autodistill
Images to inference with no labeling (use foundation models to train supervised models).
Science Score: 44.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
○Academic publication links
-
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (13.0%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
Images to inference with no labeling (use foundation models to train supervised models).
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: autodistill
- License: apache-2.0
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://docs.autodistill.com
- Size: 1.16 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 2,285
- Watchers: 19
- Forks: 185
- Open Issues: 44
- Releases: 3
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
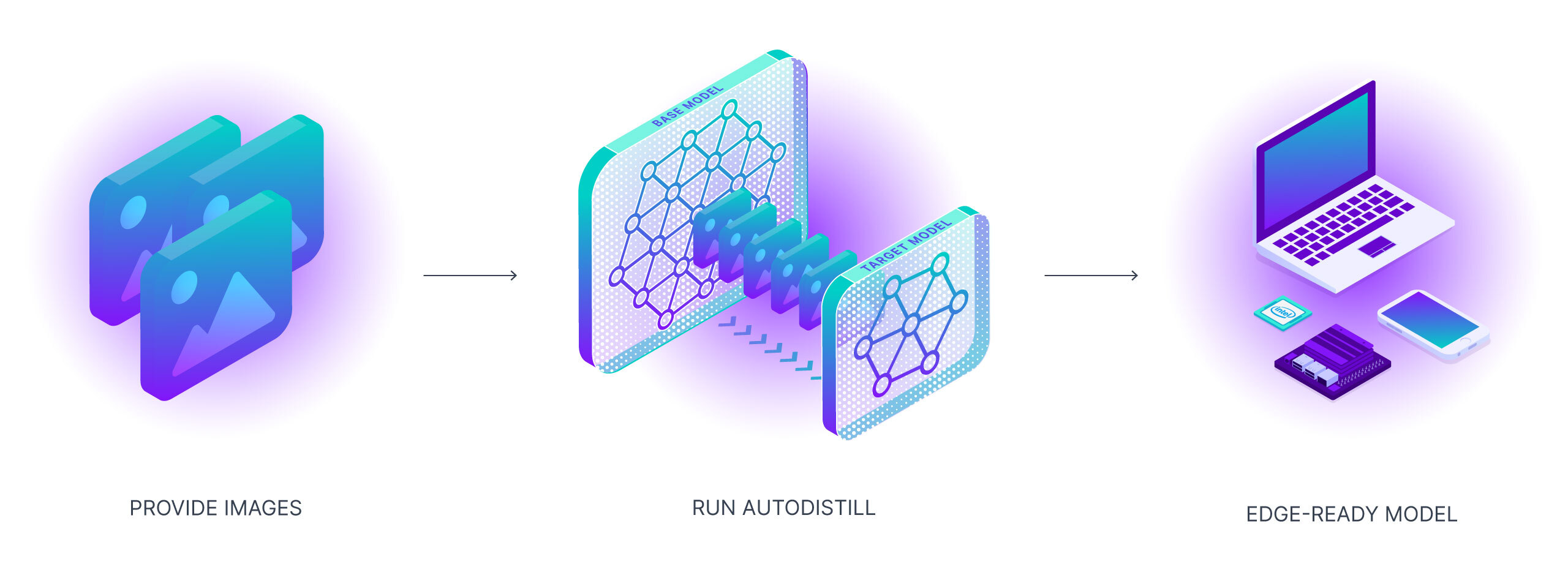
Autodistill uses big, slower foundation models to train small, faster supervised models. Using autodistill, you can go from unlabeled images to inference on a custom model running at the edge with no human intervention in between.
[!TIP] You can use Autodistill on your own hardware, or use the Roboflow hosted version of Autodistill to label images in the cloud.
Currently, autodistill supports vision tasks like object detection and instance segmentation, but in the future it can be expanded to support language (and other) models.
