qonnx
QONNX: Arbitrary-Precision Quantized Neural Networks in ONNX
Science Score: 77.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 5 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org, frontiersin.org, zenodo.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
6 of 26 committers (23.1%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (13.0%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Repository
QONNX: Arbitrary-Precision Quantized Neural Networks in ONNX
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: fastmachinelearning
- License: apache-2.0
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://qonnx.readthedocs.io/
- Size: 5.49 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 149
- Watchers: 23
- Forks: 50
- Open Issues: 49
- Releases: 3
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
QONNX: Arbitrary-Precision Quantized Neural Networks in ONNX
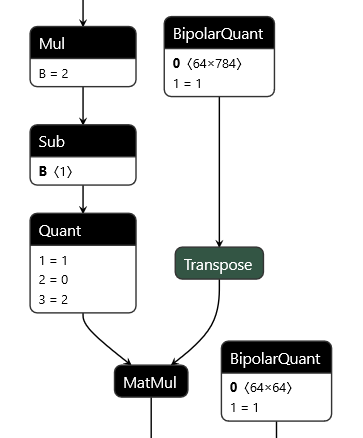
QONNX (Quantized ONNX) introduces several custom operators -- IntQuant, FloatQuant, BipolarQuant, and Trunc -- in order to represent arbitrary-precision integer and minifloat quantization in ONNX. This enables:
* Representation of binary, ternary, 3-bit, 4-bit, 6-bit or any other integer/fixed-point quantization.
* Representation of minifloat quantization with configurable exponent and mantissa bits.
* Quantization is an operator itself, and can be applied to any parameter or layer input.
* Flexible choices for scaling factor and zero-point granularity, also enabling OCP MX datatypes.
* Quantized values are carried using standard float datatypes to remain ONNX protobuf-compatible.
This repository contains a set of Python utilities to work with QONNX models, including but not limited to: * executing QONNX models for (slow) functional verification * shape inference, constant folding and other basic optimizations * summarizing the inference cost of a QONNX model in terms of mixed-precision MACs, parameter and activation volume * Python infrastructure for writing transformations and defining executable, shape-inferencable custom ops * (experimental) data layout conversion from standard ONNX NCHW to custom QONNX NHWC ops
Quickstart
Operator definitions
- Quant for 2-to-arbitrary-bit quantization, with scaling and zero-point
- BipolarQuant for 1-bit (bipolar) quantization, with scaling and zero-point
- Trunc for truncating to a specified number of bits, with scaling and zero-point
Installation
pip install qonnx
Export, Import and Model Zoo
The following quantization-aware training (QAT) frameworks support exporting to QONNX:
The following NN inference frameworks support importing QONNX models for deployment:
Head to the QONNX model zoo to download pre-trained QONNX models on various datasets.
Model Visualization
We recommend Netron for visualizing QONNX models.
Executing ONNX graph with QONNX custom nodes
Using the qonnx-exec command line utility, with top-level inputs supplied from in0.npy and in1.npy:
qonnx-exec my-qonnx-model.onnx in0.npy in1.npy
Using the Python API:
``` from qonnx.core.modelwrapper import ModelWrapper from qonnx.core.onnxexec import executeonnx
model = ModelWrapper("my-qonnx-model.onnx") idict = {"in0" : np.load("in0.npy), "in1" : np.load("in1.npy")} odict = execute_onnx(idict) ```
Calculate inference cost for QONNX model
Using the qonnx-inference-cost command line utility for the CNV_2W2A example:
qonnx-inference-cost CNV_2W2A.onnx
Which will print a inference cost dictionary like the following:
Inference cost for CNV_2W2A.onnx
{
"discount_sparsity": true, # discount MAC counts by layer sparsity (disregard zero-valued MACs and params)
# mem_o_X: number of layer outputs with datatype X
"mem_o_INT32": 142602.0, # number of INT32 output elements
# mem_o_X: number of layer parameters (weights) with datatype X
"mem_w_INT2": 908033.0, # number of INT2 parameters (weights)
# op_mac_X_Y: number of MAC operations, datatype X by datatype Y
# scaled integer datatypes have a tensor- or channelwise scale factor
"op_mac_SCALEDINT<8>_INT2": 1345500.0, # number of scaled int8 x int2 MACs
"op_mac_INT2_INT2": 35615771.0, # number of int2 x int2 MACs
"total_bops": 163991084.0, # total number of MACs normalized to bit-ops (BOPS)
"total_mem_o_bits": 4563264.0, # total number of bits for layer outputs
"total_mem_w_bits": 1816066.0, # total number of bits for layer parameters
"unsupported": "set()"
}
You can use the --cost-breakdown option to generate a more detailed report that covers per-node (by name) and per-op-type information.
