Science Score: 72.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
5 of 22 committers (22.7%) from academic institutions -
✓Institutional organization owner
Organization thunlp has institutional domain (nlp.csai.tsinghua.edu.cn) -
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (13.8%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
An Open-Source Framework for Prompt-Learning.
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: thunlp
- License: apache-2.0
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://thunlp.github.io/OpenPrompt/
- Size: 14.4 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 4,720
- Watchers: 46
- Forks: 476
- Open Issues: 100
- Releases: 4
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
 **An Open-Source Framework for Prompt-learning.**
------
**An Open-Source Framework for Prompt-learning.**
------
Overview • Installation • How To Use • Docs • Paper • Citation • Performance •
What's New?
- ❗️ April 2023: $\color{red}{\normalsize{\textbf{Want to build your Chat AI?}}}$ We are releasing UltraChat, use OpenPrompt and UltraChat to conduct supervised instruction tuning, see
./tutorial/9_UltraChat.py. - Aug 2022: Thanks to contributor zhiyongLiu1114, OpenPrompt now supports ERNIE 1.0 in PaddlePaddle.
- July 2022: OpenPrompt supports OPT now.
- June 2022: OpenPrompt wins ACL 2022 Best Demo Paper Award.
- Mar 2022: We add a tutorial as the response to issue 124, which uses a customized tokenizer_wrapper to perform tasks that are not in the default configuration of OpenPrompt (e.g., Bert tokenizer+T5 model).
- Feb 2022: Check out our sister repo OpenDelta!
- Dec 2021:
pip install openprompt - Dec 2021: SuperGLUE performance are added
- Dec 2021: We support generation paradigm for all tasks by adding a new verbalizer:GenerationVerbalizer and a tutorial: 4.1alltasksaregeneration.py
- Nov 2021: Now we have released a paper OpenPrompt: An Open-source Framework for Prompt-learning.
- Nov 2021 PrefixTuning supports t5 now.
- Nov 2021: We made some major changes from the last version, where a flexible template language is newly introduced! Part of the docs is outdated and we will fix it soon.
Overview
Prompt-learning is the latest paradigm to adapt pre-trained language models (PLMs) to downstream NLP tasks, which modifies the input text with a textual template and directly uses PLMs to conduct pre-trained tasks. This library provides a standard, flexible and extensible framework to deploy the prompt-learning pipeline. OpenPrompt supports loading PLMs directly from huggingface transformers. In the future, we will also support PLMs implemented by other libraries. For more resources about prompt-learning, please check our paper list.
