lorepy
A library to create lore plots (logistic regression of the prevalence of a categorical variable in function of a continuous feature)
Science Score: 54.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
✓Academic publication links
Links to: zenodo.org -
○Academic email domains
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (15.7%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
A library to create lore plots (logistic regression of the prevalence of a categorical variable in function of a continuous feature)
Basic Info
Statistics
- Stars: 16
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 3
- Releases: 9
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
lorepy: Logistic Regression Plots for Python
Logistic Regression plots are used to plot the distribution of a categorical dependent variable in function of a continuous independent variable.
If you prefer an R implementation of this package, have a look at loreplotr.
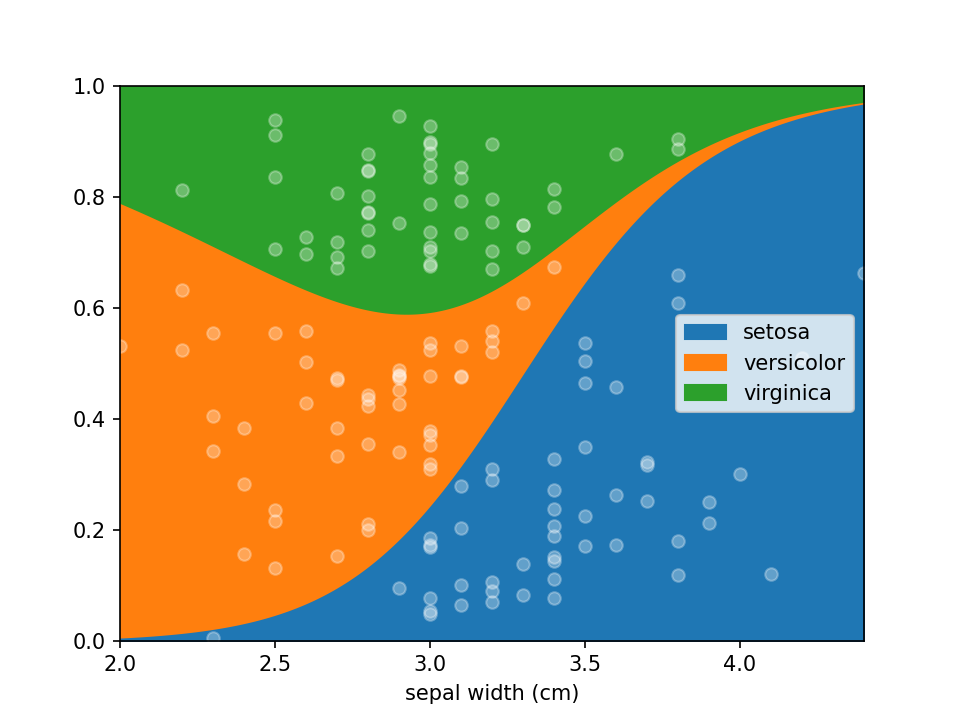
Why use lorepy ?
Lorepy offers distinct advantages over traditional methods like stacked bar plots. By employing a linear model, Lorepy captures overall trends across the entire feature range. It avoids arbitrary cut-offs and segmentation, enabling the visualization of uncertainty throughout the data range.
You can find examples of the Iris data visualized using stacked bar plots here for comparison.
Installation
Lorepy can be installed using pip using the command below.
pip install lorepy
Usage
Data needs to be provided as a DataFrame and the columns for the x (independent continuous) and y (dependant categorical)
variables need to be defined. Here the iris dataset is loaded and converted to an appropriate DataFrame. Once the data
is in shape it can be plotted using a single line of code loreplot(data=iris_df, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species").
```python from lorepy import loreplot
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd
irisobj = loadiris() irisdf = pd.DataFrame(irisobj.data, columns=irisobj.featurenames)
irisdf["species"] = [irisobj.targetnames[s] for s in irisobj.target]
loreplot(data=iris_df, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species")
plt.show() ```
Options
While lorepy has very few customizations, it is possible to pass arguments through to Pandas' DataFrame.plot.area and Matplotlib's pyplot.scatter to change the aesthetics of the plots.
