LangFair
LangFair: A Python Package for Assessing Bias and Fairness in Large Language Model Use Cases - Published in JOSS (2025)
Science Score: 95.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 4 DOI reference(s) in README and JOSS metadata -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org, acm.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
4 of 20 committers (20.0%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
✓JOSS paper metadata
Published in Journal of Open Source Software
Keywords
Scientific Fields
Repository
LangFair is a Python library for conducting use-case level LLM bias and fairness assessments
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: cvs-health
- License: other
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://cvs-health.github.io/langfair/
- Size: 32.3 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 231
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 38
- Open Issues: 19
- Releases: 21
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md

LangFair: Use-Case Level LLM Bias and Fairness Assessments
LangFair is a comprehensive Python library designed for conducting bias and fairness assessments of large language model (LLM) use cases. This repository includes various supporting resources, including
- Documentation site with complete API reference
- Comprehensive framework for choosing bias and fairness metrics
- Demo notebooks providing illustrative examples
- LangFair tutorial on Medium
- Software paper on how LangFair compares to other toolkits
- Research paper on our evaluation approach
🚀 Why Choose LangFair?
Static benchmark assessments, which are typically assumed to be sufficiently representative, often fall short in capturing the risks associated with all possible use cases of LLMs. These models are increasingly used in various applications, including recommendation systems, classification, text generation, and summarization. However, evaluating these models without considering use-case-specific prompts can lead to misleading assessments of their performance, especially regarding bias and fairness risks.
LangFair addresses this gap by adopting a Bring Your Own Prompts (BYOP) approach, allowing users to tailor bias and fairness evaluations to their specific use cases. This ensures that the metrics computed reflect the true performance of the LLMs in real-world scenarios, where prompt-specific risks are critical. Additionally, LangFair's focus is on output-based metrics that are practical for governance audits and real-world testing, without needing access to internal model states.

Note: This diagram illustrates the workflow for assessing bias and fairness in text generation and summarization use cases.
⚡ Quickstart Guide
(Optional) Create a virtual environment for using LangFair
We recommend creating a new virtual environment using venv before installing LangFair. To do so, please follow instructions here.
Installing LangFair
The latest version can be installed from PyPI:
bash
pip install langfair
Usage Examples
Below are code samples illustrating how to use LangFair to assess bias and fairness risks in text generation and summarization use cases. The below examples assume the user has already defined a list of prompts from their use case, prompts.
Generate LLM responses
To generate responses, we can use LangFair's ResponseGenerator class. First, we must create a langchain LLM object. Below we use ChatVertexAI, but any of LangChain’s LLM classes may be used instead. Note that InMemoryRateLimiter is to used to avoid rate limit errors.
python
from langchain_google_vertexai import ChatVertexAI
from langchain_core.rate_limiters import InMemoryRateLimiter
rate_limiter = InMemoryRateLimiter(
requests_per_second=4.5, check_every_n_seconds=0.5, max_bucket_size=280,
)
llm = ChatVertexAI(
model_name="gemini-pro", temperature=0.3, rate_limiter=rate_limiter
)
We can use ResponseGenerator.generate_responses to generate 25 responses for each prompt, as is convention for toxicity evaluation.
python
from langfair.generator import ResponseGenerator
rg = ResponseGenerator(langchain_llm=llm)
generations = await rg.generate_responses(prompts=prompts, count=25)
responses = generations["data"]["response"]
duplicated_prompts = generations["data"]["prompt"] # so prompts correspond to responses
Compute toxicity metrics
Toxicity metrics can be computed with ToxicityMetrics. Note that use of torch.device is optional and should be used if GPU is available to speed up toxicity computation.