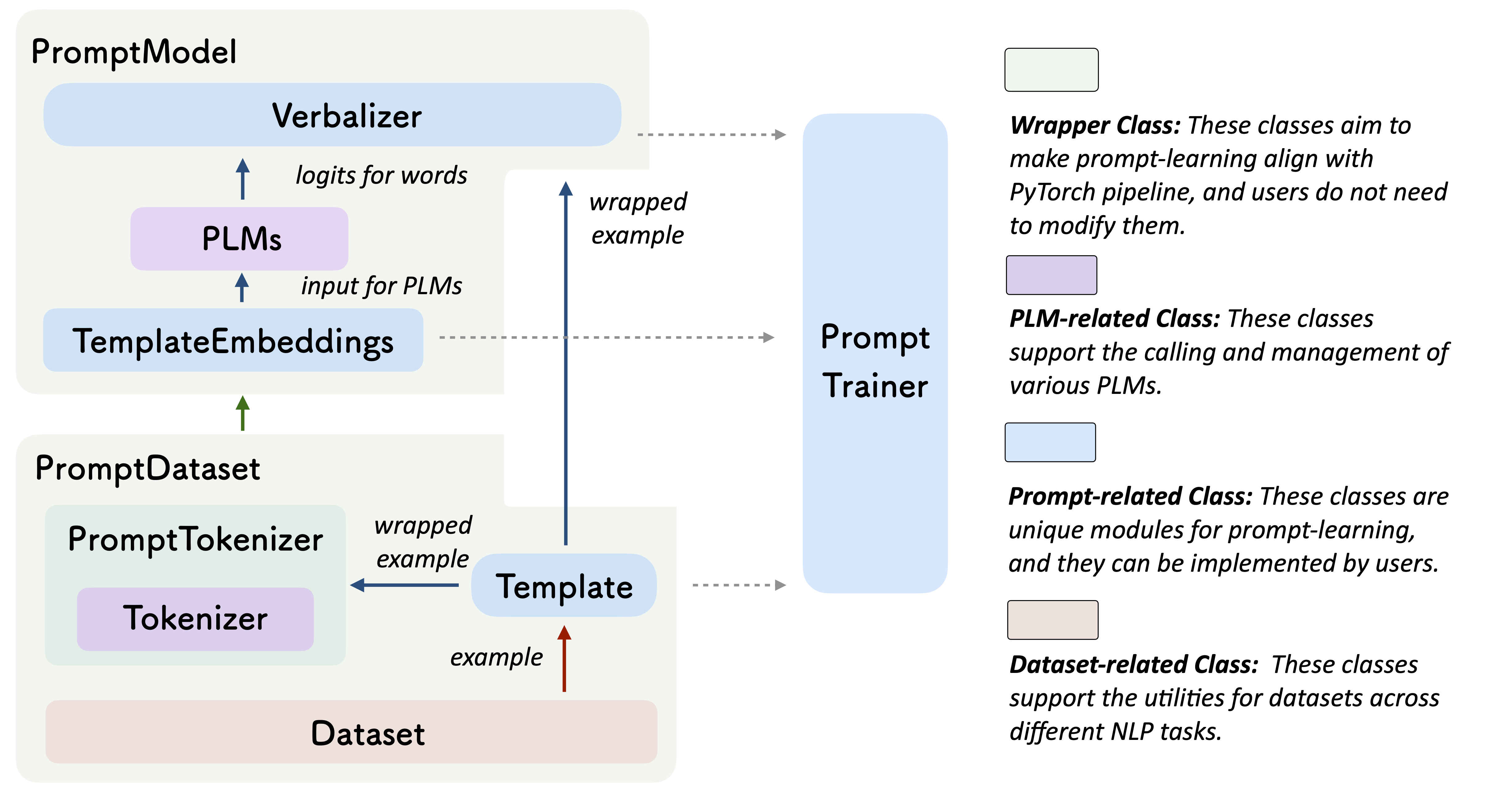
What Can You Do via OpenPrompt?

- Use the implementations of current prompt-learning approaches.* We have implemented various of prompting methods, including templating, verbalizing and optimization strategies under a unified standard. You can easily call and understand these methods.
- Design your own prompt-learning work. With the extensibility of OpenPrompt, you can quickly practice your prompt-learning ideas.
Installation
Note: Please use Python 3.8+ for OpenPrompt
Using Pip
Our repo is tested on Python 3.8+ and PyTorch 1.8.1+, install OpenPrompt using pip as follows:
shell
pip install openprompt
To play with the latest features, you can also install OpenPrompt from the source.
Using Git
Clone the repository from github:
shell
git clone https://github.com/thunlp/OpenPrompt.git
cd OpenPrompt
pip install -r requirements.txt
python setup.py install
Modify the code
python setup.py develop
Use OpenPrompt
Base Concepts
A PromptModel object contains a PLM, a (or multiple) Template and a (or multiple) Verbalizer, where the Template class is defined to wrap the original input with templates, and the Verbalizer class is to construct a projection between labels and target words in the current vocabulary. And a PromptModel object practically participates in training and inference.
Introduction by a Simple Example
With the modularity and flexibility of OpenPrompt, you can easily develop a prompt-learning pipeline.
Step 1: Define a task
The first step is to determine the current NLP task, think about what’s your data looks like and what do you want from the data! That is, the essence of this step is to determine the classes and the InputExample of the task. For simplicity, we use Sentiment Analysis as an example. tutorial_task.
python
from openprompt.data_utils import InputExample
classes = [ # There are two classes in Sentiment Analysis, one for negative and one for positive
"negative",
"positive"
]
dataset = [ # For simplicity, there's only two examples
# text_a is the input text of the data, some other datasets may have multiple input sentences in one example.
InputExample(
guid = 0,
text_a = "Albert Einstein was one of the greatest intellects of his time.",
),
InputExample(
guid = 1,
text_a = "The film was badly made.",
),
]
Step 2: Define a Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) as backbone.
Choose a PLM to support your task. Different models have different attributes, we encourge you to use OpenPrompt to explore the potential of various PLMs. OpenPrompt is compatible with models on huggingface.
python
from openprompt.plms import load_plm
plm, tokenizer, model_config, WrapperClass = load_plm("bert", "bert-base-cased")
Step 3: Define a Template.