You can read more about the BOPS metric in this paper, Section 4.2 Bit Operations.
Convert between different quantization representations
Using the qonnx-convert command line utility you can convert from QONNX to QCDQ-style quantization:
qonnx-convert CNV_2W2A.onnx
This will convert Quant nodes to QuantizeLinear -> Clip -> DequantizeLinear nodes where possible.
Please see the documentation of the QuantToQCDQ transformation to learn more about the limitations.
Development
Install in editable mode in a Python virtual environment:
git clone https://github.com/fastmachinelearning/qonnx
cd qonnx
virtualenv -p python3.10 venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -e .[qkeras,testing]
Running tests
Run entire test suite, parallelized across CPU cores:
pytest -n auto --verbose
Run a particular test and fall into pdb if it fails:
pytest --pdb -k "test_extend_partition.py::test_extend_partition[extend_id1-2]"
Linting
If you plan to make pull requests to the qonnx repo, linting will be required.
We use a pre-commit hook to auto-format Python code and check for issues. See https://pre-commit.com/ for installation. Once you have pre-commit,
you can install the hooks into your local clone of the qonnx repo:
cd qonnx
source venv/bin/activate
pip install pre-commit
pre-commit install
Every time you commit some code, the pre-commit hooks will first run, performing various checks and fixes. In some cases pre-commit won’t be able to fix the issues and you may have to fix it manually, then run git commit once again. The checks are configured in .pre-commit-config.yaml under the repo root.
Why QONNX?
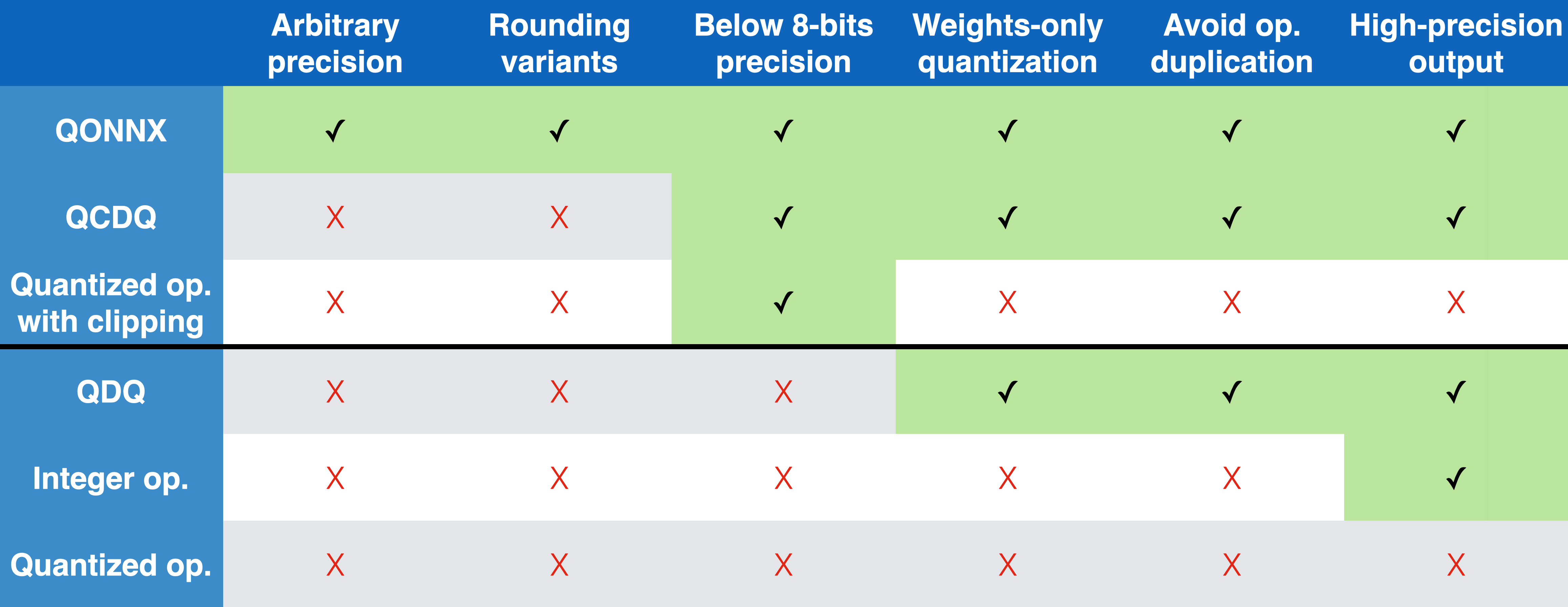
The QONNX representation has several advantages compared to other alternatives, as summarized in the table below. These include a compact but flexible, single-node quantization representation that avoids operator duplication and can support arbitrary precision up to the container datatype limit.
Community