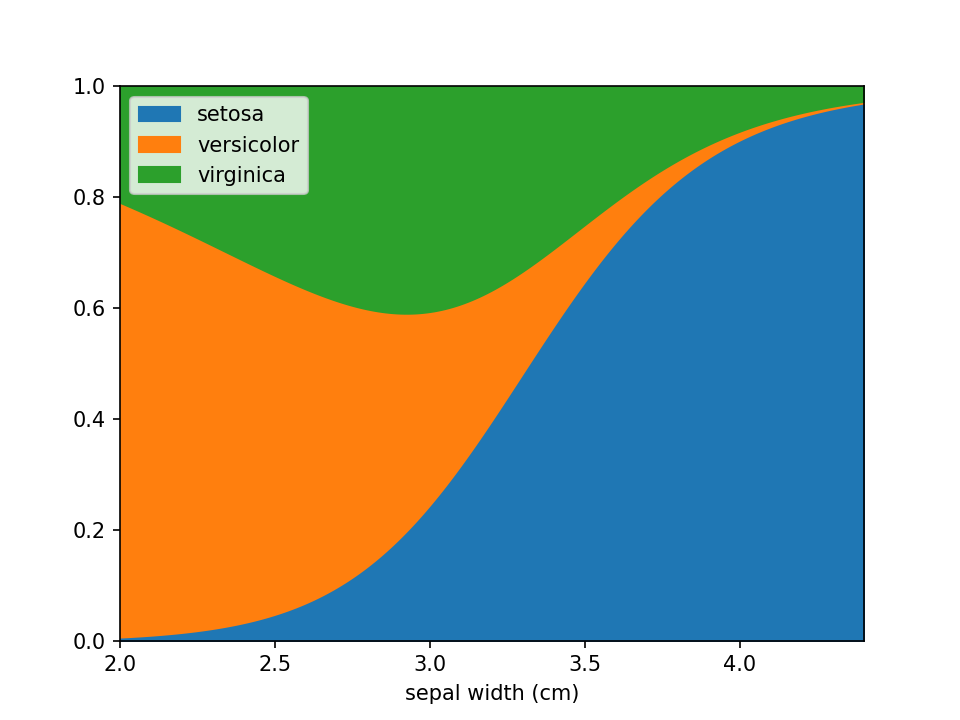
Disable sample dots
Dots indicating where samples are located can be en-/disabled using the add_dots argument.
python
loreplot(data=iris_df, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", add_dots=False)
plt.show()
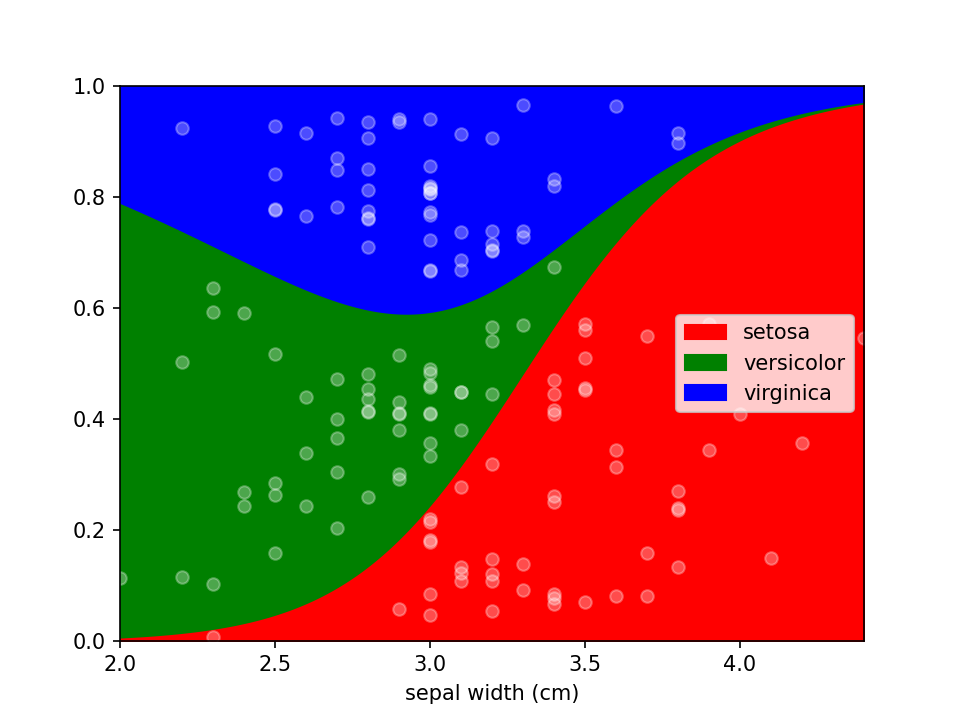
Custom styles
Additional keyword arguments are passed to Pandas' DataFrame.plot.area. This can be used, among other things, to define a custom colormap. For more options to customize these plots consult Pandas' documentation.
