Shekar: A Python Toolkit for Persian Natural Language Processing
Shekar: A Python Toolkit for Persian Natural Language Processing - Published in JOSS (2025)
Science Score: 93.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 1 DOI reference(s) in JOSS metadata -
○Academic publication links
-
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
✓JOSS paper metadata
Published in Journal of Open Source Software
Keywords
Repository
Simplifying Persian NLP for Modern Applications
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: amirivojdan
- License: mit
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://lib.shekar.io
- Size: 21.9 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 39
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
- Releases: 26
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md

Simplifying Persian NLP for Modern Applications
Shekar (meaning 'sugar' in Persian) is an open-source Python library for Persian natural language processing, named after the influential satirical story "فارسی شکر است" (Persian is Sugar) published in 1921 by Mohammad Ali Jamalzadeh. The story became a cornerstone of Iran's literary renaissance, advocating for accessible yet eloquent expression. Shekar embodies this philosophy in its design and development.
It provides tools for text preprocessing, tokenization, part-of-speech(POS) tagging, named entity recognition(NER), embeddings, spell checking, and more. With its modular pipeline design, Shekar makes it easy to build reproducible workflows for both research and production applications.
📖 Documentation: https://lib.shekar.io/
Table of Contents
- Installation
- Preprocessing
- Tokenization
- Embeddings
- Stemming
- Lemmatization
- Part-of-Speech Tagging
- Named Entity Recognition (NER)
- Sentiment Analysis
- Toxicity Detection
- Keyword Extraction
- Spell Checking
- WordCloud
- Command-Line Interface (CLI)
- Download Models
Installation
You can install Shekar with pip. By default, the CPU runtime of ONNX is included, which works on all platforms.
CPU Installation (All Platforms)
bash
$ pip install shekar
This works on Windows, Linux, and macOS (including Apple Silicon M1/M2/M3).
GPU Acceleration (NVIDIA CUDA)
If you have an NVIDIA GPU and want hardware acceleration, you need to replace the CPU runtime with the GPU version.
Prerequisites
- NVIDIA GPU with CUDA support
- Appropriate CUDA Toolkit installed
- Compatible NVIDIA drivers
bash
$ pip install shekar && pip uninstall -y onnxruntime && pip install onnxruntime-gpu
Preprocessing
Normalizer
The built-in Normalizer class provides a ready-to-use pipeline that combines the most common filters and normalization steps, offering a default configuration that covers the majority of use cases.
```python from shekar import Normalizer
normalizer = Normalizer() text = "«فارسی شِکَر است» نام داستان ڪوتاه طنز آمێزی از محمد علی جمالــــــــزاده ی گرامی می باشد که در سال 1921 منتشر شده است و آغاز ڱر تحول بزرگی در ادَبێات معاصر ایران 🇮🇷 بۃ شمار میرود."
print(normalizer(text)) ```
shell
«فارسی شکر است» نام داستان کوتاه طنزآمیزی از محمدعلی جمالزادهی گرامی میباشد که در سال ۱۹۲۱ منتشر شدهاست و آغازگر تحول بزرگی در ادبیات معاصر ایران به شمار میرود.
Customization
For advanced customization, Shekar offers a modular and composable framework for text preprocessing. It includes components such as filters, normalizers, and maskers, which can be applied individually or flexibly combined using the Pipeline class with the | operator.
You can combine any of the preprocessing components using the | operator:
```python from shekar.preprocessing import EmojiRemover, PunctuationRemover
text = "ز ایران دلش یاد کرد و بسوخت! 🌍🇮🇷" pipeline = EmojiRemover() | PunctuationRemover() output = pipeline(text) print(output) ```
shell
ز ایران دلش یاد کرد و بسوخت
Tokenization
WordTokenizer
The WordTokenizer class in Shekar is a simple, rule-based tokenizer for Persian that splits text based on punctuation and whitespace using Unicode-aware regular expressions.
```python from shekar import WordTokenizer
tokenizer = WordTokenizer()
text = "چه سیبهای قشنگی! حیات نشئهٔ تنهایی است." tokens = list(tokenizer(text)) print(tokens) ```
shell
["چه", "سیبهای", "قشنگی", "!", "حیات", "نشئهٔ", "تنهایی", "است", "."]
