pydvl
pyDVL is a library of stable implementations of algorithms for data valuation and influence function computation
Science Score: 36.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
✓Academic publication links
Links to: zenodo.org -
○Academic email domains
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (13.0%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
pyDVL is a library of stable implementations of algorithms for data valuation and influence function computation
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: aai-institute
- License: lgpl-3.0
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: develop
- Homepage: https://pydvl.org
- Size: 436 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 130
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 7
- Open Issues: 77
- Releases: 15
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
A library for data valuation.
pyDVL collects algorithms for Data Valuation and Influence Function computation. Here is the list of all methods implemented.
Data Valuation for machine learning is the task of assigning a scalar to each element of a training set which reflects its contribution to the final performance or outcome of some model trained on it. Some concepts of value depend on a specific model of interest, while others are model-agnostic. pyDVL focuses on model-dependent methods.

Comparison of different data valuation methods on best sample removal.
The Influence Function is an infinitesimal measure of the effect that single training points have over the parameters of a model, or any function thereof. In particular, in machine learning they are also used to compute the effect of training samples over individual test points.
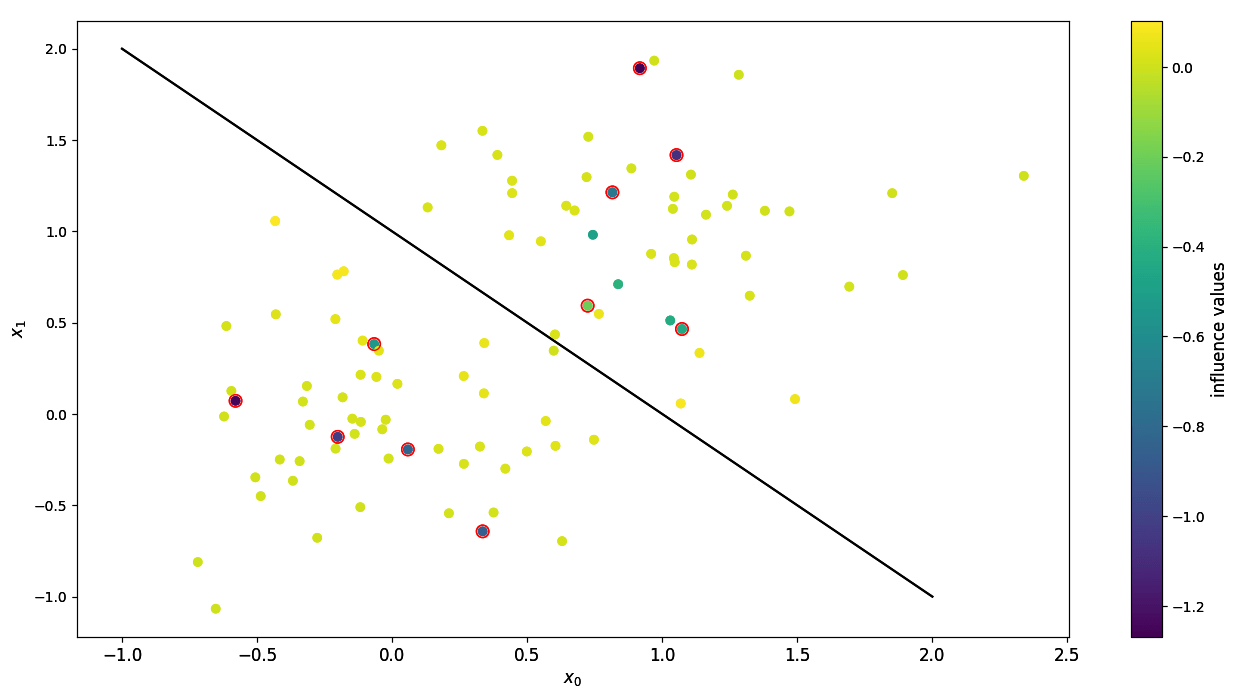
Influences of input points with corrupted data. Highlighted points have flipped labels.
Installation
To install the latest release use:
shell
$ pip install pyDVL
You can also install the latest development version from TestPyPI:
shell
pip install pyDVL --index-url https://test.pypi.org/simple/
pyDVL has also extra dependencies for certain functionalities,
e.g. for using influence functions run
shell
$ pip install pyDVL[influence]
For more instructions and information refer to Installing pyDVL in the documentation.