```python from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
colormap=ListedColormap(['red', 'green', 'blue'])
loreplot(data=iris_df, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", colormap=colormap)
plt.show()
```
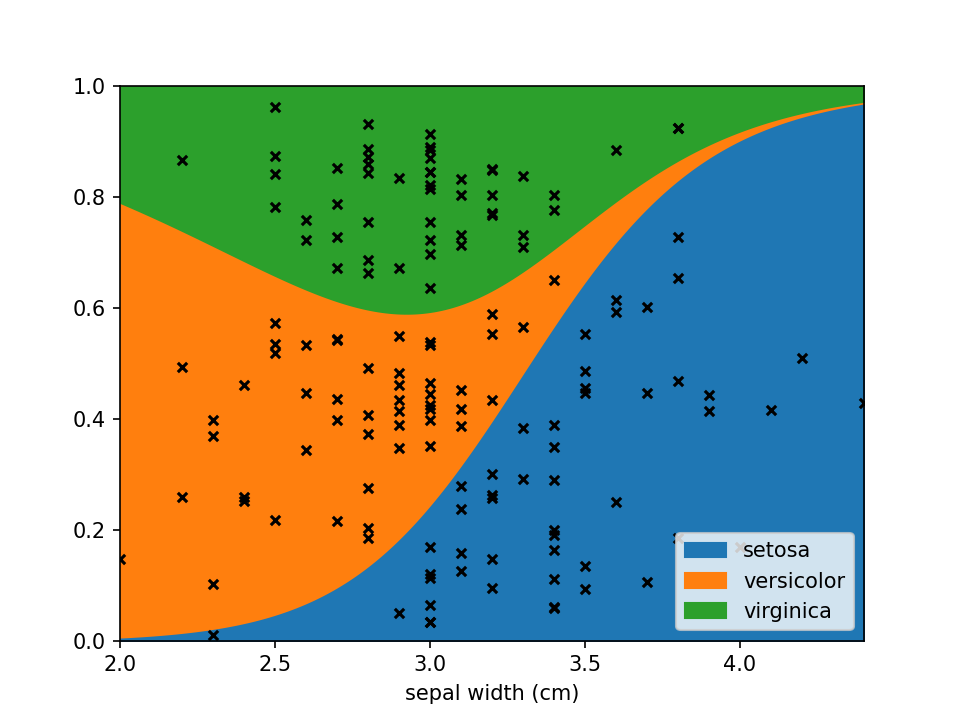
Using scatter_kws arguments for pyplot.scatter
can be set to change the appearance of the sample markers.