A Template is a modifier of the original input text, which is also one of the most important modules in prompt-learning.
We have defined text_a in Step 1.
python
from openprompt.prompts import ManualTemplate
promptTemplate = ManualTemplate(
text = '{"placeholder":"text_a"} It was {"mask"}',
tokenizer = tokenizer,
)
Step 4: Define a Verbalizer
A Verbalizer is another important (but not necessary) in prompt-learning,which projects the original labels (we have defined them as classes, remember?) to a set of label words. Here is an example that we project the negative class to the word bad, and project the positive class to the words good, wonderful, great.
python
from openprompt.prompts import ManualVerbalizer
promptVerbalizer = ManualVerbalizer(
classes = classes,
label_words = {
"negative": ["bad"],
"positive": ["good", "wonderful", "great"],
},
tokenizer = tokenizer,
)
Step 5: Combine them into a PromptModel
Given the task, now we have a PLM, a Template and a Verbalizer, we combine them into a PromptModel. Note that although the example naively combine the three modules, you can actually define some complicated interactions among them.
python
from openprompt import PromptForClassification
promptModel = PromptForClassification(
template = promptTemplate,
plm = plm,
verbalizer = promptVerbalizer,
)
Step 6: Define a DataLoader
A PromptDataLoader is basically a prompt version of pytorch Dataloader, which also includes a Tokenizer, a Template and a TokenizerWrapper.
python
from openprompt import PromptDataLoader
data_loader = PromptDataLoader(
dataset = dataset,
tokenizer = tokenizer,
template = promptTemplate,
tokenizer_wrapper_class=WrapperClass,
)
Step 7: Train and inference
Done! We can conduct training and inference the same as other processes in Pytorch.
```python import torch
making zero-shot inference using pretrained MLM with prompt
promptModel.eval() with torch.nograd(): for batch in dataloader: logits = promptModel(batch) preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim = -1) print(classes[preds])
predictions would be 1, 0 for classes 'positive', 'negative'
```
Please refer to our tutorial scripts, and documentation for more details.
Datasets
We provide a series of download scripts in the dataset/ folder, feel free to use them to download benchmarks.
Performance Report
There are too many possible combinations powered by OpenPrompt. We are trying our best to test the performance of different methods as soon as possible. The performance will be constantly updated into the Tables. We also encourage the users to find the best hyper-parameters for their own tasks and report the results by making pull request.
Known Issues
Major improvement/enhancement in future.
- We made some major changes from the last version, so part of the docs is outdated. We will fix it soon.
Citation
Please cite our paper if you use OpenPrompt in your work
bibtex
@article{ding2021openprompt,
title={OpenPrompt: An Open-source Framework for Prompt-learning},
author={Ding, Ning and Hu, Shengding and Zhao, Weilin and Chen, Yulin and Liu, Zhiyuan and Zheng, Hai-Tao and Sun, Maosong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.01998},
year={2021}
}
Contributors
We thank all the contributors to this project, more contributors are welcome!
Owner
- Name: THUNLP
- Login: thunlp
- Kind: organization
- Email: thunlp@gmail.com
- Location: FIT Building, Tsinghua University, Beijing
- Website: http://nlp.csai.tsinghua.edu.cn
- Repositories: 117
- Profile: https://github.com/thunlp
Natural Language Processing Lab at Tsinghua University
Citation (CITATION.cff)
cff-version: "1.0.0"
message: "If you use this toolkit, please cite it using these metadata."
