Science Score: 49.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 3 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org, acm.org -
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (12.9%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Keywords from Contributors
Repository
State-of-the-art native debugging tools
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: HyperDbg
- License: gpl-3.0
- Language: C
- Default Branch: master
- Homepage: https://hyperdbg.org
- Size: 43.7 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 3,437
- Watchers: 87
- Forks: 430
- Open Issues: 11
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
HyperDbg Debugger
 HyperDbg Debugger is an open-source, community-driven, hypervisor-assisted, user-mode, and kernel-mode Windows debugger with a focus on using modern hardware technologies. It is a debugger designed for analyzing, fuzzing, and reversing.
HyperDbg Debugger is an open-source, community-driven, hypervisor-assisted, user-mode, and kernel-mode Windows debugger with a focus on using modern hardware technologies. It is a debugger designed for analyzing, fuzzing, and reversing.
You can follow HyperDbg on Twitter or Mastodon to get notified about new releases, or join any of the HyperDbg groups, where you can ask developers and open-source reversing enthusiasts for help setting up and using HyperDbg.
Description
HyperDbg is designed with a focus on using modern hardware technologies to provide new features to the debuggers' world. It operates on top of Windows by virtualizing an already running system using Intel VT-x and EPT. This debugger aims not to use any APIs and software debugging mechanisms, but instead, it uses Second Layer Page Table (a.k.a. Extended Page Table or EPT) extensively to monitor both kernel and user executions.
HyperDbg comes with features like hidden hooks, which are as fast as old inline hooks, but also stealth. It mimics hardware debug registers for (read & write) to a specific location, but this time entirely invisible for both Windows kernel and the programs, and of course, without any limitation in size or count!Using TLB-splitting, and having features such as measuring code coverage and monitoring all mov(s) to/from memory by a function, makes HyperDbg a unique debugger.
Although it has novel features, HyperDbg tries to be as stealthy as possible. It doesnt use any debugging APIs to debug Windows or any application, so classic anti-debugging methods wont detect it. Also, it resists the exploitation of time delta methods (e.g., RDTSC/RDTSCP) to detect the presence of hypervisors, therefore making it much harder for applications, packers, protectors, malware, anti-cheat engines, etc. to discover the debugger.
Build & Installation
You can download the latest compiled binary files from releases; otherwise, if you want to build HyperDbg, you should clone HyperDbg with the --recursive flag.
git clone --recursive https://github.com/HyperDbg/HyperDbg.git
Please visit Build & Install and Quick Start for a detailed explanation of how to start with HyperDbg. You can also see the FAQ for more information, or if you previously used other native debuggers like GDB, LLDB, or WinDbg, you could see the command map.
Tutorials
The OpenSecurityTraining2's "Reversing with HyperDbg (Dbg3301)" tutorial series, available on OST2's website (preferred) and YouTube is the recommended way to get started with and learn HyperDbg. It guides you through the initial steps of using HyperDbg, covering essential concepts, principles, and debugging functionalities, along with practical examples and numerous reverse engineering methods that are unique to HyperDbg.
If you're interested in understanding the internal design and architecture of hypervisors and HyperDbg, you can read the Hypervisor From Scratch tutorials.
Publications
In case you use one of HyperDbg's components in your work, please consider citing our papers.
