Science Score: 64.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
3 of 28 committers (10.7%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (14.7%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Repository
Tabular Deep Learning Library for PyTorch
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: pyg-team
- License: mit
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: master
- Homepage: https://pytorch-frame.readthedocs.io
- Size: 5.22 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 698
- Watchers: 15
- Forks: 69
- Open Issues: 26
- Releases: 7
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md

**A modular deep learning framework for building neural network models on heterogeneous tabular data.** ______________________________________________________________________ [![arXiv][arxiv-image]][arxiv-url] [](https://pypi.org/project/pytorch-frame/) [![PyPI Version][pypi-image]][pypi-url] [![Testing Status][testing-image]][testing-url] [![Docs Status][docs-image]][docs-url] [![Contributing][contributing-image]][contributing-url] [![Slack][slack-image]][slack-url]
PyTorch Frame is a deep learning extension for PyTorch, designed for heterogeneous tabular data with different column types, including numerical, categorical, time, text, and images. It offers a modular framework for implementing existing and future methods. The library features methods from state-of-the-art models, user-friendly mini-batch loaders, benchmark datasets, and interfaces for custom data integration.
PyTorch Frame democratizes deep learning research for tabular data, catering to both novices and experts alike. Our goals are:
Facilitate Deep Learning for Tabular Data: Historically, tree-based models (e.g., GBDT) excelled at tabular learning but had notable limitations, such as integration difficulties with downstream models, and handling complex column types, such as texts, sequences, and embeddings. Deep tabular models are promising to resolve the limitations. We aim to facilitate deep learning research on tabular data by modularizing its implementation and supporting the diverse column types.
Integrates with Diverse Model Architectures like Large Language Models: PyTorch Frame supports integration with a variety of different architectures including LLMs. With any downloaded model or embedding API endpoint, you can encode your text data with embeddings and train it with deep learning models alongside other complex semantic types. We support the following (but not limited to):

OpenAI Embedding Code Example |

Cohere Embed v3 Code Example |

Hugging Face Code Example |

Voyage AI Code Example |
- Library Highlights
- Architecture Overview
- Quick Tour
- Implemented Deep Tabular Models
- Benchmark
- Installation
Library Highlights
PyTorch Frame builds directly upon PyTorch, ensuring a smooth transition for existing PyTorch users. Key features include:
- Diverse column types:
PyTorch Frame supports learning across various column types:
numerical,categorical,multicategorical,text_embedded,text_tokenized,timestamp,image_embedded, andembedding. See here for the detailed tutorial. - Modular model design: Enables modular deep learning model implementations, promoting reusability, clear coding, and experimentation flexibility. Further details in the architecture overview.
- Models Implements many state-of-the-art deep tabular models as well as strong GBDTs (XGBoost, CatBoost, and LightGBM) with hyper-parameter tuning.
- Datasets: Comes with a collection of readily-usable tabular datasets. Also supports custom datasets to solve your own problem. We benchmark deep tabular models against GBDTs.
- PyTorch integration: Integrates effortlessly with other PyTorch libraries, facilitating end-to-end training of PyTorch Frame with downstream PyTorch models. For example, by integrating with PyG, a PyTorch library for GNNs, we can perform deep learning over relational databases. Learn more in RelBench and example code.