```python scatter_options = { 's': 20, # Marker size 'alpha': 1, # Fully opaque 'color': 'black', # Set color to black 'marker': 'x' # Set style to crosses }
loreplot(data=irisdf, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", scatterkws=scatter_options)
plt.show()
```
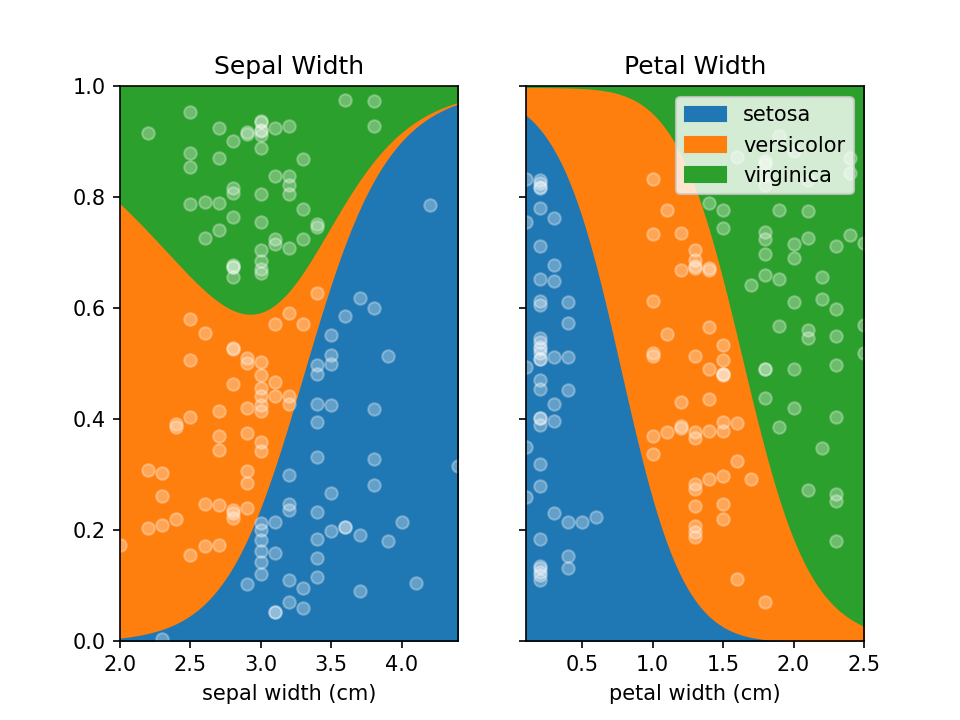
You can use LoRePlots in subplots as you would expect.
```python fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2, sharex=False, sharey=True) loreplot(data=irisdf, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", ax=ax[0]) loreplot(data=irisdf, x="petal width (cm)", y="species", ax=ax[1])
ax[0].getlegend().remove() ax[0].settitle("Sepal Width") ax[1].set_title("Petal Width")
plt.savefig('./docs/img/loreplot_subplot.png', dpi=150) plt.show() ```
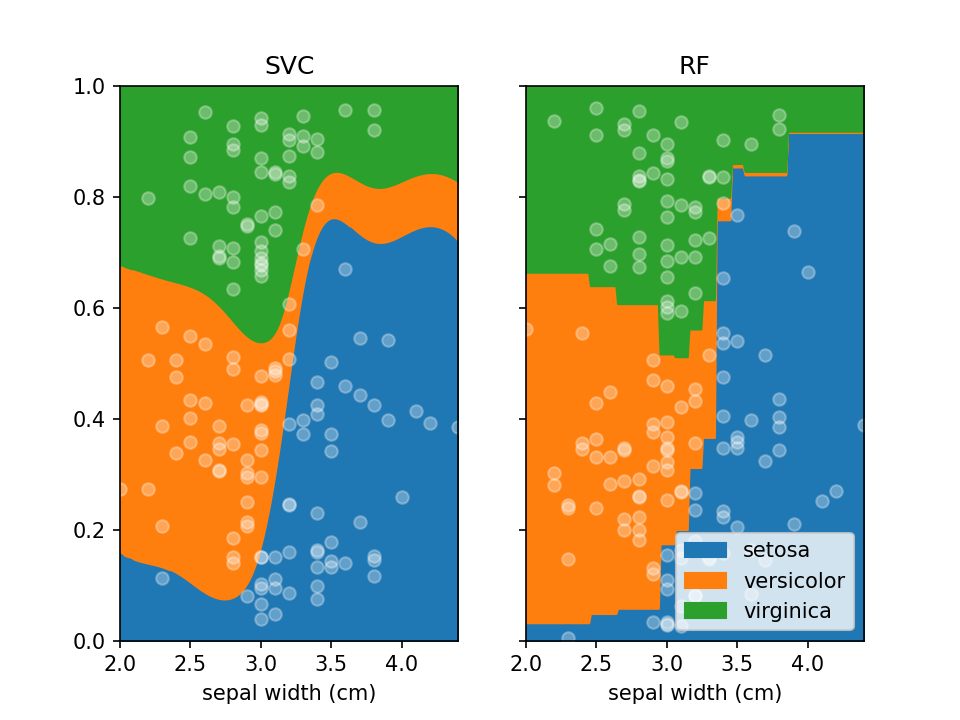
By default lorepy uses a multi-class logistic regression model, however this can be replaced with any classifier
from scikit-learn that implements predict_proba and fit. Below you can see the code and output with a
Support Vector Classifier (SVC) and Random Forest Classifier (RF).
