symbolfit
Automatic parametric modeling with symbolic regression [Comput Softw Big Sci 9, 12 (2025)]
Science Score: 67.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 4 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org -
○Academic email domains
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (12.1%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
Automatic parametric modeling with symbolic regression [Comput Softw Big Sci 9, 12 (2025)]
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: hftsoi
- License: mit
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://symbolfit.readthedocs.io
- Size: 86.9 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 51
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 35
- Releases: 9
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
[](https://doi.org/10.1007/s41781-025-00140-9) | [](https://github.com/hftsoi/symbolfit/blob/main/symbolfit.pdf) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/hftsoi/symbolfit/blob/main/colab_demo/symbolfit_colab.ipynb) |
[](https://github.com/hftsoi/symbolfit/releases)
[](https://github.com/hftsoi/symbolfit/releases) | [](https://pypi.org/project/symbolfit)
[](https://www.pepy.tech/projects/symbolfit) | [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/symbolfit)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/symbolfit) |
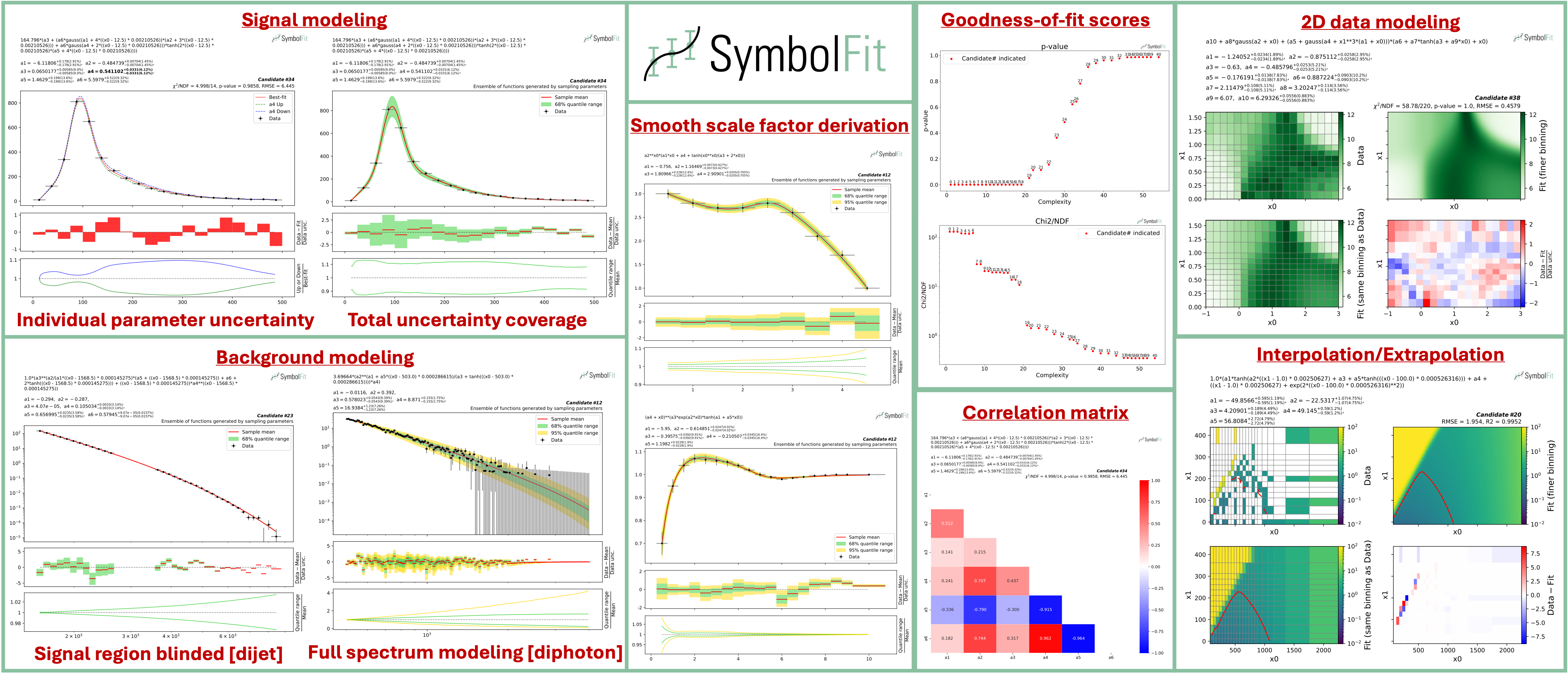
An API to automate parametric modeling with symbolic regression, originally developed for data analysis in the experimental high-energy physics community, but also applicable beyond.