🔗 Quicklinks
| Tutorial | Docs | Supported Models | Contribute | | :-----------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------: | :------------------------------------: | :---------------------------: |
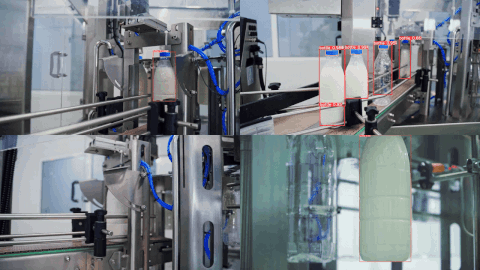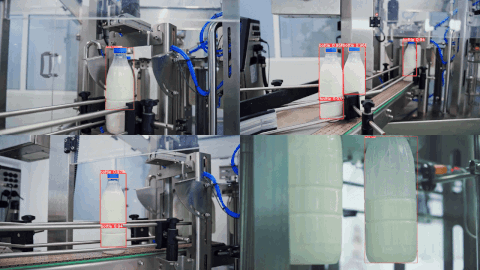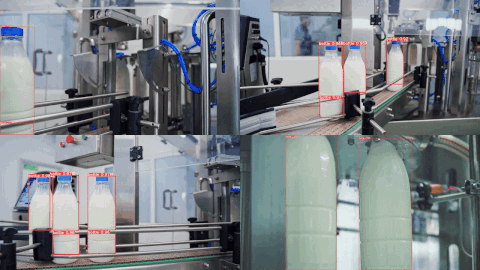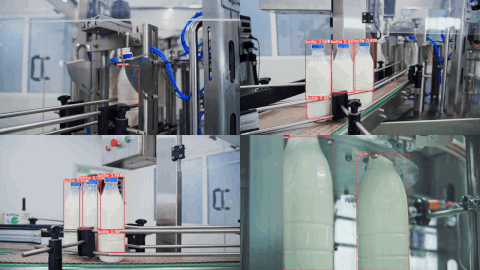
👀 Example Output
Here are example predictions of a Target Model detecting milk bottles and bottlecaps after being trained on an auto-labeled dataset using Autodistill (see the Autodistill YouTube video for a full walkthrough):
🚀 Features
- 🔌 Pluggable interface to connect models together
- 🤖 Automatically label datasets
- 🐰 Train fast supervised models
- 🔒 Own your model
- 🚀 Deploy distilled models to the cloud or the edge
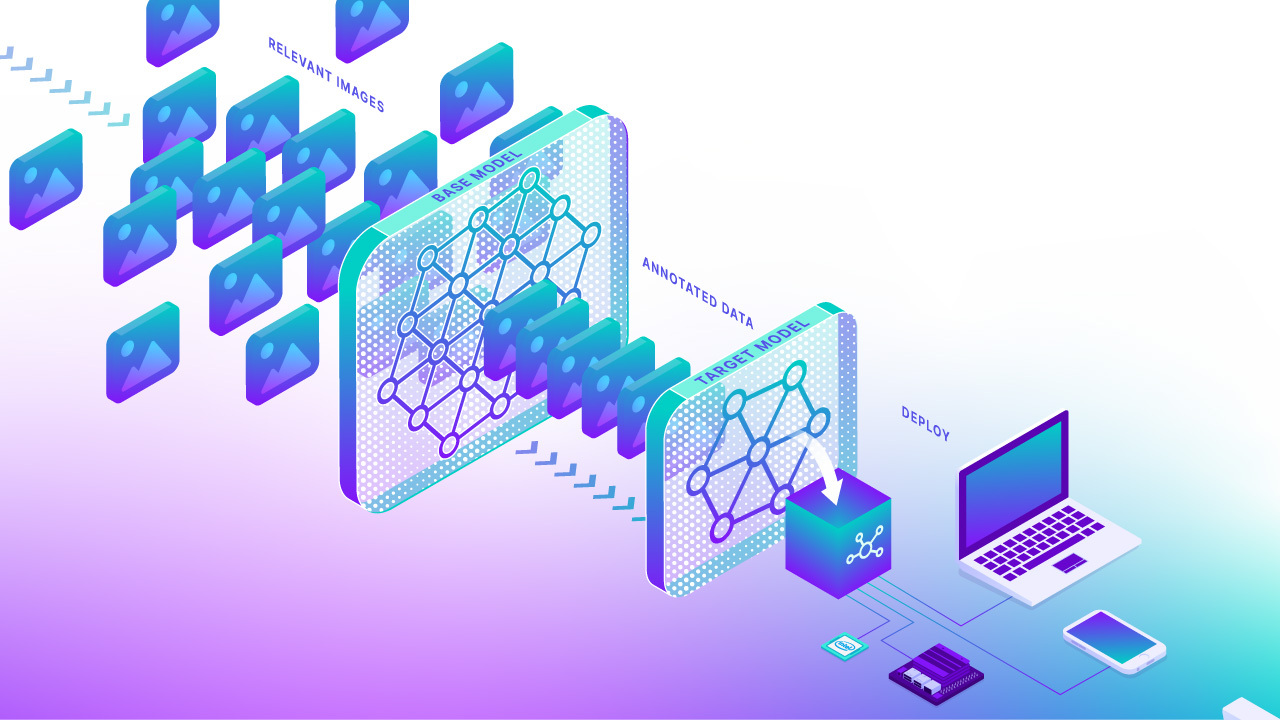
📚 Basic Concepts
To use autodistill, you input unlabeled data into a Base Model which uses an Ontology to label a Dataset that is used to train a Target Model which outputs a Distilled Model fine-tuned to perform a specific Task.