1. HyperDbg: Reinventing Hardware-Assisted Debugging (CCS'22) [arXiv]
@inproceedings{karvandi2022hyperdbg,
title={HyperDbg: Reinventing Hardware-Assisted Debugging},
author={Karvandi, Mohammad Sina and Gholamrezaei, MohammadHosein and Khalaj Monfared, Saleh and Meghdadizanjani, Soroush and Abbassi, Behrooz and Amini, Ali and Mortazavi, Reza and Gorgin, Saeid and Rahmati, Dara and Schwarz, Michael},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 2022 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security},
pages={1709--1723},
year={2022}
}
2. The Reversing Machine: Reconstructing Memory Assumptions [arXiv]
@article{karvandi2024reversing,
title={The Reversing Machine: Reconstructing Memory Assumptions},
author={Karvandi, Mohammad Sina and Meghdadizanjani, Soroush and Arasteh, Sima and Monfared, Saleh Khalaj and Fallah, Mohammad K and Gorgin, Saeid and Lee, Jeong-A and van der Kouwe, Erik},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.00298},
year={2024}
}
3. hwdbg: Debugging Hardware Like Software (EuroSec'25) [PDF]
@inproceedings{karvandi2025hwdbg,
title={hwdbg: Debugging Hardware Like Software},
author={Karvandi, Mohammad Sina and Meghdadizanjani, Soroush and Monfared, Saleh Khalaj and van der Kouwe, Erik and Slowinska, Asia},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 18th European Workshop on Systems Security},
pages={56--62},
year={2025}
}
You can also read this article as it describes the overall architecture, technical difficulties, design decisions, and internals of HyperDbg Debugger, this article about our efforts on vm-exit transparency, this article about chasing bugs within hypervisors, and this article about new reverse engineering techniques introduced in HyperDbg. More articles, posts, and resources are available at the awesome repo, and in addition, the slides repo provides presentation slides for further reference.
Unique Features
- Advanced Hypervisor-based Kernel Mode Debugger [link][link][link]
- Classic EPT Hook (Hidden Breakpoint) [link][link][link]
- Inline EPT Hook (Inline Hook) [link][link]
- Monitor Memory For R/W (Emulating Hardware Debug Registers Without Limitation) [link][link][link]
