pararealgpu.jl
A distributed and GPU-based implementation of the Parareal algorithm for parallel-in-time integration of equations of motion.
Science Score: 44.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
○DOI references
-
○Academic publication links
-
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (14.4%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
A distributed and GPU-based implementation of the Parareal algorithm for parallel-in-time integration of equations of motion.
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: NonDairyNeutrino
- License: gpl-3.0
- Language: Julia
- Default Branch: trunk
- Homepage: http://pararealgpu.computationalphysics.net/
- Size: 34.7 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 2
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
PararealGPU.jl
A Julia implementation of the Parareal algorithm from parallel-in-time integration using high-performance methods including GPU (e.g. CUDA.jl) and distributed (e.g. Distributed.jl) computing. The main aim of this work is to support the efficient simulation of equations of motion. Documentation can be found at https://nathanwchapman.com/PararealGPU.jl/dev/.
Installation
This work is not yet included in the Julia General Repository of packages as it is not yet completed. If you still want to tinker around with it, you can use Julia's package manager via
pkg> add https://github.com/NonDairyNeutrino/PararealGPU.jl
What is the Parareal Algorithm?
The Parareal algorithm (PA) comes from a class of algorithms dubbed parallel-in-time integration algorithms as their main goal is to accelerate the approximation of solutions to initial-value differential equations. The PA is one of the most widely studied methods in this class [1].
The key idea is that a single "root" initial value problem (IVP) can be broken into smaller IVPs using the data from an inaccurate "root" solution as the initial values of the subproblems. These subproblems are then solved in parallel using traditional, accurate methods. The final values of the resulting subsolutions are sequentially combined with those at the same time in the root solution to give a more accurate root solution. This process is then repeated until the root solution matches what would have ben obtained if the accurate method were used directly.
The Parareal Algorithm at Scale
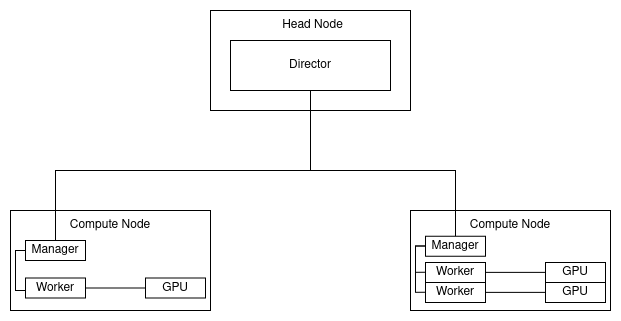
Because the PA leads to a quasi-pleasingly parallel set of problems that only need arithmetic operations to solve, the PA is well-suited to be implemented on massively parallel architectures such as GPUs, distributed systems, and supercomputers. The basic idea of the PA being executed on a single GPU is shown below, with an example cluster topology showing how the head node interacts with GPUs on remote machines; these images are sourced from my thesis, where this work was developed.

Example - The Simple Harmonic Oscillator
This implementation can be used to solve any problem you would traditionally, including the simple
harmonic oscillator. Here, nodeVector = String["Electromagnetism"] represents that the machine on
which this program is going to be executed can connect to a machine identified by "Electromagnetism"
via password-less ssh. The only information needed is these
ssh-identifiers; prepCluster automatically identifies and assigns all GPUs in the cluster
(including multiple GPUs in a single machine) to their own process.
An example cluster topology is shown below. This cluster is composed of a head node, a compute node with one GPU, and a compute node with two GPUs. The head node is a machine that only has a single Julia process. This process is the "director" process that manages all other processes, and computes the sequential combination of the subsolutions and the root solution. The compute nodes have "middle manager" processes that manage the "worker" processes on the same machine; there is a worker process for every GPU in the machine.
```julia using Plots using PararealGPU const nodeVector = String["Electromagnetism"] devPool = prepCluster(nodeVector)
println("Creating initial value problems")
DEFINE THE COARSE AND FINE PROPAGATION SCHEMES
const INITIALDISCRETIZATION = Threads.nthreads() const COARSEPROPAGATOR = Propagator(symplecticEuler, INITIALDISCRETIZATION) const FINEPROPAGATOR = Propagator(velocityVerlet, 2^0 * INITIALDISCRETIZATION)
@everywhere @inline function acceleration(position :: Vector{T}, velocity :: Vector{T}; k = 1) :: Vector{T} where T <: Real return -k^2 * position # this encodes the differential equation u''(t) = -k^2 u end const INITIALPOSITION = [0.] const INITIALVELOCITY = [1.] const DOMAIN = Interval(0., 2^2 * pi)
ivpVector = Vector{SecondOrderIVP}(undef, length(devPool)) for k in 1:length(devPool) ivpVector[k] = SecondOrderIVP(DOMAIN, (x, v) -> acceleration(x, v; k), INITIALPOSITION, INITIALVELOCITY) end
println("Beginning parareal evaluation on workers") solutionVector = pmap(ivp -> parareal(ivp, COARSEPROPAGATOR, FINEPROPAGATOR), devPool, ivpVector) println("Parareal evaluation finished")
for (k, rootSolution) in enumerate(solutionVector) plot!( rootSolution.domain, [rootSolution.positionSequence .|> first, rootSolution.velocitySequence .|> first], label = ["position - $k" "velocity - $k"], title = "discretization: $INITIALDISCRETIZATION k <= $k" ) end println("Plot saved at ", pwd(), "/cos.png") savefig("cos.png") ```
Still Interested?
If you're still interested in learning more about the context surrounding this project, it was the central element of my master's thesis Scalable Parallel-in-Time Integration for Equations of Motion.
Owner
- Name: Nathan Chapman
- Login: NonDairyNeutrino
- Kind: user
- Location: Washington State
- Company: Central Washington University
- Website: nathanwchapman.com
- Twitter: NDNeutrino
- Repositories: 2
- Profile: https://github.com/NonDairyNeutrino
Computational Science MS student at Central Washington University focusing on computational physics and gravitational analogs
Citation (CITATION.cff)
# This CITATION.cff file was generated with cffinit.
# Visit https://bit.ly/cffinit to generate yours today!
cff-version: 1.2.0
title: PararealGPU.jl
message: >-
If you use this software, please cite it using the
metadata from this file.
type: software
authors:
- given-names: Nathan
family-names: Chapman
email: nathaniel.chapman@cwu.edu
affiliation: Central Washington University
repository-code: 'https://github.com/NonDairyNeutrino/PararealGPU.jl'
url: 'https://nathanwchapman.com/PararealGPU.jl/dev/'
repository: 'https://github.com/NonDairyNeutrino/Thesis'
abstract: ' A distributed and GPU-based implementation of the Parareal algorithm for parallel-in-time integration of equations of motion. '
keywords:
- parareal
- parallel-in-time-integration
- parallel
- cuda
- distributed
- high-performance-computing
- computational-science
- computational-physics
- differential-equations
- julialang
license: GPL-3.0
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 1
- Watch event: 4
- Delete event: 3
- Issue comment event: 4
- Push event: 133
- Pull request event: 1
- Create event: 6
Last Year
- Issues event: 1
- Watch event: 4
- Delete event: 3
- Issue comment event: 4
- Push event: 133
- Pull request event: 1
- Create event: 6
Committers
Last synced: 8 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| nondairyneutrino | c****9@g****m | 236 |
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 8 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 1
- Total pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Total issue authors: 1
- Total pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 3.0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 1
- Pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 1
- Pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 3.0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- ChrisRackauckas (1)
Pull Request Authors
- dependabot[bot] (1)