SentenceTokenizer
The SentenceTokenizer class is designed to split a given text into individual sentences. This class is particularly useful in natural language processing tasks where understanding the structure and meaning of sentences is important. The SentenceTokenizer class can handle various punctuation marks and language-specific rules to accurately identify sentence boundaries.
Below is an example of how to use the SentenceTokenizer:
```python from shekar.tokenization import SentenceTokenizer
text = "هدف ما کمک به یکدیگر است! ما میتوانیم با هم کار کنیم." tokenizer = SentenceTokenizer() sentences = tokenizer(text)
for sentence in sentences: print(sentence) ```
output
هدف ما کمک به یکدیگر است!
ما میتوانیم با هم کار کنیم.
Embeddings
Shekar offers two main embedding classes:
WordEmbedder: Provides static word embeddings using pre-trained FastText models.ContextualEmbedder: Provides contextual embeddings using a fine-tuned ALBERT model.
Both classes share a consistent interface:
embed(text)returns a NumPy vector.transform(text)is an alias forembed(text)to integrate with pipelines.
Word Embeddings
WordEmbedder supports two static FastText models:
fasttext-d100: A 100-dimensional CBOW model trained on Persian Wikipedia.fasttext-d300: A 300-dimensional CBOW model trained on the large-scale Naab dataset.
```python from shekar.embeddings import WordEmbedder
embedder = WordEmbedder(model="fasttext-d100")
embedding = embedder("کتاب") print(embedding.shape)
similarwords = embedder.mostsimilar("کتاب", topn=5) print(similarwords) ```
Contextual Embeddings
ContextualEmbedder uses an ALBERT model trained with Masked Language Modeling (MLM) on the Naab dataset to generate high-quality contextual embeddings.
The resulting embeddings are 768-dimensional vectors representing the semantic meaning of entire phrases or sentences.
```python from shekar.embeddings import ContextualEmbedder
embedder = ContextualEmbedder(model="albert")
sentence = "کتابها دریچهای به جهان دانش هستند." embedding = embedder(sentence) print(embedding.shape) # (768,) ```
Stemming
The Stemmer is a lightweight, rule-based reducer for Persian word forms. It trims common suffixes while respecting Persian orthography and Zero Width Non-Joiner usage. The goal is to produce stable stems for search, indexing, and simple text analysis without requiring a full morphological analyzer.
```python from shekar import Stemmer
stemmer = Stemmer()
print(stemmer("نوهام")) print(stemmer("کتابها")) print(stemmer("خانههایی")) ```
output
نوه
کتاب
خانه
Lemmatization
The Lemmatizer maps Persian words to their base dictionary form. Unlike stemming, which only trims affixes, lemmatization uses explicit verb conjugation rules, vocabulary lookups, and a stemmer fallback to ensure valid lemmas. This makes it more accurate for tasks like part-of-speech tagging, text normalization, and linguistic analysis where the canonical form of a word is required.
```python from shekar import Lemmatizer
lemmatizer = Lemmatizer()
print(lemmatizer("رفتند")) print(lemmatizer("کتابها")) print(lemmatizer("خانههایی")) print(lemmatizer("گفته بودهایم")) ```
output
رفت/رو
کتاب
خانه
گفت/گو
Part-of-Speech Tagging
The POSTagger class provides part-of-speech tagging for Persian text using a transformer-based model (default: ALBERT). It returns one tag per word based on Universal POS tags (following the Universal Dependencies standard).
Example usage:
```python from shekar import POSTagger
pos_tagger = POSTagger() text = "نوروز، جشن سال نو ایرانی، بیش از سه هزار سال قدمت دارد و در کشورهای مختلف جشن گرفته میشود."
result = pos_tagger(text) for word, tag in result: print(f"{word}: {tag}") ```
output
نوروز: PROPN
،: PUNCT
جشن: NOUN
سال: NOUN
نو: ADJ
ایرانی: ADJ
،: PUNCT
بیش: ADJ
از: ADP
سه: NUM
هزار: NUM
سال: NOUN
قدمت: NOUN
دارد: VERB
و: CCONJ
در: ADP
کشورهای: NOUN
مختلف: ADJ
جشن: NOUN
گرفته: VERB
میشود: VERB
.: PUNCT
Named Entity Recognition (NER)
The NER module offers a fast, quantized Named Entity Recognition pipeline using a fine-tuned ALBERT model. It detects common Persian entities such as persons, locations, organizations, and dates. This model is designed for efficient inference and can be easily combined with other preprocessing steps.