Autodistill defines several basic primitives:
- Task - A Task defines what a Target Model will predict. The Task for each component (Base Model, Ontology, and Target Model) of an
autodistillpipeline must match for them to be compatible with each other. Object Detection and Instance Segmentation are currently supported through thedetectiontask.classificationsupport will be added soon. - Base Model - A Base Model is a large foundation model that knows a lot about a lot. Base models are often multimodal and can perform many tasks. They're large, slow, and expensive. Examples of Base Models are GroundedSAM and GPT-4's upcoming multimodal variant. We use a Base Model (along with unlabeled input data and an Ontology) to create a Dataset.
- Ontology - an Ontology defines how your Base Model is prompted, what your Dataset will describe, and what your Target Model will predict. A simple Ontology is the
CaptionOntologywhich prompts a Base Model with text captions and maps them to class names. Other Ontologies may, for instance, use a CLIP vector or example images instead of a text caption. - Dataset - a Dataset is a set of auto-labeled data that can be used to train a Target Model. It is the output generated by a Base Model.
- Target Model - a Target Model is a supervised model that consumes a Dataset and outputs a distilled model that is ready for deployment. Target Models are usually small, fast, and fine-tuned to perform a specific task very well (but they don't generalize well beyond the information described in their Dataset). Examples of Target Models are YOLOv8 and DETR.
- Distilled Model - a Distilled Model is the final output of the
autodistillprocess; it's a set of weights fine-tuned for your task that can be deployed to get predictions.
💡 Theory and Limitations
Human labeling is one of the biggest barriers to broad adoption of computer vision. It can take thousands of hours to craft a dataset suitable for training a production model. The process of distillation for training supervised models is not new, in fact, traditional human labeling is just another form of distillation from an extremely capable Base Model (the human brain 🧠).
Foundation models know a lot about a lot, but for production we need models that know a lot about a little.
As foundation models get better and better they will increasingly be able to augment or replace humans in the labeling process. We need tools for steering, utilizing, and comparing these models. Additionally, these foundation models are big, expensive, and often gated behind private APIs. For many production use-cases, we need models that can run cheaply and in realtime at the edge.
Autodistill's Base Models can already create datasets for many common use-cases (and through creative prompting and few-shotting we can expand their utility to many more), but they're not perfect yet. There's still a lot of work to do; this is just the beginning and we'd love your help testing and expanding the capabilities of the system!
💿 Installation
Autodistill is modular. You'll need to install the autodistill package (which defines the interfaces for the above concepts) along with Base Model and Target Model plugins (which implement specific models).
By packaging these separately as plugins, dependency and licensing incompatibilities are minimized and new models can be implemented and maintained by anyone.
Example:
bash
pip install autodistill autodistill-grounded-sam autodistill-yolov8
Install from source
You can also clone the project from GitHub for local development: ```bash git clone https://github.com/roboflow/autodistill cd autodistill pip install -e . ```Additional Base and Target models are enumerated below.
🚀 Quickstart
See the demo Notebook for a quick introduction to autodistill. This notebook walks through building a milk container detection model with no labeling.
Below, we have condensed key parts of the notebook for a quick introduction to autodistill.