SymbolFit takes binned data with measurement/systematic uncertainties (optional) as input, utilizes PySR to perform a machine-search for batches of functional forms that model the data, parameterizes these functions, and utilizes LMFIT to re-optimize the functions and provide uncertainty estimation, all in one go. It is designed to maximize automation with minimal human input. Each run produces a batch of functions with uncertainty estimation, which are evaluated, saved, and plotted automatically into readable output files, ready for downstream tasks.
Note: This API is actively being updated to accommodate more use cases, so any feedback and contributions are very much welcomed and appreciated! If you encounter any problems while using it, please don’t hesitate to: - Report bugs or suggest new features at
- Ask for specific help and recommendations for your dataset at
If you don't feel like sharing your data in public, please feel free to drop me a message or
. We are happy to assist in getting it to work on your data!
Installation
Prerequisite (Julia)
Install Julia (backend for PySR):
curl -fsSL https://install.julialang.org | sh
Then check if installed properly:
julia --version
If julia is not found, most probably it is not yet included in PATH. To include, do:
export PATH="$PATH:/path/to/<Julia directory>/bin"
Check out here for platform-specific instructions.
Afterward, it is recommended to start from an empty virtual environment for installing and running SymbolFit.
Installation via PyPI
With python>=3.10 and pip:
pip install symbolfit
Installation via conda
(to be updated for >= v0.2.0, please use pip for now) ``` conda create --name symbolfit_env python=3.10 conda activate symbolfit_env conda install -c conda-forge symbolfit ```Editable installation for developers
``` git clone https://github.com/hftsoi/symbolfit.git cd symbolfit pip install -e . ```Getting Started
To run an example fit, get the example datasets by cloning this repo:
git clone https://github.com/hftsoi/symbolfit.git
cd symbolfit
Then within a python session (or simply do python fit_example.py):
```
from symbolfit.symbolfit import *
dataset = importlib.importmodule('examples.datasets.toydataset1.dataset') pysrconfig = importlib.importmodule('examples.pysrconfigs.pysrconfiggauss').pysr_config
model = SymbolFit( x = dataset.x, y = dataset.y, yup = dataset.yup, ydown = dataset.ydown, pysrconfig = pysrconfig, maxcomplexity = 60, inputrescale = True, scaleyby = 'mean', maxstderr = 20, fityunc = True, randomseed = None, loss_weights = None )
model.fit()
After the fit, save results to csv files:
model.savetocsv(outputdir = 'outputdir/')
and plot results to pdf files:
model.plottopdf(
outputdir = 'outputdir/',
binwidths1d = dataset.binwidths1d,
plotlogy = False,
plotlogx = False,
sampling95quantile = False,
#binedges2d = dataset.binedges2d,
#plotlogx0 = False,
#plotlogx1 = False,
#cbarmin = None,
#cbarmax = None,
#cmap = None,
#contour = None,
# ^ additional options for 2D plotting
)
Candidate functions with full substitutions can be printed promptly:
model.printcandidate(candidate_number = 20)
```
When preparing for your own data, a graphical illustration of the input data format can be found here.
Each fit will produce a batch of candidate functions and will automatically save all results to six output files:
1) candidates.csv: saves all candidate functions and evaluations in a csv table.
2) candidates_compact.csv: saves a reduced version for essential information without intermediate results.
3) candidates.pdf: plots all candidate functions (1D/2D only for now) with associated uncertainties one by one for fit quality evaluation.
4) candidates_sampling.pdf: plots all candidate functions (1D only for now) with total uncertainty coverage generated by sampling parameters.
5) candidates_gof.pdf: plots the goodness-of-fit scores.
6) candidates_correlation.pdf: plots the correlation matrices for the parameters of the candidate functions.
Output files from an example fit can be found and downloaded here for illustration.