Usage
Please read Getting Started in the documentation for more instructions. We provide several examples for data valuation and for influence functions in our Example Gallery.
Influence Functions
- Import the necessary packages (the exact ones depend on your specific use case).
- Create PyTorch data loaders for your train and test splits.
- Instantiate your neural network model and define your loss function.
- Instantiate an
InfluenceFunctionModeland fit it to the training data - For small input data, you can call the
influences()method on the fitted instance. The result is a tensor of shape(training samples, test samples)that contains at index(i, j) the influence of training sampleion test samplej. - For larger datasets, wrap the model into a "calculator" and call methods on it. This splits the computation into smaller chunks and allows for lazy evaluation and out-of-core computation.
The higher the absolute value of the influence of a training sample on a test sample, the more influential it is for the chosen test sample, model and data loaders. The sign of the influence determines whether it is useful (positive) or harmful (negative).
Note pyDVL currently only support PyTorch for Influence Functions. We plan to add support for Jax next.
```python import torch from torch import nn from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
from pydvl.influence import SequentialInfluenceCalculator from pydvl.influence.torch import DirectInfluence from pydvl.influence.torch.util import ( NestedTorchCatAggregator, TorchNumpyConverter, )
inputdim = (5, 5, 5) outputdim = 3 trainx, trainy = torch.rand((10, *inputdim)), torch.rand((10, outputdim)) testx, testy = torch.rand((5, *inputdim)), torch.rand((5, outputdim)) traindataloader = DataLoader(TensorDataset(trainx, trainy), batchsize=2) testdataloader = DataLoader(TensorDataset(testx, testy), batchsize=1) model = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(inchannels=5, outchannels=3, kernel_size=3), nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(27, 3), ) loss = nn.MSELoss()
inflmodel = DirectInfluence(model, loss, hessianregularization=0.01) inflmodel = inflmodel.fit(traindataloader)
For small datasets, instantiate the full influence matrix:
influences = inflmodel.influences(testx, testy, trainx, train_y)
For larger datasets, use the Influence calculators:
inflcalc = SequentialInfluenceCalculator(inflmodel)
Lazy object providing arrays batch-wise in a sequential manner
lazyinfluences = inflcalc.influences(testdataloader, traindataloader)
Trigger computation and pull results to memory
influences = lazy_influences.compute(aggregator=NestedTorchCatAggregator())
Trigger computation and write results batch-wise to disk
lazyinfluences.tozarr("influences_result", TorchNumpyConverter()) ```
Data Valuation
The steps required to compute data values for your samples are:
- Import the necessary packages (the exact ones will depend on your specific
use case, but most of the interface is exposed through
pydvl.valuation). - Create two
Datasetobjects with your train and test splits. There are some factories to do this from arrays or scikit-learn toy datasets. - Create an instance of a
SupervisedScorer, with any sklearn scorer and a "valuation set" over which your model will be scored. - Wrap model and scorer in a
ModelUtility. - Use one of the methods defined in the library to compute the values. In the example below, we use the most basic Montecarlo Shapley with uniform sampling, an approximate method for computing Data Shapley values.
- Call
fitin a joblib parallel context. The result is a variable of typeValuationResultthat contains the indices and their values as well as other attributes. This object can be sliced, sorted and inspected directly, or you can convert it to a dataframe for convenience.
The higher the value for an index, the more important it is for the chosen model, dataset and scorer. Reciprocally, low-value points could be mislabelled, or out-of-distribution, and dropping them can improve the model's performance.
```python from joblib import parallelconfig from sklearn.datasets import loadiris from sklearn.svm import SVC from pydvl.valuation import Dataset, ShapleyValuation, UniformSampler,\ MinUpdates, ModelUtility, SupervisedScorer
seed = 42 model = SVC(kernel="linear", probability=True, random_state=seed)
train, val = Dataset.fromsklearn(loadiris(), trainsize=0.6, randomstate=24) scorer = SupervisedScorer(model, val, default=0.0) utility = ModelUtility(model, scorer) sampler = UniformSampler(batch_size=2 ** 6, seed=seed) stopping = MinUpdates(1000) valuation = ShapleyValuation(utility, sampler, stopping, progress=True)
with parallelconfig(njobs=32): valuation.fit(train)
result = valuation.result ```
Deprecation notice
Up until v0.9.2 valuation methods were available through the pydvl.value
module, which is now deprecated in favour of the design showcased above,
available under pydvl.valuation. The old module will be removed in a future
release.