```python from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex=False, sharey=True)
svc = SVC(probability=True) rf = RandomForestClassifier(nestimators=10, maxdepth=2)
loreplot(data=irisdf, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", clf=svc, ax=ax[0]) loreplot(data=irisdf, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", clf=rf, ax=ax[1])
ax[0].getlegend().remove() ax[0].settitle("SVC") ax[1].set_title("RF")
plt.savefig("./docs/img/loreplototherclf.png", dpi=150) plt.show() ```
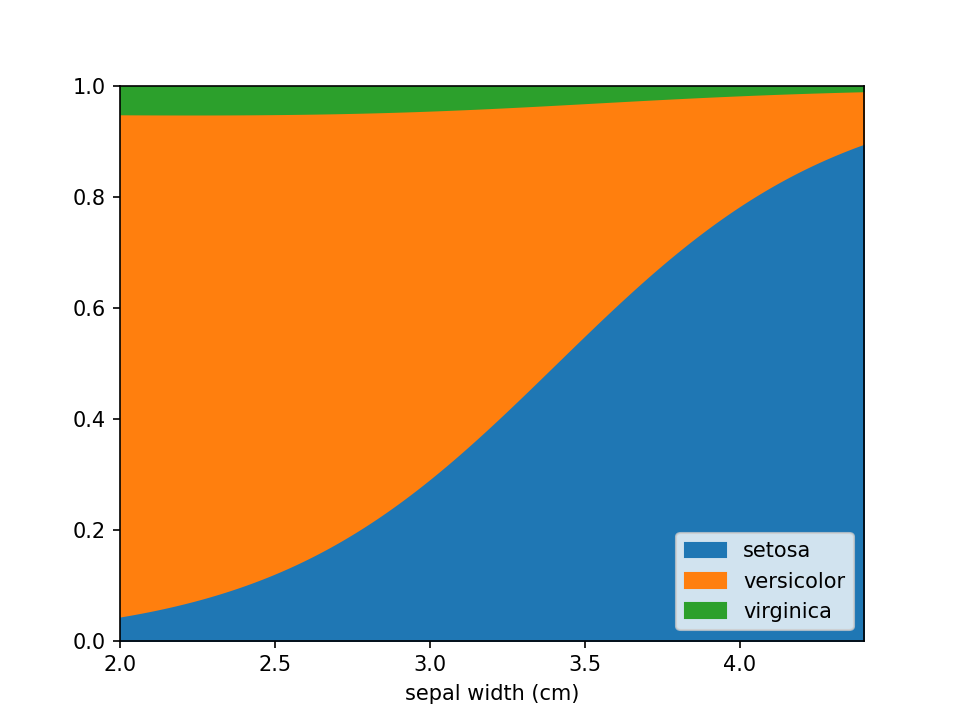
In case there are confounders, these can be taken into account using the confounders argument. This requires a
list of tuples, with the feature and the reference value for that feature to use in plots. E.g. if you wish to deconfound
for Body Mass Index (BMI) and use a BMI of 25 in plots, set this to [("BMI", 25)].