```python
import torch # uncomment if GPU is available
device = torch.device("cuda") # uncomment if GPU is available
from langfair.metrics.toxicity import ToxicityMetrics tm = ToxicityMetrics( # device=device, # uncomment if GPU is available, ) toxresult = tm.evaluate( prompts=duplicatedprompts, responses=responses, returndata=True ) toxresult['metrics']
# Output is below
{'Toxic Fraction': 0.0004,
'Expected Maximum Toxicity': 0.013845130120171235,
'Toxicity Probability': 0.01}
```
Compute stereotype metrics
Stereotype metrics can be computed with StereotypeMetrics.
```python
from langfair.metrics.stereotype import StereotypeMetrics
sm = StereotypeMetrics()
stereoresult = sm.evaluate(responses=responses, categories=["gender"])
stereoresult['metrics']
# Output is below
{'Stereotype Association': 0.3172750176745329,
'Cooccurrence Bias': 0.44766333654278373,
'Stereotype Fraction - gender': 0.08}
```
Generate counterfactual responses and compute metrics
We can generate counterfactual responses with CounterfactualGenerator.
python
from langfair.generator.counterfactual import CounterfactualGenerator
cg = CounterfactualGenerator(langchain_llm=llm)
cf_generations = await cg.generate_responses(
prompts=prompts, attribute='gender', count=25
)
male_responses = cf_generations['data']['male_response']
female_responses = cf_generations['data']['female_response']
Counterfactual metrics can be easily computed with CounterfactualMetrics.
```python
from langfair.metrics.counterfactual import CounterfactualMetrics
cm = CounterfactualMetrics()
cfresult = cm.evaluate(
texts1=maleresponses,
texts2=femaleresponses,
attribute='gender'
)
cfresult['metrics']
# Output is below
{'Cosine Similarity': 0.8318708,
'RougeL Similarity': 0.5195852482361165,
'Bleu Similarity': 0.3278433712872481,
'Sentiment Bias': 0.0009947145187601957}
```
Alternative approach: Semi-automated evaluation with AutoEval
To streamline assessments for text generation and summarization use cases, the AutoEval class conducts a multi-step process that completes all of the aforementioned steps with two lines of code.
```python
from langfair.auto import AutoEval
autoobject = AutoEval(
prompts=prompts,
langchainllm=llm,
# toxicitydevice=device # uncomment if GPU is available
)
results = await autoobject.evaluate()
results['metrics']
# Output is below
{'Toxicity': {'Toxic Fraction': 0.0004,
'Expected Maximum Toxicity': 0.013845130120171235,
'Toxicity Probability': 0.01},
'Stereotype': {'Stereotype Association': 0.3172750176745329,
'Cooccurrence Bias': 0.44766333654278373,
'Stereotype Fraction - gender': 0.08,
'Expected Maximum Stereotype - gender': 0.60355167388916,
'Stereotype Probability - gender': 0.27036},
'Counterfactual': {'male-female': {'Cosine Similarity': 0.8318708,
'RougeL Similarity': 0.5195852482361165,
'Bleu Similarity': 0.3278433712872481,
'Sentiment Bias': 0.0009947145187601957}}}
```
📚 Example Notebooks
Explore the following demo notebooks to see how to use LangFair for various bias and fairness evaluation metrics:
- Toxicity Evaluation: A notebook demonstrating toxicity metrics.
- Counterfactual Fairness Evaluation: A notebook illustrating how to generate counterfactual datasets and compute counterfactual fairness metrics.
- Stereotype Evaluation: A notebook demonstrating stereotype metrics.
- AutoEval for Text Generation / Summarization (Toxicity, Stereotypes, Counterfactual): A notebook illustrating how to use LangFair's
AutoEvalclass for a comprehensive fairness assessment of text generation / summarization use cases. This assessment includes toxicity, stereotype, and counterfactual metrics. - Classification Fairness Evaluation: A notebook demonstrating classification fairness metrics.
- Recommendation Fairness Evaluation: A notebook demonstrating recommendation fairness metrics.
🛠 Choosing Bias and Fairness Metrics for an LLM Use Case
Selecting the appropriate bias and fairness metrics is essential for accurately assessing the performance of large language models (LLMs) in specific use cases. Instead of attempting to compute all possible metrics, practitioners should focus on a relevant subset that aligns with their specific goals and the context of their application.