Contributing
Please open new issues for bugs, feature requests and extensions. You can read about the structure of the project, the toolchain and workflow in the guide for contributions.
License
pyDVL is distributed under LGPL-3.0. A complete version can be found in two files: here and here.
All contributions will be distributed under this license.
Owner
- Name: appliedAI Institute gGmbH
- Login: aai-institute
- Kind: organization
- Location: Germany
- Website: https://transferlab.appliedai.de
- Repositories: 1
- Profile: https://github.com/aai-institute
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 30
- Release event: 1
- Issues event: 49
- Watch event: 30
- Delete event: 40
- Member event: 2
- Issue comment event: 46
- Push event: 193
- Pull request review comment event: 3
- Pull request review event: 13
- Pull request event: 51
- Fork event: 1
Last Year
- Create event: 30
- Release event: 1
- Issues event: 49
- Watch event: 30
- Delete event: 40
- Member event: 2
- Issue comment event: 46
- Push event: 193
- Pull request review comment event: 3
- Pull request review event: 13
- Pull request event: 51
- Fork event: 1
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 34
- Total pull requests: 30
- Average time to close issues: 9 months
- Average time to close pull requests: about 1 month
- Total issue authors: 8
- Total pull request authors: 4
- Average comments per issue: 1.21
- Average comments per pull request: 0.2
- Merged pull requests: 19
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 2
Past Year
- Issues: 21
- Pull requests: 28
- Average time to close issues: 3 months
- Average time to close pull requests: 14 days
- Issue authors: 4
- Pull request authors: 4
- Average comments per issue: 0.95
- Average comments per pull request: 0.07
- Merged pull requests: 19
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 2
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- mdbenito (41)
- schroedk (32)
- AnesBenmerzoug (24)
- janosg (8)
- kosmitive (3)
- jakobkruse1 (3)
- seyedamirshobeiri (2)
- Xuzzo (1)
- sleepymalc (1)
- qiyandeng (1)
- danielkaplan137 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- schroedk (28)
- mdbenito (28)
- AnesBenmerzoug (14)
- dependabot[bot] (8)
- janosg (6)
- jakobkruse1 (3)
- Xuzzo (1)
- opcode81 (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 126 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 15
- Total maintainers: 2
pypi.org: pydvl
The Python Data Valuation Library
- Documentation: https://pydvl.org
- License: GNU Lesser General Public License v3 (LGPLv3)
-
Latest release: 0.10.0
published 11 months ago
Rankings
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v4 composite
- actions/cache v3 composite
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v4 composite
- actions/stale v6 composite
- actions/cache v3 composite
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/download-artifact v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v4 composite
- actions/upload-artifact v3 composite
- peaceiris/actions-gh-pages v3 composite
- memcached latest
- datasets ==2.6.1
- pillow ==9.3.0
- torch ==1.13.1
- torchvision ==0.14.1
- black * development
- bump2version * development
- jupyter * development
- mypy * development
- nbconvert * development
- pre-commit * development
- pytest * development
- pytest-timeout * development
- tox * development
- tox-wheel * development
- twine * development
- types-tqdm * development
- cloudpickle *
- joblib *
- matplotlib *
- numpy >=1.20
- pandas >=1.3
- pymemcache *
- ray >=0.8
- scikit-learn *
- tqdm *
- for *
- if *
- line *
- actions/setup-python v4 composite
- GitPython *
- markdown-captions *
- mike *
- mkdocs ==1.5.2
- mkdocs-alias-plugin >=0.6.0
- mkdocs-autorefs *
- mkdocs-bibtex *
- mkdocs-gen-files *
- mkdocs-git-revision-date-localized-plugin *
- mkdocs-glightbox *
- mkdocs-literate-nav *
- mkdocs-macros-plugin *
- mkdocs-material *
- mkdocs-section-index *
- mkdocstrings >=0.18
- mknotebooks >=0.8.0
- neoteroi-mkdocs *
- pygments *
- pypandoc *