Architecture Overview
Models in PyTorch Frame follow a modular design of FeatureEncoder, TableConv, and Decoder, as shown in the figure below:
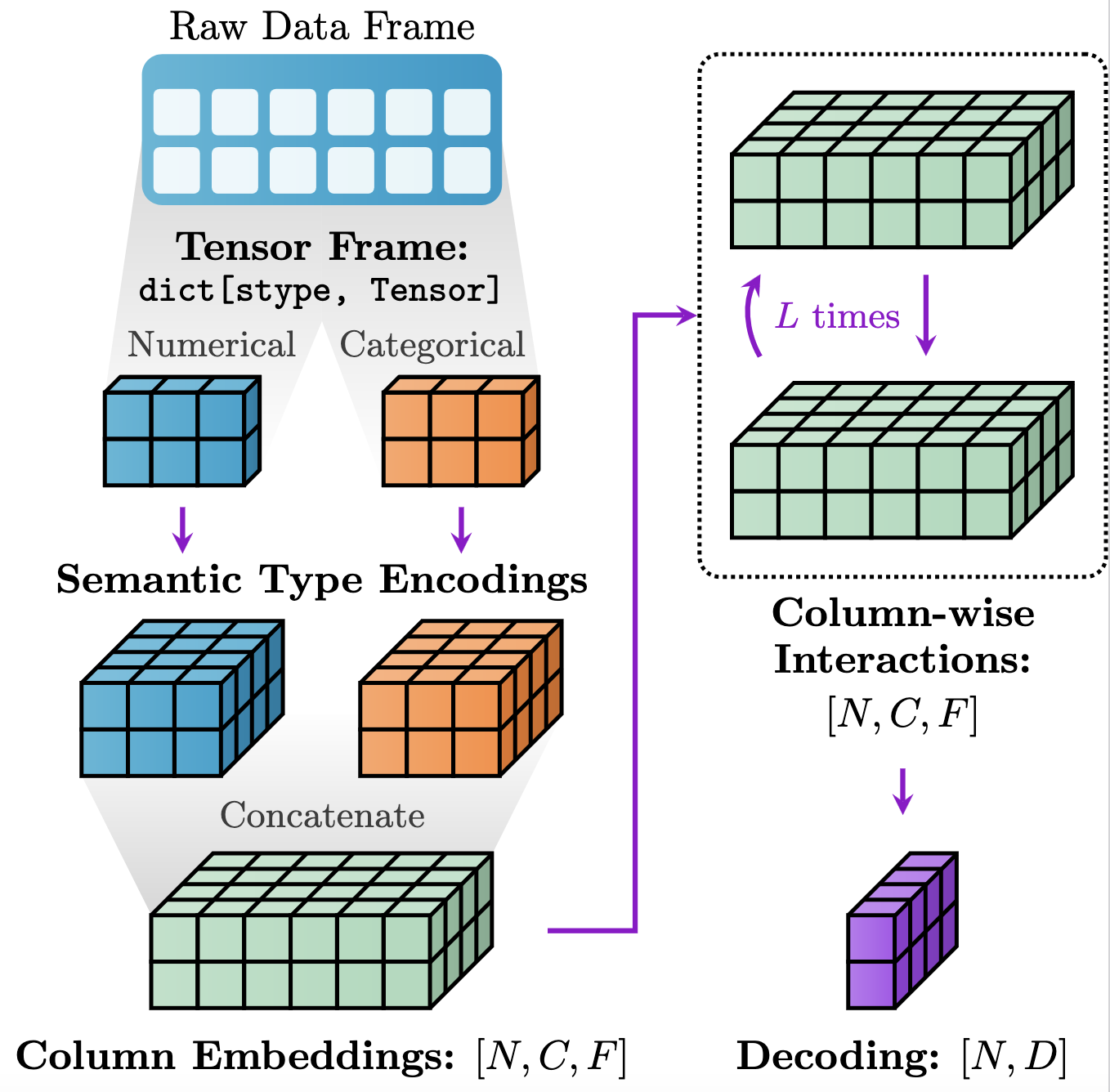
In essence, this modular setup empowers users to effortlessly experiment with myriad architectures:
Materializationhandles converting the raw pandasDataFrameinto aTensorFramethat is amenable to Pytorch-based training and modeling.FeatureEncoderencodesTensorFrameinto hidden column embeddings of size[batch_size, num_cols, channels].TableConvmodels column-wise interactions over the hidden embeddings.Decodergenerates embedding/prediction per row.
Quick Tour
In this quick tour, we showcase the ease of creating and training a deep tabular model with only a few lines of code.
Build and train your own deep tabular model
As an example, we implement a simple ExampleTransformer following the modular architecture of Pytorch Frame.
In the example below:
self.encodermaps an inputTensorFrameto an embedding of size[batch_size, num_cols, channels].self.convsiteratively transforms the embedding of size[batch_size, num_cols, channels]into an embedding of the same size.self.decoderpools the embedding of size[batch_size, num_cols, channels]into[batch_size, out_channels].
```python from torch import Tensor from torch.nn import Linear, Module, ModuleList
from torchframe import TensorFrame, stype from torchframe.nn.conv import TabTransformerConv from torch_frame.nn.encoder import ( EmbeddingEncoder, LinearEncoder, StypeWiseFeatureEncoder, )
class ExampleTransformer(Module): def init( self, channels, outchannels, numlayers, numheads, colstats, colnamesdict, ): super().init() self.encoder = StypeWiseFeatureEncoder( outchannels=channels, colstats=colstats, colnamesdict=colnamesdict, stypeencoderdict={ stype.categorical: EmbeddingEncoder(), stype.numerical: LinearEncoder() }, ) self.convs = ModuleList([ TabTransformerConv( channels=channels, numheads=numheads, ) for _ in range(numlayers) ]) self.decoder = Linear(channels, out_channels)
def forward(self, tf: TensorFrame) -> Tensor:
x, _ = self.encoder(tf)
for conv in self.convs:
x = conv(x)
out = self.decoder(x.mean(dim=1))
return out
```
To prepare the data, we can quickly instantiate a pre-defined dataset and create a PyTorch-compatible data loader as follows:
```python from torchframe.datasets import Yandex from torchframe.data import DataLoader
dataset = Yandex(root='/tmp/adult', name='adult') dataset.materialize() traindataset = dataset[:0.8] trainloader = DataLoader(traindataset.tensorframe, batch_size=128, shuffle=True) ```
Then, we just follow the standard PyTorch training procedure to optimize the model parameters. That's it!