The QONNX efforts were started by the FINN and hls4ml communities working together to create a common, arbitrary-precision representation that both frameworks could ingest. However, QONNX aims to build an open-source community for practitioners and researchers working with mixed-precision quantized neural networks by providing useful tools and a discussion forum.


Resources
You can read more about QONNX in this paper. If you find QONNX useful in your work, please consider citing:
```bibtex @inproceedings{Pappalardo:2022nxk, author = "Pappalardo, Alessandro and Umuroglu, Yaman and Blott, Michaela and Mitrevski, Jovan and Hawks, Ben and Tran, Nhan and Loncar, Vladimir and Summers, Sioni and Borras, Hendrik and Muhizi, Jules and Trahms, Matthew and Hsu, Shih-Chieh Hsu and Hauck, Scott and Duarte, Javier" title = "{QONNX: Representing Arbitrary-Precision Quantized Neural Networks}", booktitle = "{4th Workshop on Accelerated Machine Learning (AccML) at HiPEAC 2022 Conference}", eprint = "2206.07527", archivePrefix = "arXiv", primaryClass = "cs.LG", reportNumber = "FERMILAB-CONF-22-471-SCD", month = "6", year = "2022", url = "https://accml.dcs.gla.ac.uk/papers/2022/4thAccMLpaper1(12).pdf" }
@software{yamanumuroglu2023_7622236, author = "Umuroglu, Yaman and Borras, Hendrik and Loncar, Vladimir, and Summers, Sioni and Duarte, Javier", title = "fastmachinelearning/qonnx", month = {06}, year = 2022, publisher = {Zenodo}, doi = {10.5281/zenodo.7622236}, url = {https://github.com/fastmachinelearning/qonnx} } ```
Owner
- Name: Fast Machine Learning Lab
- Login: fastmachinelearning
- Kind: organization
- Email: fml@fastmachinelearning.org
- Website: http://fastmachinelearning.org/
- Repositories: 21
- Profile: https://github.com/fastmachinelearning
Real-time and accelerated ML for fundamental sciences
Citation (CITATION.cff)
# This CITATION.cff file was generated with cffinit.
# Visit https://bit.ly/cffinit to generate yours today!
cff-version: 1.2.0
title: QONNX
message: 'If you use this software, please cite it as below.'
