rliable
[NeurIPS'21 Outstanding Paper] Library for reliable evaluation on RL and ML benchmarks, even with only a handful of seeds.
Science Score: 54.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org -
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (11.6%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Repository
[NeurIPS'21 Outstanding Paper] Library for reliable evaluation on RL and ML benchmarks, even with only a handful of seeds.
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: google-research
- License: apache-2.0
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Default Branch: master
- Homepage: https://agarwl.github.io/rliable
- Size: 1.85 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 840
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 49
- Open Issues: 4
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
rliable is an open-source Python library for reliable evaluation, even with a handful
of runs, on reinforcement learning and machine learnings benchmarks.
| Desideratum | Current evaluation approach | Our Recommendation |
| --------------------------------- | ----------- | --------- |
| Uncertainty in aggregate performance | Point estimates:
- Ignore statistical uncertainty
- Hinder results reproducibility
- Overwhelming beyond a few tasks
- Standard deviations frequently omitted
- Incomplete picture for multimodal and heavy-tailed distributions
- Show tail distribution of scores on combined runs across tasks
- Allow qualitative comparisons
- Easily read any score percentile
- Often dominated by performance on outlier tasks
- Statistically inefficient (requires a large number of runs to claim improvements)
- Poor indicator of overall performance: 0 scores on nearly half the tasks doesn't change it
- Performance on middle 50% of combined runs
- Robust to outlier scores but more statistically efficient than median
rliable provides support for:
- Stratified Bootstrap Confidence Intervals (CIs)
- Performance Profiles (with plotting functions)
- Aggregate metrics
- Interquartile Mean (IQM) across all runs
- Optimality Gap
- Probability of Improvement
Interactive colab
We provide a colab at bit.ly/statisticalprecipicecolab, which shows how to use the library with examples of published algorithms on widely used benchmarks including Atari 100k, ALE, DM Control and Procgen.
Data for individual runs on Atari 100k, ALE, DM Control and Procgen
You can access the data for individual runs using the public GCP bucket here (you might need to sign in with your gmail account to use Gcloud) : https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser/rl-benchmark-data. The interactive colab above also allows you to access the data programatically.
Paper
For more details, refer to the accompanying NeurIPS 2021 paper (Outstanding Paper Award): Deep Reinforcement Learning at the Edge of the Statistical Precipice.
Installation
To install rliable, run:
python
pip install -U rliable
To install latest version of rliable as a package, run:
python
pip install git+https://github.com/google-research/rliable
To import rliable, we suggest:
python
from rliable import library as rly
from rliable import metrics
from rliable import plot_utils
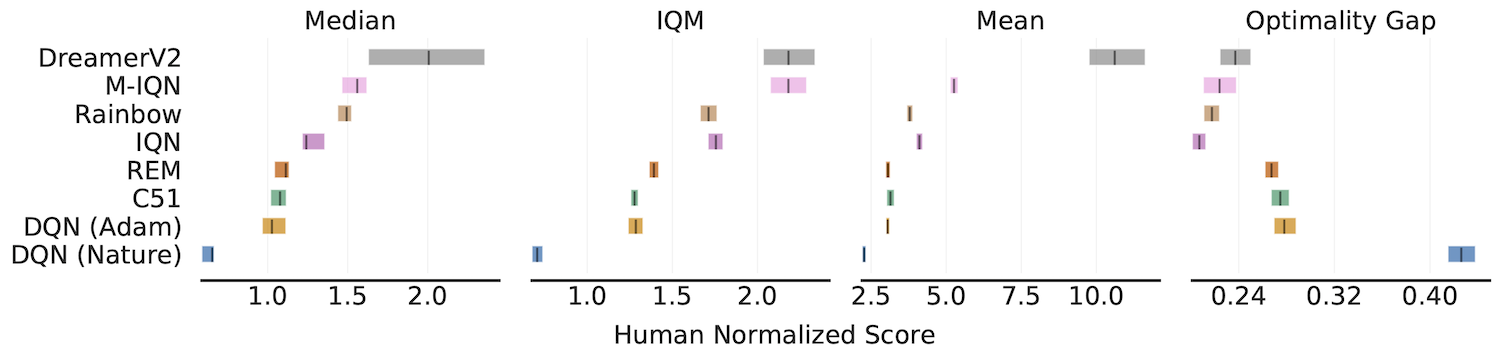
Aggregate metrics with 95% Stratified Bootstrap CIs
IQM, Optimality Gap, Median, Mean
```python algorithms = ['DQN (Nature)', 'DQN (Adam)', 'C51', 'REM', 'Rainbow', 'IQN', 'M-IQN', 'DreamerV2']
Load ALE scores as a dictionary mapping algorithms to their human normalized
score matrices, each of which is of size (num_runs x num_games).