Note: The function space is usually huge, even when constrained by the pysr config. This means that if you are not satisfied with the results from a fit, you can simply rerun it with the exact same config and obtain a completely different set of candidate functions—the only difference being the random seed that initiates the seeding functions. Therefore, you can rerun the fit as many times as you want until you are satisfied with the results. If you use
model = SymbolFit(..., random_seed = None, ...), nothing needs to be changed—just rerun the fit. If you set a specificrandom_seed, change its value before rerunning. However, if you are still not satisfied with the results after many trials, it might indicate an issue with the config. Then you might want to try a different config, tune it, and start new runs.
For detailed instructions and more demonstrations, please check out the Colab notebook and the documentation.
Documentation
The documentation can be found here for more information and demonstrations.
Citation
If you find this useful in your research, please consider citing SymbolFit:
@article{Tsoi:2024pbn,
author = "Tsoi, Ho Fung and Rankin, Dylan and Caillol, Cecile and Cranmer, Miles and Dasu, Sridhara and Duarte, Javier and Harris, Philip and Lipeles, Elliot and Loncar, Vladimir",
title = "{SymbolFit: Automatic Parametric Modeling with Symbolic Regression}",
eprint = "2411.09851",
archivePrefix = "arXiv",
primaryClass = "hep-ex",
doi = "10.1007/s41781-025-00140-9",
journal = "Comput. Softw. Big Sci.",
volume = "9",
pages = "12",
year = "2025"
}
and PySR:
@misc{cranmerInterpretableMachineLearning2023,
title = {Interpretable {Machine} {Learning} for {Science} with {PySR} and {SymbolicRegression}.jl},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2305.01582},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2305.01582},
urldate = {2023-07-17},
publisher = {arXiv},
author = {Cranmer, Miles},
month = may,
year = {2023},
note = {arXiv:2305.01582 [astro-ph, physics:physics]},
keywords = {Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics, Computer Science - Machine Learning, Computer Science - Neural and Evolutionary Computing, Computer Science - Symbolic Computation, Physics - Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability},
}
Owner
- Name: Ho-Fung Tsoi
- Login: hftsoi
- Kind: user
- Location: Geneva, Switzerland
- Company: CMS Collaboration at CERN
- Repositories: 4
- Profile: https://github.com/hftsoi
Citation (CITATION.bib)
@article{Tsoi:2024pbn,
author = "Tsoi, Ho Fung and Rankin, Dylan and Caillol, Cecile and Cranmer, Miles and Dasu, Sridhara and Duarte, Javier and Harris, Philip and Lipeles, Elliot and Loncar, Vladimir",
title = "{SymbolFit: Automatic Parametric Modeling with Symbolic Regression}",
eprint = "2411.09851",
archivePrefix = "arXiv",
primaryClass = "hep-ex",
doi = "10.1007/s41781-025-00140-9",
journal = "Comput. Softw. Big Sci.",
volume = "9",
pages = "12",
year = "2025"
}
@misc{cranmerInterpretableMachineLearning2023,
title = {Interpretable {Machine} {Learning} for {Science} with {PySR} and {SymbolicRegression}.jl},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2305.01582},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2305.01582},
urldate = {2023-07-17},
publisher = {arXiv},
author = {Cranmer, Miles},
month = may,
year = {2023},
note = {arXiv:2305.01582 [astro-ph, physics:physics]},
keywords = {Astrophysics - Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics, Computer Science - Machine Learning, Computer Science - Neural and Evolutionary Computing, Computer Science - Symbolic Computation, Physics - Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability},
}
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 8
- Issues event: 41
- Release event: 8
- Watch event: 50
- Issue comment event: 21
- Push event: 262
- Fork event: 3
Last Year
- Create event: 8
- Issues event: 41
- Release event: 8
- Watch event: 50
- Issue comment event: 21
- Push event: 262
- Fork event: 3
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 75 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 9
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: symbolfit
Automatic parametric modeling with symbolic regression
- Homepage: https://github.com/hftsoi/symbolfit
- Documentation: https://symbolfit.readthedocs.io/
- License: MIT
-
Latest release: 0.2.0
published 11 months ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- lmfit ==1.2.2
- matplotlib ==3.8.2
- pandas ==2.2.3
- pysr ==0.16.9
- seaborn ==0.13.2
- sphinx ==7.1.2
- sphinx-rtd-theme ==1.3.0rc1