```python import torch import torch.nn.functional as F
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.isavailable() else 'cpu') model = ExampleTransformer( channels=32, outchannels=dataset.numclasses, numlayers=2, numheads=8, colstats=traindataset.colstats, colnamesdict=traindataset.tensorframe.colnamesdict, ).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
for epoch in range(50): for tf in trainloader: tf = tf.to(device) pred = model.forward(tf) loss = F.crossentropy(pred, tf.y) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() ```
Implemented Deep Tabular Models
We list currently supported deep tabular models:
- Trompt from Chen et al.: Trompt: Towards a Better Deep Neural Network for Tabular Data (ICML 2023) [Example]
- FTTransformer from Gorishniy et al.: Revisiting Deep Learning Models for Tabular Data (NeurIPS 2021) [Example]
- ResNet from Gorishniy et al.: Revisiting Deep Learning Models for Tabular Data (NeurIPS 2021) [Example]
- TabNet from Arık et al.: TabNet: Attentive Interpretable Tabular Learning (AAAI 2021) [Example]
- ExcelFormer from Chen et al.: ExcelFormer: A Neural Network Surpassing GBDTs on Tabular Data [Example]
- TabTransformer from Huang et al.: TabTransformer: Tabular Data Modeling Using Contextual Embeddings [Example]
In addition, we implemented XGBoost, CatBoost, and LightGBM examples with hyperparameter-tuning using Optuna for users who'd like to compare their model performance with GBDTs.
Benchmark
We benchmark recent tabular deep learning models against GBDTs over diverse public datasets with different sizes and task types.
The following chart shows the performance of various models on small regression datasets, where the row represents the model names and the column represents dataset indices (we have 13 datasets here). For more results on classification and larger datasets, please check the benchmark documentation.
| Model Name | dataset0 | dataset1 | dataset2 | dataset3 | dataset4 | dataset5 | dataset6 | dataset7 | dataset8 | dataset9 | dataset10 | dataset11 | dataset_12 | | :------------------ | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | :-------------- | | XGBoost | 0.250±0.000 | 0.038±0.000 | 0.187±0.000 | 0.475±0.000 | 0.328±0.000 | 0.401±0.000 | 0.249±0.000 | 0.363±0.000 | 0.904±0.000 | 0.056±0.000 | 0.820±0.000 | 0.857±0.000 | 0.418±0.000 | | CatBoost | 0.265±0.000 | 0.062±0.000 | 0.128±0.000 | 0.336±0.000 | 0.346±0.000 | 0.443±0.000 | 0.375±0.000 | 0.273±0.000 | 0.881±0.000 | 0.040±0.000 | 0.756±0.000 | 0.876±0.000 | 0.439±0.000 | | LightGBM | 0.253±0.000 | 0.054±0.000 | 0.112±0.000 | 0.302±0.000 | 0.325±0.000 | 0.384±0.000 | 0.295±0.000 | 0.272±0.000 | 0.877±0.000 | 0.011±0.000 | 0.702±0.000 | 0.863±0.000 | 0.395±0.000 | | Trompt | 0.261±0.003 | 0.015±0.005 | 0.118±0.001 | 0.262±0.001 | 0.323±0.001 | 0.418±0.003 | 0.329±0.009 | 0.312±0.002 | OOM | 0.008±0.001 | 0.779±0.006 | 0.874±0.004 | 0.424±0.005 | | ResNet | 0.288±0.006 | 0.018±0.003 | 0.124±0.001 | 0.268±0.001 | 0.335±0.001 | 0.434±0.004 | 0.325±0.012 | 0.324±0.004 | 0.895±0.005 | 0.036±0.002 | 0.794±0.006 | 0.875±0.004 | 0.468±0.004 | | FTTransformerBucket | 0.325±0.008 | 0.096±0.005 | 0.360±0.354 | 0.284±0.005 | 0.342±0.004 | 0.441±0.003 | 0.345±0.007 | 0.339±0.003 | OOM | 0.105±0.011 | 0.807±0.010 | 0.885±0.008 | 0.468±0.006 | | ExcelFormer | 0.262±0.004 | 0.099±0.003 | 0.128±0.000 | 0.264±0.003 | 0.331±0.003 | 0.411±0.005 | 0.298±0.012 | 0.308±0.007 | OOM | 0.011±0.001 | 0.785±0.011 | 0.890±0.003 | 0.431±0.006 | | FTTransformer | 0.335±0.010 | 0.161±0.022 | 0.140±0.002 | 0.277±0.004 | 0.335±0.003 | 0.445±0.003 | 0.361±0.018 | 0.345±0.005 | OOM | 0.106±0.012 | 0.826±0.005 | 0.896±0.007 | 0.461±0.003 | | TabNet | 0.279±0.003 | 0.224±0.016 | 0.141±0.010 | 0.275±0.002 | 0.348±0.003 | 0.451±0.007 | 0.355±0.030 | 0.332±0.004 | 0.992±0.182 | 0.015±0.002 | 0.805±0.014 | 0.885±0.013 | 0.544±0.011 | | TabTransformer | 0.624±0.003 | 0.229±0.003 | 0.369±0.005 | 0.340±0.004 | 0.388±0.002 | 0.539±0.003 | 0.619±0.005 | 0.351±0.001 | 0.893±0.005 | 0.431±0.001 | 0.819±0.002 | 0.886±0.005 | 0.545±0.004 |
