Science Score: 41.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
○codemeta.json file
-
○.zenodo.json file
-
✓DOI references
Found 4 DOI reference(s) in README -
○Academic publication links
-
✓Committers with academic emails
1 of 2 committers (50.0%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (14.7%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Repository
F-1 method
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: briochemc
- License: mit
- Language: Julia
- Default Branch: master
- Size: 502 KB
Statistics
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 1
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
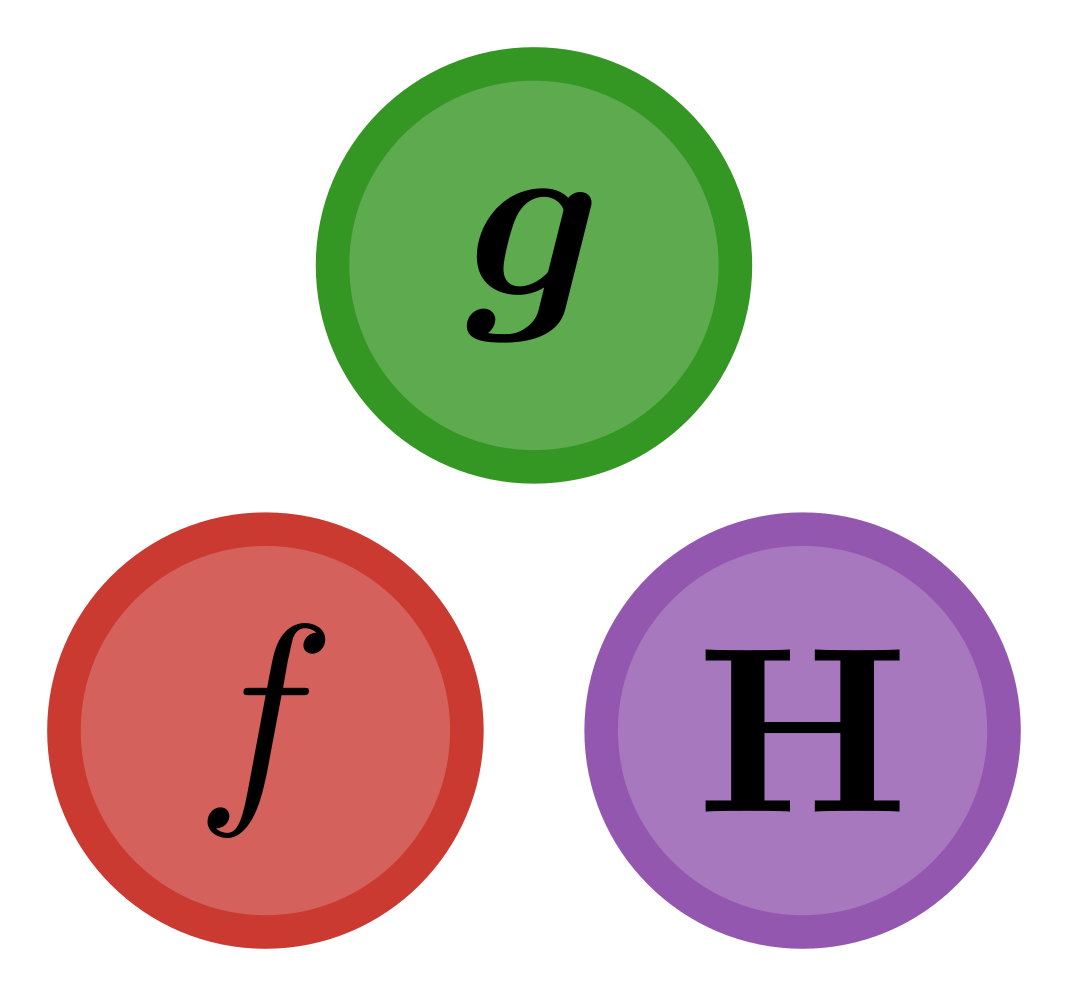
F-1 algorithm
This package implements the F-1 algorithm described in Pasquier and Primeau (in preparation). It allows for efficient quasi-auto-differentiation of an objective function defined implicitly by the solution of a steady-state problem.
Consider a discretized system of nonlinear partial differential equations that takes the form
F(x,p) = 0
where x is a column vector of the model state variables and p is a vector of parameters.
The F-1 algorithm then allows for an efficient computation of both the gradient vector and the Hessian matrix of a generic objective function defined by
objective(p) = f(s(p),p)
where s(p) is the steady-state solution of the system, i.e., such that F(s(p),p) = 0 and where f(x,p) is for example a measure of the mismatch between observed state, parameters, and observations.
Optimizing the model is then simply done by minimizing objective(p).
(See Pasquier and Primeau (in preparation), for more details.)