You can also run Autodistill in one command. First, install autodistill:
bash
pip install autodistill
Then, run:
bash
autodistill images --base="grounding_dino" --target="yolov8" --ontology '{"prompt": "label"}' --output="./dataset"
This command will label all images in a directory called images with Grounding DINO and use the labeled images to train a YOLOv8 model. Grounding DINO will label all images with the "prompt" and save the label as the "label". You can specify as many prompts and labels as you want. The resulting dataset will be saved in a folder called dataset.
Install Packages
For this example, we'll show how to distill GroundedSAM into a small YOLOv8 model using autodistill-grounded-sam and autodistill-yolov8.
pip install autodistill autodistill-grounded-sam autodistill-yolov8
Distill a Model
```python from autodistillgroundedsam import GroundedSAM from autodistill.detection import CaptionOntology from autodistill_yolov8 import YOLOv8
define an ontology to map class names to our GroundingDINO prompt
the ontology dictionary has the format {caption: class}
where caption is the prompt sent to the base model, and class is the label that will
be saved for that caption in the generated annotations
base_model = GroundedSAM(ontology=CaptionOntology({"shipping container": "container"}))
label all images in a folder called context_images
basemodel.label( inputfolder="./images", output_folder="./dataset" )
targetmodel = YOLOv8("yolov8n.pt") targetmodel.train("./dataset/data.yaml", epochs=200)
run inference on the new model
pred = target_model.predict("./dataset/valid/your-image.jpg", confidence=0.5) print(pred)
optional: upload your model to Roboflow for deployment
from roboflow import Roboflow
rf = Roboflow(apikey="APIKEY") project = rf.workspace().project("PROJECTID") project.version(DATASETVERSION).deploy(modeltype="yolov8", modelpath=f"./runs/detect/train/") ```
Visualize Predictions
To plot the annotations for a single image using `autodistill`, you can use the code below. This code is helpful to visualize the annotations generated by your base model (i.e. GroundedSAM) and the results from your target model (i.e. YOLOv8). ```python import supervision as sv import cv2 img_path = "./images/your-image.jpeg" image = cv2.imread(img_path) detections = base_model.predict(img_path) # annotate image with detections box_annotator = sv.BoxAnnotator() label_annotator = sv.LabelAnnotator() labels = [ f"{base_model.ontology.classes()[class_id]} {confidence:0.2f}" for _, _, confidence, class_id, _, _ in detections ] annotated_frame = box_annotator.annotate( scene=image.copy(), detections=detections ) annotated_frame = label_annotator.annotate( scene=annotated_frame, detections=detections, labels=labels ) sv.plot_image(annotated_frame, (16, 16)) ```📍 Available Models
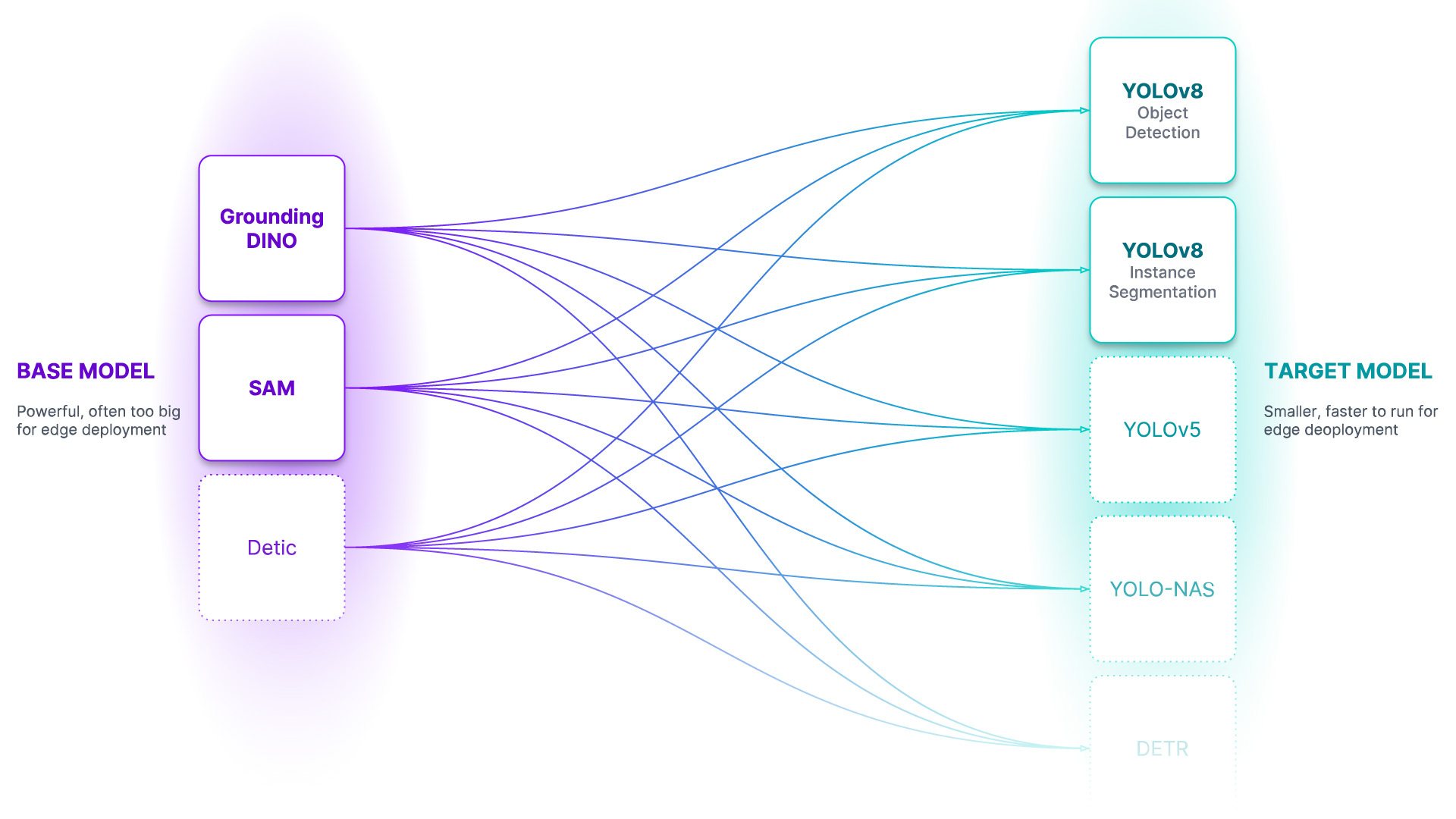
Our goal is for autodistill to support using all foundation models as Base Models and most SOTA supervised models as Target Models. We focused on object detection and segmentation