Example usage:
```python from shekar import NER from shekar import Normalizer
input_text = ( "شاهرخ مسکوب به سالِ ۱۳۰۴ در بابل زاده شد و دوره ابتدایی را در تهران و در مدرسه علمیه پشت " "مسجد سپهسالار گذراند. از کلاس پنجم ابتدایی مطالعه رمان و آثار ادبی را شروع کرد. از همان زمان " "در دبیرستان ادب اصفهان ادامه تحصیل داد. پس از پایان تحصیلات دبیرستان در سال ۱۳۲۴ از اصفهان به تهران رفت و " "در رشته حقوق دانشگاه تهران مشغول به تحصیل شد." )
normalizer = Normalizer() normalizedtext = normalizer(inputtext)
albertner = NER() entities = albertner(normalized_text)
for text, label in entities: print(f"{text} → {label}") ```
output
شاهرخ مسکوب → PER
سال ۱۳۰۴ → DAT
بابل → LOC
دوره ابتدایی → DAT
تهران → LOC
مدرسه علمیه → LOC
مسجد سپهسالار → LOC
دبیرستان ادب اصفهان → LOC
در سال ۱۳۲۴ → DAT
اصفهان → LOC
تهران → LOC
دانشگاه تهران → ORG
فرانسه → LOC
Sentiment Analysis
The SentimentClassifier module enables automatic sentiment analysis of Persian text using transformer-based models. It currently supports the AlbertBinarySentimentClassifier, a lightweight ALBERT model fine-tuned on Snapfood dataset to classify text as positive or negative, returning both the predicted label and its confidence score.
Example usage:
```python from shekar import SentimentClassifier
sentiment_classifier = SentimentClassifier()
print(sentimentclassifier("سریال قصههای مجید عالی بود!")) print(sentimentclassifier("فیلم ۳۰۰ افتضاح بود!")) ```
output
('positive', 0.9923112988471985)
('negative', 0.9330866932868958)
Toxicity Detection
The toxicity module currently includes a Logistic Regression classifier trained on TF-IDF features extracted from the Naseza (ناسزا) dataset, a large-scale collection of Persian text labeled for offensive and neutral language. The OffensiveLanguageClassifier processes input text to determine whether it is neutral or offensive, returning both the predicted label and its confidence score.
```python from shekar.toxicity import OffensiveLanguageClassifier
offensive_classifier = OffensiveLanguageClassifier()
print(offensiveclassifier("زبان فارسی میهن من است!")) print(offensiveclassifier("تو خیلی احمق و بیشرفی!")) ```
output
('neutral', 0.7651197910308838)
('offensive', 0.7607775330543518)
Keyword Extraction
The shekar.keyword_extraction module provides tools for automatically identifying and extracting key terms and phrases from Persian text. These algorithms help identify the most important concepts and topics within documents.
```python from shekar import KeywordExtractor
extractor = KeywordExtractor(maxlength=2, topn=10)
input_text = ( "زبان فارسی یکی از زبانهای مهم منطقه و جهان است که تاریخچهای کهن دارد. " "زبان فارسی با داشتن ادبیاتی غنی و شاعرانی برجسته، نقشی بیبدیل در گسترش فرهنگ ایرانی ایفا کرده است. " "از دوران فردوسی و شاهنامه تا دوران معاصر، زبان فارسی همواره ابزار بیان اندیشه، احساس و هنر بوده است. " )
keywords = extractor(input_text)
for kw in keywords:
print(kw)
output
فرهنگ ایرانی
گسترش فرهنگ
ایرانی ایفا
زبان فارسی
تاریخچهای کهن
```
Spell Checking
The SpellChecker class provides simple and effective spelling correction for Persian text. It can automatically detect and fix common errors such as extra characters, spacing mistakes, or misspelled words. You can use it directly as a callable on a sentence to clean up the text, or call suggest() to get a ranked list of correction candidates for a single word.