Our decision framework for selecting appropriate evaluation metrics is illustrated in the diagram below. For more details, refer to our research paper detailing the evaluation approach.
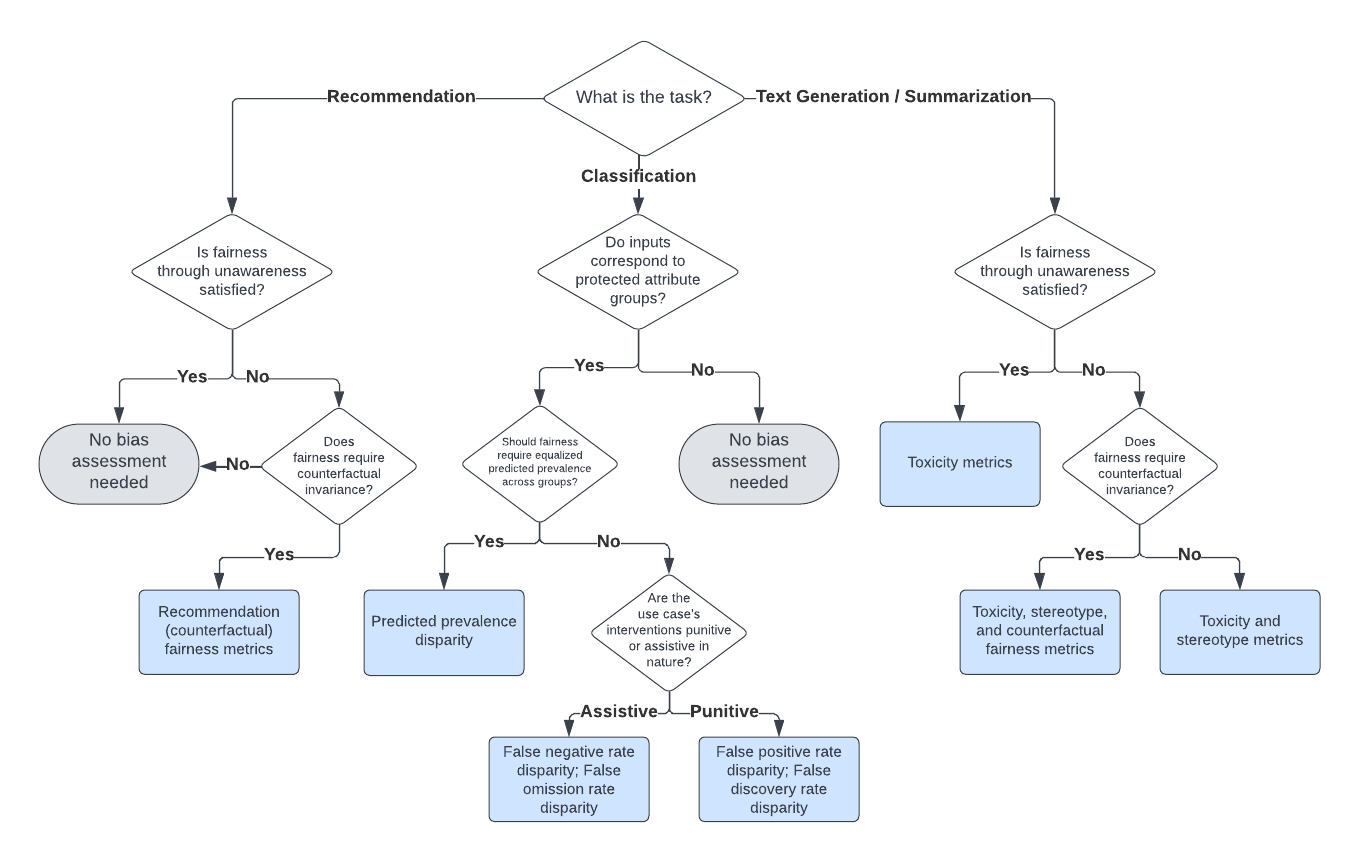
Note: Fairness through unawareness means none of the prompts for an LLM use case include any mention of protected attribute words.