tasks first but plan to launch classification support soon! In the future, we hope autodistill will also be used for models beyond computer vision.
- ✅ - complete (click row/column header to go to repo)
- 🚧 - work in progress
object detection
| base / target | YOLOv8 | YOLO-NAS | YOLOv5 | DETR | YOLOv6 | YOLOv7 | MT-YOLOv6 | | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------: | :----: | :----: | :-------: | | Grounded SAM 2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | DETIC | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | GroundedSAM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | GroundingDINO | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | OWL-ViT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | SAM-CLIP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | LLaVA-1.5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | Kosmos-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | OWLv2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | Roboflow Universe Models (50k+ pre-trained models) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | CoDet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | Azure Custom Vision | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | AWS Rekognition | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | | | Google Vision | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | |
instance segmentation
| base / target | YOLOv8 | YOLO-NAS | YOLOv5 | YOLOv7 | Segformer | | :--------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------: | :----: | :-------: | | GroundedSAM | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | | | | SAM-CLIP | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | | | | SegGPT | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | | | | FastSAM | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | | |
classification
| base / target | ViT | YOLOv8 | YOLOv5 | | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------: | | CLIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | MetaCLIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | DINOv2 | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | BLIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | ALBEF | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | FastViT | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | AltCLIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | EvaCLIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | Gemini | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | | Fuyu | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | | Open Flamingo | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | | GPT-4 | | | | | PaLM-2 | | | |
Roboflow Model Deployment Support
You can optionally deploy some Target Models trained using Autodistill on Roboflow. Deploying on Roboflow allows you to use a range of concise SDKs for using your model on the edge, from roboflow.js for web deployment to NVIDIA Jetson devices.