title: "openprompt"
repository-code: "https://github.com/thunlp/OpenPrompt"
authors:
- family-names: Ding
given-names: Ning
- family-names: Hu
given-names: Shengding
- family-names: Zhao
given-names: Weilin
- family-names: Chen
given-names: Yulin
- family-names: Liu
given-names: Zhiyuan
- family-names: Zheng
given-names: Hai-Tao
- family-names: Sun
given-names: Maosong
preferred-citation:
type: article
title: "OpenPrompt: An Open-source Framework for Prompt-learning"
authors:
- family-names: Ding
given-names: Ning
- family-names: Hu
given-names: Shengding
- family-names: Zhao
given-names: Weilin
- family-names: Chen
given-names: Yulin
- family-names: Liu
given-names: Zhiyuan
- family-names: Zheng
given-names: Hai-Tao
- family-names: Sun
given-names: Maosong
journal: "arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.01998"
year: 2021
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 6
- Watch event: 386
- Issue comment event: 4
- Pull request review event: 2
- Pull request event: 7
- Fork event: 35
Last Year
- Issues event: 6
- Watch event: 386
- Issue comment event: 4
- Pull request review event: 2
- Pull request event: 7
- Fork event: 35
Committers
Last synced: 9 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| StingNing | d****8@m****n | 54 |
| shengdinghu | s****u@g****m | 52 |
| Achazwl | 3****7@q****m | 33 |
| cyl628 | y****7@m****n | 20 |
| cyl628 | y****1@m****n | 16 |
| liuzy6 | l****6@a****m | 5 |
| BMDN | 8****1@q****m | 4 |
| Chathulanka Gamage | 6****s | 3 |
| cgq15 | 7****4@q****m | 3 |
| 肖朝军 | x****0@m****n | 3 |
| blmoistawinde | b****e@q****m | 2 |
| Daniel | z****t@1****m | 1 |
| Kexuan (Michael) Huang | h****x@u****u | 1 |
| Kian-Meng Ang | k****g@c****g | 1 |
| Yulv-git | y****i@q****m | 1 |
| bugface-vh | x****g@v****m | 1 |
| zzy | z****y | 1 |
| xiongchao | x****o@d****m | 1 |
| hlzhang109 | h****9@g****m | 1 |
| luoyifan | 1****0@q****m | 1 |
| wangpeng | 3****k | 1 |
| 骑马小猫 | 1****6@q****m | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 117
- Total pull requests: 30
- Average time to close issues: about 1 month
- Average time to close pull requests: 4 months
- Total issue authors: 97
- Total pull request authors: 19
- Average comments per issue: 1.17
- Average comments per pull request: 0.1
- Merged pull requests: 7
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 5
- Pull requests: 7
- Average time to close issues: less than a minute
- Average time to close pull requests: 23 days
- Issue authors: 5
- Pull request authors: 4
- Average comments per issue: 0.0
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- BAOOOOOM (4)
- lihuiliullh (3)
- shaoyuyoung (3)
- YamenAjjour (3)
- cmgchess (3)
- ZHUANG-jt (3)
- komi786 (2)
- ngavcc (2)
- FelliYang (2)
- indunil-19 (2)
- brunoedcf (2)
- MosheAbG (2)
- qinglongheu (2)
- zihaohe123 (1)
- treena908 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- cmgchess (4)
- cyyever (2)
- shaoyuyoung (2)
- aemartinez (2)
- AlisherRogov (2)
- starmountain1997 (2)
- indunil-19 (2)
- omidk56 (2)
- ady-31 (2)
- xiyang-vh (1)
- z4forzubair (1)
- harshkaria (1)
- Raibows (1)
- kx-Huang (1)
- abdumaa (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 3
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 790 last-month
-
Total dependent packages: 2
(may contain duplicates) -
Total dependent repositories: 9
(may contain duplicates) - Total versions: 12
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: openprompt
An open source framework for prompt-learning.
- Homepage: https://github.com/thunlp/OpenPrompt
- Documentation: https://openprompt.readthedocs.io/
- License: Apache
-
Latest release: 1.0.1
published over 3 years ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
proxy.golang.org: github.com/thunlp/openprompt
- Documentation: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/thunlp/openprompt#section-documentation
- License: apache-2.0
-
Latest release: v1.0.0
published almost 4 years ago
Rankings
proxy.golang.org: github.com/thunlp/OpenPrompt
- Documentation: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/thunlp/OpenPrompt#section-documentation
- License: apache-2.0
-
Latest release: v1.0.0
published almost 4 years ago
Rankings
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/setup-python v2 composite
- ad-m/github-push-action master composite
- nltk *
- scikit-learn ==0.24.2
- sentencepiece ==0.1.96
- sphinx ==4.2.0
- sphinx-copybutton *
- sphinx-rtd-theme ==1.0.0
- torch ==1.9.0
- tqdm ==4.62.2
- transformers ==4.10.0
- yacs *
- datasets *
- dill *
- nltk *
- pyarrow *
- rouge ==1.0.0
- scipy *
- sentencepiece ==0.1.96
- tensorboardX *
- tqdm >=4.62.2
- transformers >=4.19.0
- yacs *