type: software
doi: 10.5281/zenodo.7622236
license: Apache-2.0
date-released: 2022-06-24
version: 0.1
url: "https://github.com/fastmachinelearning/qonnx"
authors:
- given-names: Yaman
family-names: Umuroglu
affiliation: AMD
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3700-5935'
- given-names: Hendrik
family-names: Borras
affiliation: Heidelberg University
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2411-2416'
- given-names: Vladimir
family-names: Loncar
affiliation: MIT
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3651-0232'
- given-names: Sioni
family-names: Summers
affiliation: CERN
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4244-2061'
- given-names: Javier
family-names: Duarte
affiliation: UC San Diego
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5076-7096'
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 20
- Release event: 1
- Issues event: 9
- Watch event: 28
- Delete event: 14
- Member event: 4
- Issue comment event: 45
- Push event: 128
- Pull request review event: 33
- Pull request review comment event: 33
- Pull request event: 74
- Fork event: 9
Last Year
- Create event: 20
- Release event: 1
- Issues event: 9
- Watch event: 28
- Delete event: 14
- Member event: 4
- Issue comment event: 45
- Push event: 128
- Pull request review event: 33
- Pull request review comment event: 33
- Pull request event: 74
- Fork event: 9
Committers
Last synced: 9 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Yaman Umuroglu | m****r@g****m | 321 |
| Hendrik Borras | h****s@w****e | 79 |
| icolbert | I****t@a****m | 38 |
| Javier M. Duarte | j****e@u****u | 36 |
| Christoph Berganski | c****i@g****m | 18 |
| Selwyn96 | s****6@p****u | 8 |
| jvreca | j****a@i****i | 7 |
| Harish | h****h@a****m | 5 |
| Jovan Mitrevski | j****s@f****v | 5 |
| Sioni Summers | s****0@i****k | 5 |
| auphelia | j****k@w****e | 5 |
| makoeppel | k****a@g****m | 5 |
| Harish | 6****0 | 3 |
| Vladimir Loncar | v****r | 3 |
| shashwat1198 | s****8@g****m | 3 |
| jicampos | j****8@g****m | 2 |
| klassen9 | k****9@c****e | 2 |
| lstasytis | l****1@g****m | 2 |
| mmrahorovic | m****c@h****m | 2 |
| rushtheboy | r****2@g****m | 2 |
| mdaniowi | m****i@a****m | 2 |
| klassen9 | k****9@m****e | 2 |
| mdaniowi | M****z@a****m | 1 |
| Felix Jentzsch | f****h@u****e | 1 |
| Tim Paine | 3****e | 1 |
| bwintermann | b****n@m****m | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 30
- Total pull requests: 167
- Average time to close issues: 3 months
- Average time to close pull requests: about 1 month
- Total issue authors: 15
- Total pull request authors: 35
- Average comments per issue: 0.93
- Average comments per pull request: 0.74
- Merged pull requests: 117
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 10
- Pull requests: 58
- Average time to close issues: 8 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 13 days
- Issue authors: 6
- Pull request authors: 18
- Average comments per issue: 0.7
- Average comments per pull request: 0.59
- Merged pull requests: 34
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- iksnagreb (5)
- maltanar (4)
- bwintermann (3)
- HenniOVP (2)
- Sayanti17 (2)
- sdittmeier (2)
- sducouedic (2)
- shashwat1198 (1)
- auphelia (1)
- AnouarITI (1)
- nicologhielmetti (1)
- nghielme (1)
- jmduarte (1)
- balditommaso (1)
- jmitrevs (1)
Pull Request Authors
- maltanar (63)
- iksnagreb (28)
- jurevreca12 (16)
- Harsh9650 (15)
- jmitrevs (8)
- makoeppel (8)
- mdanilow (8)
- i-colbert (7)
- jmduarte (6)
- ebby-s (6)
- nghielme (5)
- auphelia (4)
- HenniOVP (4)
- klassen9 (4)
- SpiritSeeker (3)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 26,924 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 3
- Total dependent repositories: 1
- Total versions: 4
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: qonnx
Frontend and utilities for QONNX
- Homepage: https://github.com/fastmachinelearning/qonnx
- Documentation: https://pyscaffold.org/
- License: Apache-2.0
-
Latest release: 0.4.0
published about 1 year ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- bitstring >=3.1.7
- clize ==4.1.1
- importlib-metadata *
- numpy *
- onnx ==1.11.0
- onnxruntime ==1.11.1
- protobuf ==3.20.1
- sphinx >=3.2.1
- sphinx_rtd_theme *
- toposort >=1.5.0