The following Autodistill Target Models are supported by Roboflow for deployment:
| model name | Supported? | | :--------------------------: | :--------: | | YOLOv8 Object Detection | ✅ | | YOLOv8 Instance Segmentation | ✅ | | YOLOv5 Object Detection | ✅ | | YOLOv5 Instance Segmentation | ✅ | | YOLOv8 Classification | |
🎬 Video Guides
 Autodistill: Train YOLOv8 with ZERO Annotations
Autodistill: Train YOLOv8 with ZERO Annotations
In this video, we will show you how to use a new library to train a YOLOv8 model to detect bottles moving on a conveyor line. Yes, that's right - zero annotation hours are required! We dive deep into Autodistill's functionality, covering topics from setting up your Python environment and preparing your images, to the thrilling automatic annotation of images.
💡 Community Resources
- Distill Large Vision Models into Smaller, Efficient Models with Autodistill: Announcement post with written guide on how to use Autodistill
- Comparing AI-Labeled Data to Human-Labeled Data: A qualitative evaluation of Grounding DINO used with Autodistill across various tasks and domains.
- How to Evaluate Autodistill Prompts with CVevals: Evaluate Autodistill prompts.
- Autodistill: Label and Train a Computer Vision Model in Under 20 Minutes: Building a model to detect planes in under 20 minutes.
- Comparing AI-Labeled Data to Human-Labeled Data: Explore the strengths and limitations of a base model used with Autoditsill.
- Train an Image Classification Model with No Labeling: Use Grounded SAM to automatically label images for training an Ultralytics YOLOv8 classification model.
- Train a Segmentation Model with No Labeling: Use CLIP to automatically label images for training an Ultralytics YOLOv8 segmentation model.
- File a PR to add your own resources here!
🗺️ Roadmap
Apart from adding new models, there are several areas we plan to explore with autodistill including:
- 💡 Ontology creation & prompt engineering
- 👩💻 Human in the loop support
- 🤔 Model evaluation
- 🔄 Active learning
- 💬 Language tasks
🏆 Contributing
We love your input! Please see our contributing guide to get started. Thank you 🙏 to all our contributors!
👩⚖️ License
The autodistill package is licensed under an Apache 2.0. Each Base or Target model plugin may use its own license corresponding with the license of its underlying model. Please refer to the license in each plugin repo for more information.
Frequently Asked Questions ❓
What causes the PytorchStreamReader failed reading zip archive: failed finding central directory error?
This error is caused when PyTorch cannot load the model weights for a model. Go into the ~/.cache/autodistill directory and delete the folder associated with the model you are trying to load. Then, run your code again. The model weights will be downloaded from scratch. Leave the installation process uninterrupted.
💻 explore more Roboflow open source projects
| Project | Description | | :----------------------------------------------------------------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | supervision | General-purpose utilities for use in computer vision projects, from predictions filtering and display to object tracking to model evaluation. | | Autodistill (this project) | Automatically label images for use in training computer vision models. | | Inference | An easy-to-use, production-ready inference server for computer vision supporting deployment of many popular model architectures and fine-tuned models. | | Notebooks | Tutorials for computer vision tasks, from training state-of-the-art models to tracking objects to counting objects in a zone. | | Collect | Automated, intelligent data collection powered by CLIP. |
Owner
- Name: Autodistill
- Login: autodistill
- Kind: organization
- Email: autodistill@roboflow.com
- Website: https://autodistill.com
- Repositories: 1
- Profile: https://github.com/autodistill
Use bigger slower models to train smaller faster ones
Citation (CITATION.cff)
cff-version: 1.2.0 author: Roboflow message: If you use this software, please cite using the citation below. title: autodistill version: 0.1.0 date-released: 2023-01-19 license: MIT repository-code: https://github.com/autodistill/autodistill keywords: - computer vision - knowledge distillation