```python from shekar import SpellChecker
spellchecker = SpellChecker() print(spellchecker("سسلام بر ششما ددوست من")) print(spell_checker.suggest("درود")) ```
output
سلام بر شما دوست من
['درود', 'درصد', 'ورود', 'درد', 'درون']
WordCloud
The WordCloud class offers an easy way to create visually rich Persian word clouds. It supports reshaping and right-to-left rendering, Persian fonts, color maps, and custom shape masks for accurate and elegant visualization of word frequencies.
```python import requests from collections import Counter
from shekar import WordCloud from shekar import WordTokenizer from shekar.preprocessing import ( HTMLTagRemover, PunctuationRemover, StopWordRemover, NonPersianRemover, ) preprocessing_pipeline = HTMLTagRemover() | PunctuationRemover() | StopWordRemover() | NonPersianRemover()
url = f"https://shahnameh.me/p.php?id=F82F6CED" response = requests.get(url) htmlcontent = response.text cleantext = preprocessingpipeline(htmlcontent)
wordtokenizer = WordTokenizer() tokens = wordtokenizer(clean_text)
word_freqs = Counter(tokens)
wordCloud = WordCloud( mask="Iran", width=640, height=480, maxfontsize=220, minfontsize=6, bgcolor="white", contourcolor="black", contourwidth=5, colormap="greens", )
if shows disconnect words, try again with bidi_reshape=True
image = wordCloud.generate(wordfreqs, bidireshape=False) image.show() ```
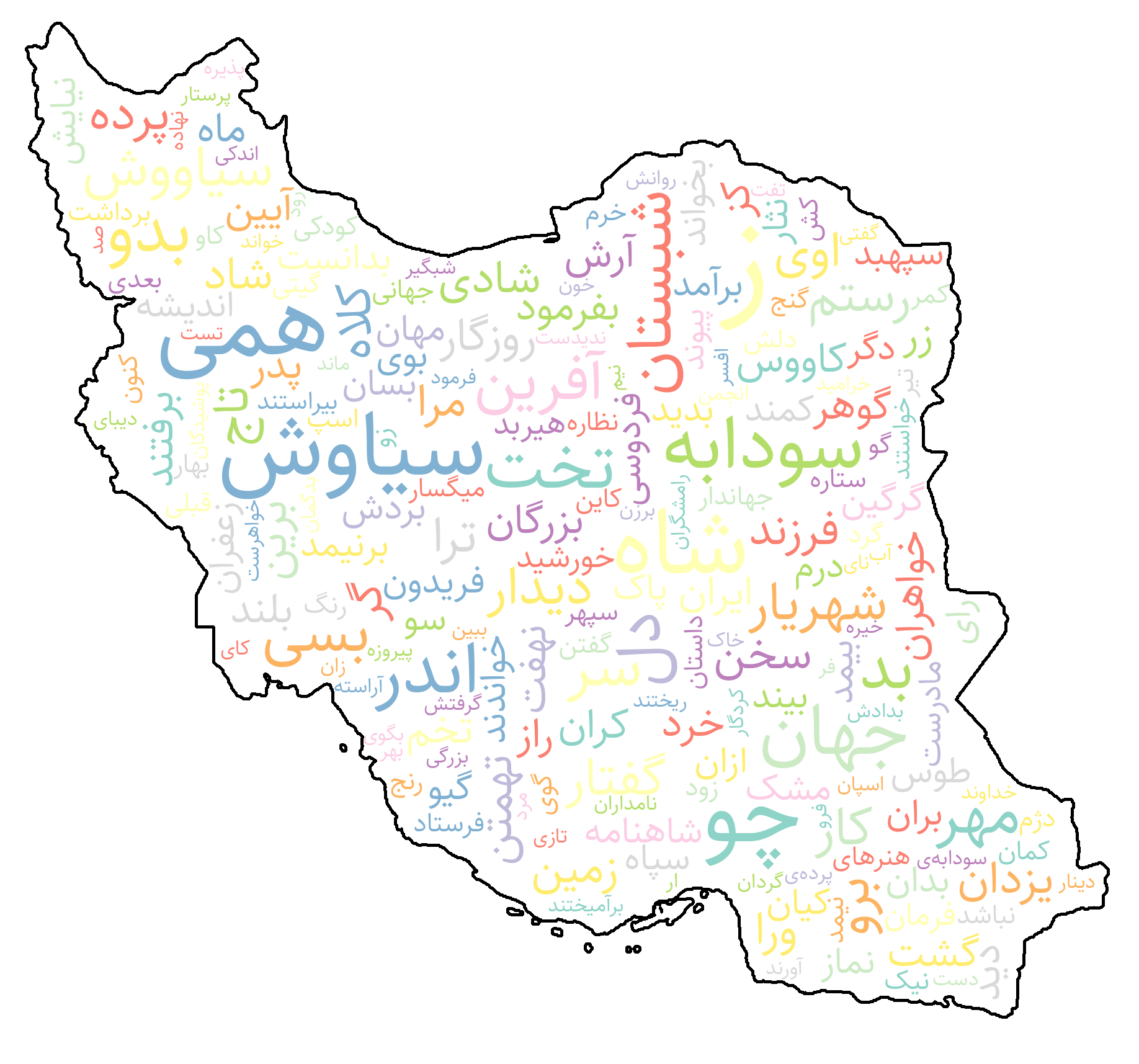
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Shekar includes a command-line interface (CLI) for quick text processing and visualization.