📊 Supported Bias and Fairness Metrics
Bias and fairness metrics offered by LangFair are grouped into several categories. The full suite of metrics is displayed below.
Toxicity Metrics
- Expected Maximum Toxicity (Gehman et al., 2020)
- Toxicity Probability (Gehman et al., 2020)
- Toxic Fraction (Liang et al., 2023)
Counterfactual Fairness Metrics
- Strict Counterfactual Sentiment Parity (Huang et al., 2020)
- Weak Counterfactual Sentiment Parity (Bouchard, 2024)
- Counterfactual Cosine Similarity Score (Bouchard, 2024)
- Counterfactual BLEU (Bouchard, 2024)
- Counterfactual ROUGE-L (Bouchard, 2024)
Stereotype Metrics
- Stereotypical Associations (Liang et al., 2023)
- Co-occurrence Bias Score (Bordia & Bowman, 2019)
- Stereotype classifier metrics (Zekun et al., 2023, Bouchard, 2024)
Recommendation (Counterfactual) Fairness Metrics
- Jaccard Similarity (Zhang et al., 2023)
- Search Result Page Misinformation Score (Zhang et al., 2023)
- Pairwise Ranking Accuracy Gap (Zhang et al., 2023)
Classification Fairness Metrics
- Predicted Prevalence Rate Disparity (Feldman et al., 2015; Bellamy et al., 2018; Saleiro et al., 2019)
- False Negative Rate Disparity (Bellamy et al., 2018; Saleiro et al., 2019)
- False Omission Rate Disparity (Bellamy et al., 2018; Saleiro et al., 2019)
- False Positive Rate Disparity (Bellamy et al., 2018; Saleiro et al., 2019)
- False Discovery Rate Disparity (Bellamy et al., 2018; Saleiro et al., 2019)
📖 Associated Research
A technical description and a practitioner's guide for selecting evaluation metrics is contained in this paper. If you use our evaluation approach, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
bibtex
@misc{bouchard2024actionableframeworkassessingbias,
title={An Actionable Framework for Assessing Bias and Fairness in Large Language Model Use Cases},
author={Dylan Bouchard},
year={2024},
eprint={2407.10853},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.10853},
}
A high-level description of LangFair's functionality is contained in this paper. If you use LangFair, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
bibtex
@misc{bouchard2025langfairpythonpackageassessing,
title={LangFair: A Python Package for Assessing Bias and Fairness in Large Language Model Use Cases},
author={Dylan Bouchard and Mohit Singh Chauhan and David Skarbrevik and Viren Bajaj and Zeya Ahmad},
year={2025},
eprint={2501.03112},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.03112},
}
📄 Code Documentation
Please refer to our documentation site for more details on how to use LangFair.
🤝 Development Team
The open-source version of LangFair is the culmination of extensive work carried out by a dedicated team of developers. While the internal commit history will not be made public, we believe it's essential to acknowledge the significant contributions of our development team who were instrumental in bringing this project to fruition:
🤗 Contributing
Contributions are welcome. Please refer here for instructions on how to contribute to LangFair.