atari200mnormalizedscoredict = ... aggregatefunc = lambda x: np.array([ metrics.aggregatemedian(x), metrics.aggregateiqm(x), metrics.aggregatemean(x), metrics.aggregateoptimalitygap(x)]) aggregatescores, aggregatescorecis = rly.getintervalestimates( atari200mnormalizedscoredict, aggregatefunc, reps=50000) fig, axes = plotutils.plotintervalestimates( aggregatescores, aggregatescorecis, metric_names=['Median', 'IQM', 'Mean', 'Optimality Gap'], algorithms=algorithms, xlabel='Human Normalized Score') ```
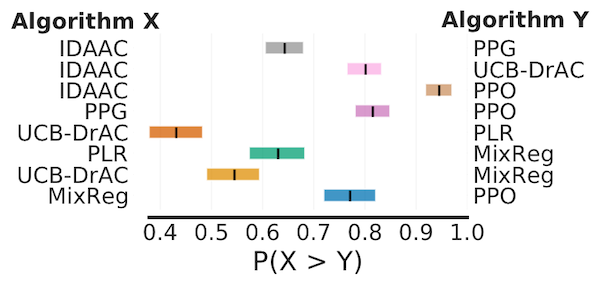
Probability of Improvement
```python
Load ProcGen scores as a dictionary containing pairs of normalized score
matrices for pairs of algorithms we want to compare
procgenalgorithmpairs = {.. , 'x,y': (scorex, scorey), ..} averageprobabilities, averageprobcis = rly.getintervalestimates( procgenalgorithmpairs, metrics.probabilityofimprovement, reps=2000) plotutils.plotprobabilityofimprovement(averageprobabilities, averageprobcis) ```
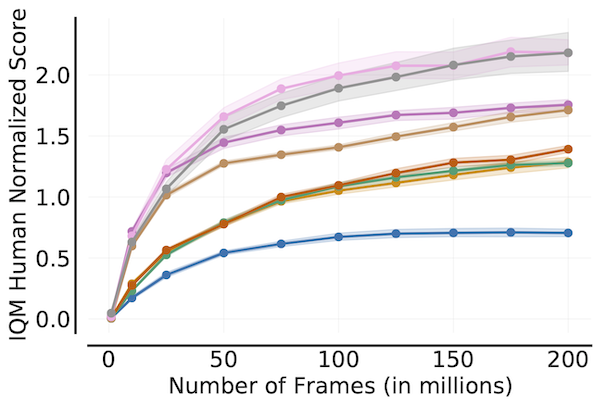
Sample Efficiency Curve
```python algorithms = ['DQN (Nature)', 'DQN (Adam)', 'C51', 'REM', 'Rainbow', 'IQN', 'M-IQN', 'DreamerV2']
Load ALE scores as a dictionary mapping algorithms to their human normalized
score matrices across all 200 million frames, each of which is of size
(num_runs x num_games x 200) where scores are recorded every million frame.
aleallframesscoresdict = ...
frames = np.array([1, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 175, 200]) - 1
aleframesscoresdict = {algorithm: score[:, :, frames] for algorithm, score
in aleallframesscoresdict.items()}
iqm = lambda scores: np.array([metrics.aggregateiqm(scores[..., frame])
for frame in range(scores.shape[-1])])
iqmscores, iqmcis = rly.getintervalestimates(
aleframesscoresdict, iqm, reps=50000)
plotutils.plotsampleefficiencycurve(
frames+1, iqmscores, iqmcis, algorithms=algorithms,
xlabel=r'Number of Frames (in millions)',
ylabel='IQM Human Normalized Score')
```
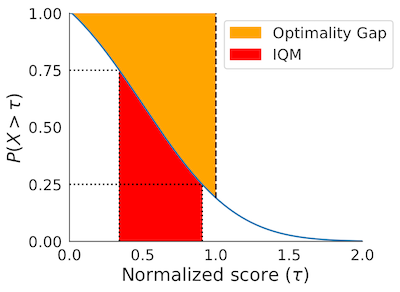
Performance Profiles
```python
Load ALE scores as a dictionary mapping algorithms to their human normalized
score matrices, each of which is of size (num_runs x num_games).
atari200mnormalizedscoredict = ...