python
loreplot(
data=iris_df,
x="sepal width (cm)",
y="species",
confounders=[("petal width (cm)", 1)],
)
plt.savefig("./docs/img/loreplot_confounder.png", dpi=150)
plt.show()
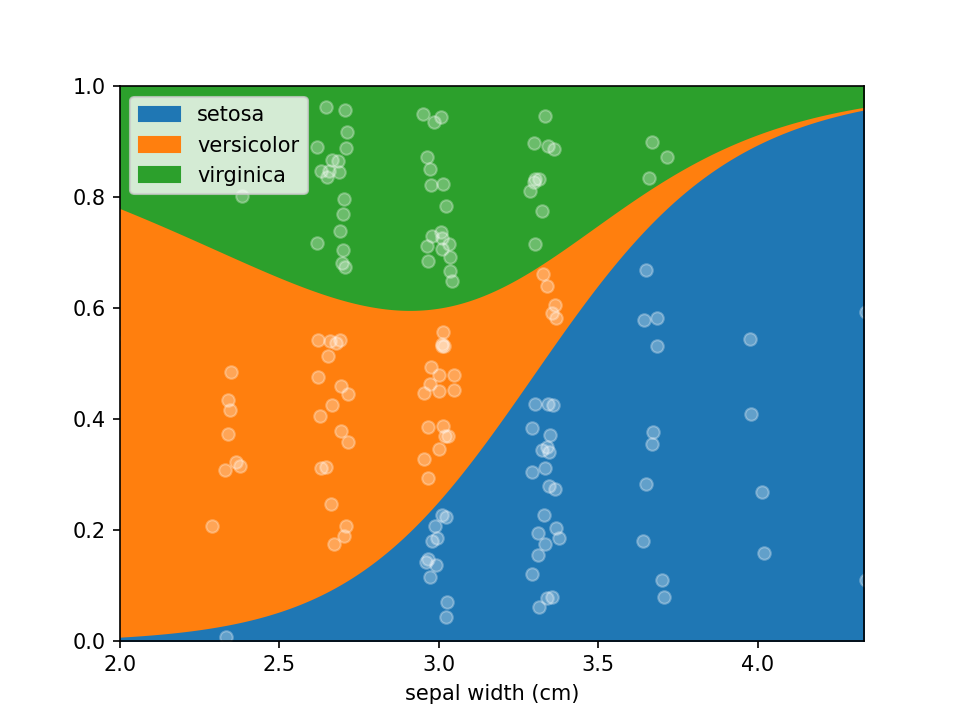
In some cases the numerical feature on the x-axis isn't continuous (e.g. an integer number), this can lead to
overplotting the dots. To avoid this to some extent a jitter feature is included, that adds some uniform noise to
the x-coordinates of the dots. The value specifies the range of the uniform noise added, the value of 0.05 in the
example sets this range to [-0.05, 0.05].
```python irisdf["sepal width (cm)"] = ( np.round(irisdf["sepal width (cm)"] * 3) / 3 ) # Round values
loreplot(data=irisdf, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", jitter=0.05)
plt.savefig("./docs/img/loreplotjitter.png", dpi=150)
plt.show()
```
Assess uncertainty
From loreplots it isn't possible to assess how certain we are of the prevalence of each group across the range. To
provide a view into this there is a function uncertainty_plot, which can be used as shown below. This will use
resampling (or jackknifing) to determine the 50% and 95% interval of predicted values and show these in a
multi-panel plot with one plot per category.