We see that some recent deep tabular models were able to achieve competitive model performance to strong GBDTs (despite being 5--100 times slower to train). Making deep tabular models even more performant with less compute is a fruitful direction for future research.
We also benchmark different text encoders on a real-world tabular dataset (Wine Reviews) with one text column. The following table shows the performance:
| Test Acc | Method | Model Name | Source | | :--------- | :------------ | :--------------------------------------------------------- | :----------- | | 0.7926 | Pre-trained | sentence-transformers/all-distilroberta-v1 (125M # params) | Hugging Face | | 0.7998 | Pre-trained | embed-english-v3.0 (dimension size: 1024) | Cohere | | 0.8102 | Pre-trained | text-embedding-ada-002 (dimension size: 1536) | OpenAI | | 0.8147 | Pre-trained | voyage-01 (dimension size: 1024) | Voyage AI | | 0.8203 | Pre-trained | intfloat/e5-mistral-7b-instruct (7B # params) | Hugging Face | | 0.8230 | LoRA Finetune | DistilBERT (66M # params) | Hugging Face |
The benchmark script for Hugging Face text encoders is in this file and for the rest of text encoders is in this file.
Installation
PyTorch Frame is available for Python 3.10 to Python 3.13.
pip install pytorch-frame
See the installation guide for other options.
Cite
If you use PyTorch Frame in your work, please cite our paper (Bibtex below).
@article{hu2024pytorch,
title={PyTorch Frame: A Modular Framework for Multi-Modal Tabular Learning},
author={Hu, Weihua and Yuan, Yiwen and Zhang, Zecheng and Nitta, Akihiro and Cao, Kaidi and Kocijan, Vid and Leskovec, Jure and Fey, Matthias},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.00776},
year={2024}
}
Owner
- Name: PyG
- Login: pyg-team
- Kind: organization
- Email: team@pyg.org
- Location: Germany
- Website: https://pyg.org
- Twitter: PyG_Team
- Repositories: 5
- Profile: https://github.com/pyg-team
Graph Neural Network Library for PyTorch
Citation (CITATION.cff)
--- cff-version: 1.2.0 message: "Please cite our paper if you use this code in your own work." title: "PyTorch Frame: A Deep Learning Framework for Tabular Data" authors: - family-names: "Hu" given-names: "Weihua" - family-names: "Yuan" given-names: "Yiwen" - family-names: "Zhang" given-names: "Zecheng" - family-names: "Nitta" given-names: "Akihiro" - family-names: "Cao" given-names: "Kaidi" - family-names: "Kocijan" given-names: "Vid" - family-names: "Leskovec" given-names: "Jure" - family-names: "Fey" given-names: "Matthias" date-released: 2023-10-24 license: MIT url: "https://github.com/pyg-team/pytorch-frame"
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 78
- Release event: 2
- Issues event: 9
- Watch event: 157
- Delete event: 80
- Issue comment event: 14
- Push event: 206
- Pull request review event: 60
- Pull request review comment event: 15
- Pull request event: 152
- Fork event: 14
Last Year
- Create event: 78
- Release event: 2
- Issues event: 9
- Watch event: 157
- Delete event: 80
- Issue comment event: 14
- Push event: 206
- Pull request review event: 60