You can normalize Persian text or generate wordclouds directly from files or inline strings.
Usage
console
shekar [COMMAND] [OPTIONS]
Examples
```console
Normalize a text file and save output
shekar normalize -i ./corpus.txt -o ./normalized_corpus.txt
Normalize inline text
shekar normalize -t "درود پرودگار بر ایران و ایرانی" ```
Download Models
If Shekar Hub is unavailable, you can manually download the models and place them in the cache directory at home/[username]/.shekar/
| Model Name | Download Link | |----------------------------|---------------| | FastText Embedding d100 | Download (50MB)| | FastText Embedding d300 | Download (500MB)| | SentenceEmbedding | Download (60MB)| | POS Tagger | Download (38MB)| | NER | Download (38MB)| | Sentiment Classifier | Download (38MB)| | Offensive Language Classifier | Download (8MB)| | AlbertTokenizer | Download (2MB)|
With ❤️ for IRAN
Owner
- Name: Ahmad Amirivojdan
- Login: amirivojdan
- Kind: user
- Location: Knoxville, TN, U.S
- Website: amirivojdan.io
- Twitter: amirivojdan
- Repositories: 13
- Profile: https://github.com/amirivojdan
Ph.D. Student in Biosystems Engineering at The University of Tennessee Knoxville
JOSS Publication
Shekar: A Python Toolkit for Persian Natural Language Processing
Tags
Natural Language Processing Persian Language Text Processing Computational Linguistics Open Source SoftwareGitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 24
- Issues event: 2
- Release event: 24
- Watch event: 22
- Delete event: 3
- Issue comment event: 5
- Public event: 1
- Push event: 116
- Pull request review event: 1
- Pull request event: 9
- Fork event: 1
Last Year
- Create event: 24
- Issues event: 2
- Release event: 24
- Watch event: 22
- Delete event: 3
- Issue comment event: 5
- Public event: 1
- Push event: 116
- Pull request review event: 1
- Pull request event: 9
- Fork event: 1
Committers
Last synced: 4 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Ahmad Amirivojdan | a****n@g****m | 237 |
| Eva Maxfield Brown | e****d@g****m | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 4 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 2
- Total pull requests: 8
- Average time to close issues: about 6 hours
- Average time to close pull requests: 2 minutes
- Total issue authors: 1
- Total pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0.5
- Average comments per pull request: 1.0
- Merged pull requests: 8
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 2
- Pull requests: 8
- Average time to close issues: about 6 hours
- Average time to close pull requests: 2 minutes
- Issue authors: 1
- Pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0.5
- Average comments per pull request: 1.0
- Merged pull requests: 8
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- linuxscout (2)
Pull Request Authors
- amirivojdan (8)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 1,126 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 30
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: shekar
Simplifying Persian NLP for Modern Applications
- Homepage: https://github.com/amirivojdan/shekar
- Documentation: https://lib.shekar.io
- License: MIT License
-
Latest release: 1.0.0
published 4 months ago