Advantages of the F-1 algorithm
The F-1 algorithm is easy to use, gives accurate results, and is computationally fast:
- Easy — The F-1 algorithm basically just needs the user to provide a solver (for finding the steady-state), the mismatch function,
f, an ODEFunction,Fwith its Jacobian, and the gradient of the objective w.r.t.∇ₓf. (Note these derivatives can be computed numerically, via the ForwardDiff package for example.) - Accurate — Thanks to ForwardDiff's nested dual numbers implementation, the accuracy of the gradient and Hessian, as computed by the F-1 algorithm, are close to machine precision.
- Fast — The F-1 algorithm is as fast as if you derived analytical formulas for every first and second derivatives and used those in the most efficient way.
This is because the bottleneck of such computations is the number of matrix factorizations, and the F-1 algorithm only requires a single one. In comparison, standard autodifferentiation methods that take the steady-state solver as a black box would require order
morm^2factorizations, wheremis the number of parameters.
What's needed?
A requirement of the F-1 algorithm is that the Jacobian matrix A = ∇ₓF can be created, stored, and factorized.
To use the F-1 algorithm, the user must:
- Make sure that there is a suitable algorithm
algto solve the steady-state equation - overload the
solvefunction and theSteadyStateProblemconstructor from SciMLBase. (An example is given in the CI tests — see, e.g., thetest/simple_setup.jlfile.) - Provide the derivatives of
fandFwith respect to the state,x.
A concrete example
Make sure you have overloaded solve from SciMLBase
(an example of how to do this is given in the documentation).
Once initial values for the state, x, and parameters, p, are chosen, simply initialize the required memory cache, mem via
```julia
Initialize the cache for storing reusable objects
mem = initialize_mem(F, ∇ₓf, x, p, alg; options...) ```
wrap the functions into functions of p only via
```julia
Wrap the objective, gradient, and Hessian functions
objective(p) = F1Method.objective(f, F, mem, p, alg; options...) gradient(p) = F1Method.gradient(f, F, ∇ₓf, mem, p, alg; options...) hessian(p) = F1Method.hessian(f, F, ∇ₓf, mem, p, alg; options...) ```
and compute the objective, gradient, or Hessian via either of
```julia objective(p)
gradient(p)
hessian(p) ```
That's it. You were told it was simple, weren't you? Now you can test how fast and accurate it is!
Citing the software
If you use this package, or implement your own package based on the F-1 algorithm please cite us. If you use the F-1 algorithm, please cite Pasquier and Primeau (in prep.). If you also use this package directly, please cite it! (Use the Zenodo link or the CITATION.bib file, which contains a bibtex entry.)
Future
This package is developed mainly for use with AIBECS.jl and is likely not in its final form. The API was just changed in v0.5 (to match the API changes in AIBECS.jl v0.11). That being said, ultimately, it would make sense for the shortcuts used here to be integrated into a package like ChainRules.jl. For the time being, AIBECS users can use F1Method.jl to speed up their optimizations.
Owner
- Name: Benoît Pasquier
- Login: briochemc
- Kind: user
- Location: Sydney, Australia
- Company: UNSW
- Website: https://www.bpasquier.com/
- Repositories: 157
- Profile: https://github.com/briochemc
Research Associate at UNSW
Citation (CITATION.bib)
@misc{F1Method.jl-2019,
author = {Beno\^{i}t Pasquier},
title = {{F1Method.jl: A julia package for computing the gradient and Hessian of an objective function defined implicitly by the solution to a steady-state problem}},
month = may,
year = 2019,
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.2667835}
}
@article{Pasquier_et_al_2019,
author = {Beno\^{i}t Pasquier and Fran\c{c}ois Primeau and J. Keith Moore},
title = {{The F-1 method: An efficient algorithm for computing the
Hessian matrix for parameter optimization and sensitivity analysis
in models described by a steady-state system of nonlinear PDEs}},
year = {In preparation}
}
GitHub Events
Total
Last Year
Committers
Last synced: over 1 year ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Benoit Pasquier | p****b@u****u | 91 |
| Julia TagBot | 5****t | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 7 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 9
- Total pull requests: 5
- Average time to close issues: 2 days
- Average time to close pull requests: about 11 hours
- Total issue authors: 3
- Total pull request authors: 2
- Average comments per issue: 0.44
- Average comments per pull request: 0.6
- Merged pull requests: 5
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 0
- Pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 0
- Pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- briochemc (7)
- ChrisRackauckas (1)
- JuliaTagBot (1)
Pull Request Authors
- briochemc (4)
- JuliaTagBot (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
- Total downloads: unknown
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 10
juliahub.com: F1Method
F-1 method
- Documentation: https://docs.juliahub.com/General/F1Method/stable/
- License: MIT
-
Latest release: 0.5.1
published about 4 years ago