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 12
- Watch event: 422
- Member event: 1
- Issue comment event: 18
- Push event: 10
- Pull request review comment event: 2
- Pull request review event: 5
- Pull request event: 12
- Fork event: 41
- Create event: 1
Last Year
- Issues event: 12
- Watch event: 422
- Member event: 1
- Issue comment event: 18
- Push event: 10
- Pull request review comment event: 2
- Pull request review event: 5
- Pull request event: 12
- Fork event: 41
- Create event: 1
Committers
Last synced: 9 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| James Gallagher | j****g@j****g | 206 |
| Brad Dwyer | b****d@r****m | 13 |
| Sachin Agarwal | s****n@r****m | 9 |
| Thomas Hansen | t****n@g****m | 8 |
| Lakshman | a****4@g****m | 7 |
| LinasKo | l****s@g****m | 6 |
| Leo Ueno | l****o@r****m | 3 |
| muhammad-usama-aleem | u****0@g****m | 3 |
| Hundsmuhlen | 6****n | 2 |
| Guo Haria | h****g | 2 |
| Andrew Healey | d****y@g****m | 2 |
| MaximeDebarbat | m****e@s****i | 1 |
| Alen Asenie | 7****0 | 1 |
| Ariuntuya Altanzaya | 6****a | 1 |
| Blake Burch | b****h@g****m | 1 |
| Hoan Nguyen | n****8@g****m | 1 |
| Ismail Mohammed | i****4@g****m | 1 |
| SkalskiP | p****2@g****m | 1 |
| Skylar Givens | s****r@r****m | 1 |
| AshAnand34 | a****9@g****m | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 109
- Total pull requests: 91
- Average time to close issues: about 2 months
- Average time to close pull requests: 30 days
- Total issue authors: 84
- Total pull request authors: 30
- Average comments per issue: 3.13
- Average comments per pull request: 1.05
- Merged pull requests: 61
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 14
- Pull requests: 15
- Average time to close issues: 8 minutes
- Average time to close pull requests: 5 days
- Issue authors: 14
- Pull request authors: 7
- Average comments per issue: 0.43
- Average comments per pull request: 0.4
- Merged pull requests: 5
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- capjamesg (4)
- lab176344 (4)
- pythonstuff8 (3)
- duckheada (3)
- kobic8 (2)
- andysingal (2)
- hahapt (2)
- ccly1996 (2)
- elpabos (2)
- AlainPilon (2)
- jeffreyianwilson (2)
- lizhiwen19900709 (2)
- shubhamchdhary (2)
- shersoni610 (2)
- apiszcz (2)
Pull Request Authors
- capjamesg (54)
- bigbitbus (6)
- lab176344 (6)
- hansent (6)
- AshAnand34 (6)
- stellasphere (4)
- Hundsmuhlen (4)
- yeldarby (3)
- stephansturges (2)
- n0kovo (2)
- tfriedel (2)
- waterdeepmage (2)
- Alaaeldinn (2)
- blakeburch (2)
- LinasKo (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 3
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 7,226 last-month
-
Total dependent packages: 39
(may contain duplicates) -
Total dependent repositories: 2
(may contain duplicates) - Total versions: 36
- Total maintainers: 4
pypi.org: autodistill
Distill large foundational models into smaller, domain-specific models for deployment
- Homepage: https://github.com/autodistill/autodistill
- Documentation: https://autodistill.readthedocs.io/
- License: Apache Software License
-
Latest release: 0.1.29
published about 1 year ago
Rankings
Maintainers (3)
proxy.golang.org: github.com/autodistill/autodistill
- Documentation: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/autodistill/autodistill#section-documentation
- License: apache-2.0
-
Latest release: v0.1.26
published about 2 years ago
Rankings
pypi.org: autodistll-grounded-sam
Automatically distill large foundational models into smaller, in-domain models for deployment
- Homepage: https://github.com/autodistill/autodistill
- Documentation: https://autodistll-grounded-sam.readthedocs.io/
- License: MIT License
-
Latest release: 0.0.5
published almost 3 years ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- actions/cache v3 composite
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v4 composite
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v2 composite
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v2 composite
- actions/first-interaction v1.1.1 composite
- lodash 4.17.21
- lodash ^4.17.21
- Pillow >=7.1.2
- PyYAML >=5.3.1
- click *
- opencv-python >=4.6.0
- supervision *
- tqdm *
- Pillow >=7.1.2
- PyYAML >=5.3.1
- click *
- opencv-python >=4.6.0
- supervision *
- tqdm *