Human normalized score thresholds
atari200mthresholds = np.linspace(0.0, 8.0, 81) scoredistributions, scoredistributionscis = rly.createperformanceprofile( atari200mnormalizedscoredict, atari200m_thresholds)
Plot score distributions
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=1, figsize=(7, 5))
plotutils.plotperformanceprofiles(
scoredistributions, atari200mthresholds,
performanceprofilecis=scoredistributionscis,
colors=dict(zip(algorithms, sns.colorpalette('colorblind'))),
xlabel=r'Human Normalized Score $(\tau)$',
ax=ax)
```
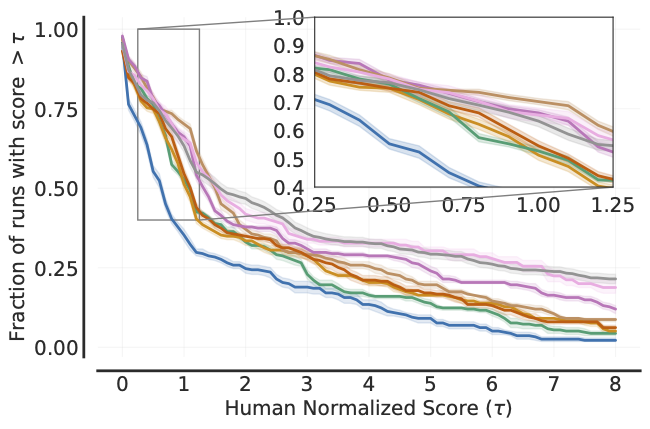
The above profile can also be plotted with non-linear scaling as follows:
python
plot_utils.plot_performance_profiles(
perf_prof_atari_200m, atari_200m_tau,
performance_profile_cis=perf_prof_atari_200m_cis,
use_non_linear_scaling=True,
xticks = [0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 8.0]
colors=dict(zip(algorithms, sns.color_palette('colorblind'))),
xlabel=r'Human Normalized Score $(\tau)$',
ax=ax)
Dependencies
The code was tested under Python>=3.7 and uses these packages:
- arch == 5.3.0
- scipy >= 1.7.0
- numpy >= 0.9.0
- absl-py >= 1.16.4
- seaborn >= 0.11.2
Citing
If you find this open source release useful, please reference in your paper:
@article{agarwal2021deep,
title={Deep Reinforcement Learning at the Edge of the Statistical Precipice},
author={Agarwal, Rishabh and Schwarzer, Max and Castro, Pablo Samuel
and Courville, Aaron and Bellemare, Marc G},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
year={2021}
}
Disclaimer: This is not an official Google product.
Owner
- Name: Google Research
- Login: google-research
- Kind: organization
- Location: Earth
- Website: https://research.google
- Repositories: 226
- Profile: https://github.com/google-research
Citation (CITATION.bib)
@article{agarwal2021deep,
title={Deep reinforcement learning at the edge of the statistical precipice},
author={Agarwal, Rishabh and Schwarzer, Max and Castro, Pablo Samuel and Courville, Aaron C and Bellemare, Marc},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={34},
year={2021}
}
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 5
- Watch event: 78
- Fork event: 4
Last Year
- Issues event: 5
- Watch event: 78
- Fork event: 4
Committers
Last synced: 9 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Rishabh Agarwal | 1****l | 49 |
| Quentin Gallouédec | 4****c | 4 |
| zclzc | 3****c | 2 |
| Dennis Soemers | d****s@g****m | 2 |
| Sebastian Markgraf | S****f@t****e | 1 |
| RLiable Team | n****y@g****m | 1 |
| Michael Panchenko | 3****h | 1 |
| Jet | 3****s | 1 |
| Antonin RAFFIN | a****n@e****g | 1 |
| Michael Panchenko | m****o@a****e | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 20
- Total pull requests: 10
- Average time to close issues: about 1 month
- Average time to close pull requests: 16 days
- Total issue authors: 17
- Total pull request authors: 8
- Average comments per issue: 2.9
- Average comments per pull request: 1.3
- Merged pull requests: 8
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 4
- Pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: 3 months
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 4
- Pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 0.5
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- amantuer (2)
- MischaPanch (2)
- slerman12 (2)
- zhefan (2)
- HYDesmondLiu (1)
- STAY-Melody (1)
- e-pet (1)
- ezhang7423 (1)
- MarcoMeter (1)
- RongpingZhou (1)
- kidd12138 (1)
- xkianteb (1)
- qgallouedec (1)
- nirbhayjm (1)
- TaoHuang13 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- MischaPanch (3)
- qgallouedec (3)
- araffin (2)
- DennisSoemers (2)
- Aladoro (1)
- sebimarkgraf (1)
- lkevinzc (1)
- jjshoots (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 2
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 1,618 last-month
- Total docker downloads: 10
-
Total dependent packages: 6
(may contain duplicates) -
Total dependent repositories: 15
(may contain duplicates) - Total versions: 12
- Total maintainers: 2
pypi.org: rliable
rliable: Reliable evaluation on reinforcement learning and machine learning benchmarks.
- Homepage: https://github.com/google-research/rliable
- Documentation: https://github.com/google-research/rliable
- License: Apache 2.0
-
Latest release: 1.2.0
published over 1 year ago
Rankings
Maintainers (2)
pypi.org: rliable-fork
rliable: Reliable evaluation on reinforcement learning and machine learning benchmarks.
- Homepage: https://github.com/aai-institute/rliable
- Documentation: https://github.com/google-research/rliable
- License: Apache 2.0
-
Latest release: 1.2.0
published over 1 year ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- absl-py *
- arch *
- numpy *
- scipy *
- seaborn *