```python from lorepy import uncertainty_plot
uncertaintyplot( data=irisdf, x="sepal width (cm)", y="species", ) plt.savefig("./docs/img/uncertainty_default.png", dpi=150) plt.show() ```
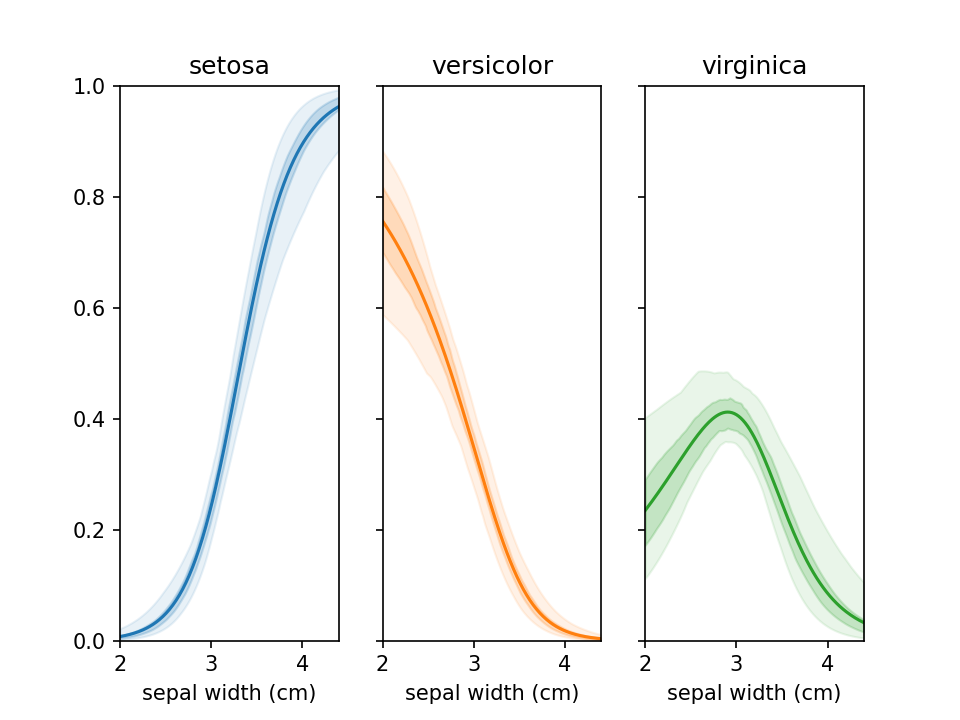
This also supports custom colors, ranges and classifiers. More examples are available in example_uncertainty.py.
Development
Additional documentation for developers is included with details on running tests, building and deploying to PyPi.
Contributing
Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated.
- Found a bug or have some suggestions? Open an issue.
- Pull requests are welcome! Though open an issue first to discuss which features/changes you wish to implement.
Contact
lorepy was developed by Sebastian Proost at the RaesLab and was based on R code written by Sara Vieira-Silva. As of version 0.2.0 lorepy is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license.
For commercial access inquiries, please contact Jeroen Raes.
Owner
- Name: Raes Lab
- Login: raeslab
- Kind: organization
- Location: Belgium
- Website: http://www.raeslab.org/
- Twitter: Raeslab
- Repositories: 4
- Profile: https://github.com/raeslab
Citation (CITATION.cff)
cff-version: 1.2.0 message: "If you use this software, please cite it as below." authors: - family-names: "Proost" given-names: "Sebastian" orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6792-9442" - family-names: "Vieira-Silva" given-names: "Sara" orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4616-7602" - family-names: "Raes" given-names: "Jeroen" orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1337-041X" title: "lorepy: Logistic Regression Plots for Python" version: 0.2.0 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.8321785 date-released: 2023-09-07 url: "https://github.com/raeslab/lorepy"
GitHub Events
Total
- Release event: 2
- Watch event: 2
- Push event: 18
- Create event: 1
Last Year
- Release event: 2
- Watch event: 2
- Push event: 18
- Create event: 1
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 41 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 8
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: lorepy
Draw Logistic Regression Plots in Python
- Homepage: https://github.com/raeslab/lorepy/
- Documentation: https://lorepy.readthedocs.io/
- License: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
-
Latest release: 0.4.4
published 11 months ago