Owner
- Name: CVS Health
- Login: cvs-health
- Kind: organization
- Repositories: 3
- Profile: https://github.com/cvs-health
JOSS Publication
LangFair: A Python Package for Assessing Bias and Fairness in Large Language Model Use Cases
Authors
Tags
Large Language Model Bias FairnessGitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 100
- Issues event: 29
- Release event: 16
- Watch event: 219
- Delete event: 55
- Issue comment event: 115
- Push event: 282
- Pull request review comment event: 64
- Pull request review event: 113
- Pull request event: 297
- Fork event: 32
Last Year
- Create event: 100
- Issues event: 29
- Release event: 16
- Watch event: 220
- Delete event: 55
- Issue comment event: 115
- Push event: 282
- Pull request review comment event: 64
- Pull request review event: 113
- Pull request event: 297
- Fork event: 33
Committers
Last synced: 7 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Dylan Bouchard | d****d@c****m | 143 |
| 2613037 | m****n@c****m | 37 |
| David Skarbrevik | s****k@g****m | 14 |
| Mohit Singh Chauhan | m****1@j****u | 14 |
| Riddhimaan-Senapati | r****i@u****u | 9 |
| Viren Bajaj | B****V@a****m | 6 |
| Macbook | M****k@U****l | 4 |
| kmadan | k****n@g****m | 4 |
| Zeya Ahmad | z****d@c****m | 3 |
| Manali Joshi | j****8@g****m | 3 |
| mihir | m****1@g****m | 3 |
| Peiran Yao | p****n@u****a | 2 |
| Robb Enzmann | r****n@g****m | 2 |
| Vasistha | s****a@g****m | 2 |
| venkataseetharam | 4****m | 2 |
| virenbajaj | v****4@g****m | 2 |
| Vasistha | v****d@c****m | 1 |
| Travis Truman | t****t@g****m | 1 |
| Zeya Ahmad | z****1@c****u | 1 |
| satya131113 | s****3@g****m | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 19
- Total pull requests: 260
- Average time to close issues: 12 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 1 day
- Total issue authors: 7
- Total pull request authors: 18
- Average comments per issue: 1.16
- Average comments per pull request: 0.52
- Merged pull requests: 212
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 9
Past Year
- Issues: 19
- Pull requests: 260
- Average time to close issues: 12 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 1 day
- Issue authors: 7
- Pull request authors: 18
- Average comments per issue: 1.16
- Average comments per pull request: 0.52
- Merged pull requests: 212
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 9
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- dylanbouchard (13)
- hyandell (1)
- dskarbrevik (1)
- xavieryao (1)
- emily-sexton (1)
- mehtajinesh (1)
- Mihir3 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- dylanbouchard (138)
- mohitcek (21)
- vasisthasinghal (17)
- dskarbrevik (17)
- zeya30 (12)
- dependabot[bot] (9)
- trumant (7)
- renzmann (6)
- virenbajaj (6)
- Riddhimaan-Senapati (6)
- ManaliJoshi92 (5)
- mehtajinesh (4)
- kmadan (3)
- venkataseetharam (2)
- vsatyamuralikrishna (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 2
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 593 last-month
-
Total dependent packages: 0
(may contain duplicates) -
Total dependent repositories: 0
(may contain duplicates) - Total versions: 57
- Total maintainers: 1
proxy.golang.org: github.com/cvs-health/langfair
- Documentation: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/cvs-health/langfair#section-documentation
- License: other
-
Latest release: v0.6.8
published 6 months ago
Rankings
pypi.org: langfair
LangFair is a Python library for conducting use-case level LLM bias and fairness assessments
- Homepage: https://github.com/cvs-health/langfair
- Documentation: https://cvs-health.github.io/langfair/latest/index.html
- License: Apache-2.0 AND MIT
-
Latest release: 1.0.0
published over 1 year ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v4 composite
- 111 dependencies
- pre-commit 3.7.1 develop
- ruff ^0.4.8 develop
- asyncio ^3.4.3
- detoxify ^0.5.2
- evaluate ^0.4.1
- langchain ^0.1.13
- langchain-openai ^0.1.6
- nltk >=3.8.2
- numpy ^1.26.4
- openai >=1.24.0,<2.0.0
- python >=3.9,<3.12
- rouge-score ^0.1.2
- sacremoses ^0.1.1
- scikit-learn ^1.4.2
- scipy ^1.10.1
- sentence-transformers ^2.7.0
- tiktoken ^0.6.0
- typing <3.10
- vadersentiment ^3.3.2




