1
- Total dependent repositories: 1
- Total versions: 17
- Total maintainers: 2
pypi.org: dynamax
Dynamic State Space Models in JAX.
- Documentation: https://dynamax.readthedocs.io/
- License: MIT License Copyright (c) 2022 Probabilistic machine learning Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
-
Latest release: 1.0.1
published 10 months ago
Rankings
Maintainers (2)
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v2.3.1 composite
- actions/setup-python v1 composite
- JamesIves/github-pages-deploy-action 3.6.2 composite
- actions/checkout v2.3.1 composite
- actions/setup-python v1 composite
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/setup-python v1 composite
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/setup-python v2 composite