- Pull request review comment event: 15
- Pull request event: 152
- Fork event: 14
Committers
Last synced: 9 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Weihua Hu | w****6@g****m | 105 |
| Akihiro Nitta | n****a@a****m | 85 |
| Yiwen Yuan | y****e@g****m | 76 |
| Zecheng Zhang | z****g@k****i | 51 |
| Matthias Fey | m****y@t****e | 33 |
| pre-commit-ci[bot] | 6****] | 25 |
| Kaidi Cao | 1****c | 7 |
| dependabot[bot] | 4****] | 6 |
| vid-koci | v****d@k****i | 5 |
| xnuohz | x****z@1****m | 5 |
| Andrei Ivanov | 3****v | 4 |
| Damian Szwichtenberg | d****g@i****m | 2 |
| Jinu Sunil | j****l@g****m | 2 |
| Xinwei He | x****i@k****i | 2 |
| toenshoff | j****f@r****e | 2 |
| Berke Kisin | k****e@g****m | 1 |
| Donald.Lee | 4****e | 1 |
| Houston2013 | 2****3 | 1 |
| Jirka Borovec | 6****a | 1 |
| LionSenSei | 1****9@q****m | 1 |
| Muhammad Anas Raza | 6****z | 1 |
| NeelKondapalli | 1****i | 1 |
| Rishabh Ranjan | r****7@g****m | 1 |
| Rishi Puri | p****8@b****u | 1 |
| Simon Popelier | 3****p | 1 |
| crunai | 1****i | 1 |
| eliia | 7****a | 1 |
| jayway | 7****y | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 35
- Total pull requests: 285
- Average time to close issues: 27 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 5 days
- Total issue authors: 26
- Total pull request authors: 28
- Average comments per issue: 1.2
- Average comments per pull request: 0.43
- Merged pull requests: 238
- Bot issues: 1
- Bot pull requests: 65
Past Year
- Issues: 12
- Pull requests: 146
- Average time to close issues: about 1 month
- Average time to close pull requests: about 17 hours
- Issue authors: 10
- Pull request authors: 14
- Average comments per issue: 0.5
- Average comments per pull request: 0.11
- Merged pull requests: 136
- Bot issues: 1
- Bot pull requests: 59
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- akihironitta (5)
- qychen2001 (4)
- XinweiHe (2)
- xnuohz (2)
- weihua916 (1)
- nimaous (1)
- toenshoff (1)
- Kksk43 (1)
- preritt (1)
- WhatAShot (1)
- luozhengdong (1)
- ggdw-maker (1)
- davidfstein (1)
- HoustonJ2013 (1)
- ValentinLo62 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- akihironitta (91)
- pre-commit-ci[bot] (52)
- weihua916 (32)
- zechengz (30)
- yiweny (26)
- rusty1s (16)
- dependabot[bot] (13)
- drivanov (7)
- vid-koci (5)
- xnuohz (5)
- Kh4L (4)
- XinweiHe (4)
- wsad1 (4)
- February24-Lee (3)
- toenshoff (3)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 5,417 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 7
- Total maintainers: 3
pypi.org: pytorch-frame
Tabular Deep Learning Library for PyTorch
- Documentation: https://pytorch-frame.readthedocs.io/
- License: MIT License
-
Latest release: 0.2.5
published about 1 year ago
Rankings
Maintainers (3)
Dependencies
- actions/setup-python v4.3.0 composite
- actions/checkout v4 composite
- dangoslen/changelog-enforcer v2 composite
- ./.github/actions/setup * composite
- actions/checkout v4 composite
- tj-actions/changed-files v34 composite
- actions/labeler v4 composite
- samspills/assign-pr-to-author v1.0 composite
- ./.github/actions/setup * composite
- actions/checkout v4 composite
- tj-actions/changed-files v34 composite
- ./.github/actions/setup * composite
- actions/checkout v4 composite
- tj-actions/changed-files v34 composite
- ./.github/actions/setup * composite
- actions/checkout v4 composite
- codecov/codecov-action v2 composite
- tj-actions/changed-files v34 composite
- numpy *
- pandas *
- pyarrow *
- torch *
- tqdm *
- actions/checkout v4 composite
- actions/setup-python v5 composite