- SYSCALL Hook (Disable EFER & Handle #UD) [link][link][link]
- SYSRET Hook (Disable EFER & Handle #UD) [link][link]
- CPUID Hook & Monitor [link][link]
- RDMSR Hook & Monitor [link][link]
- WRMSR Hook & Monitor [link][link]
- RDTSC/RDTSCP Hook & Monitor [link]
- RDPMC Hook & Monitor [link]
- VMCALL Hook & Monitor [link]
- Debug Registers Hook & Monitor [link]
- I/O Port (In Instruction) Hook & Monitor [link][link]
- I/O Port (Out Instruction) Hook & Monitor [link][link]
- MMIO Monitor [link]
- Exception (IDT < 32) Monitor [link][link][link]
- External-Interrupt (IDT > 32) Monitor [link][link][link]
- Running Automated Scripts [link]
- Transparent-mode (Anti-debugging and Anti-hypervisor Resistance) [link][link]
- Running Custom Assembly In Both VMX-root, VMX non-root (Kernel & User) [link]
- Checking For Custom Conditions [link][link]
- Process-specific & Thread-specific Debugging [link][link][link]
- VMX-root Compatible Message Tracing [link]
- Powerful Kernel Side Scripting Engine [link][link]
- Support To Symbols (Parsing PDB Files) [link][link]
- Mapping Data To Symbols & Create Structures, Enums From PDB Files [link][link][link]
- Event Forwarding (#DFIR) [link][link]
- Transparent Breakpoint Handler [link][link]
- Various Custom Scripts [link]
- HyperDbg Software Development Kit (SDK) [link]
- Event Short-circuiting [link][link]
- Tracking records of function calls and return addresses [link]
- Kernel-level Length Disassembler Engine (LDE) [link][link]
- Memory Execution Monitor & Execution Blocking [link]
- Custom Page-fault Injection [link]
- Different Event Calling Stages [link]
- Injecting Custom Interrupts/Exceptions/Faults [link][link]
- Instant events in the Debugger Mode [link]
- Detect kernel-to-user and user-to-kernel transitions [link]
- Physical memory monitoring hooks [link]
- Enumerating PCI/PCI-e Devices [link]
- Interpreting and Dumping PCI/PCI-e Configuration Space (CAM) [link]
- Dumping IDT entries, I/O APIC, and Local APIC in XAPIC and X2APIC modes [link][link][link]
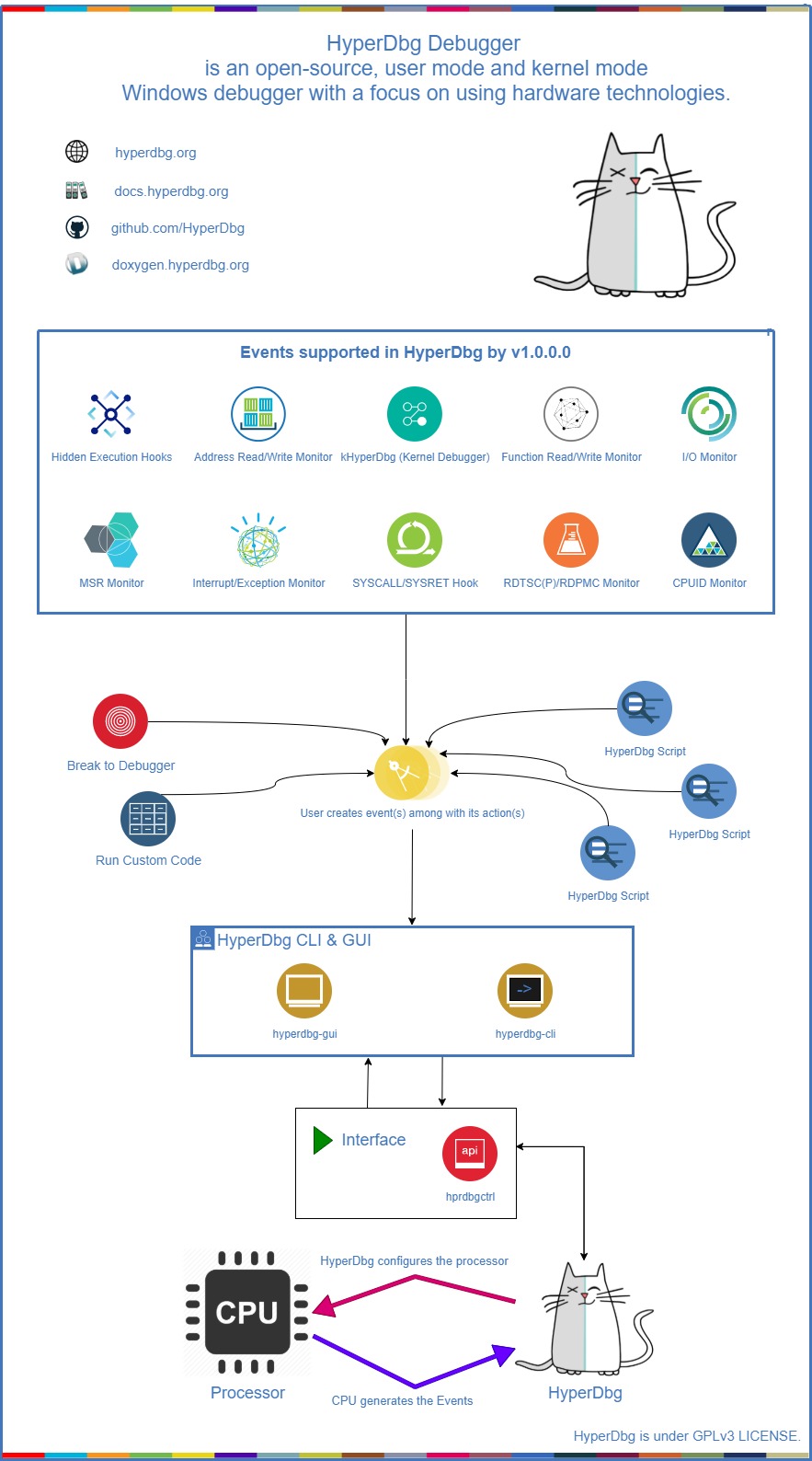
How does it work?
You can read about the internal design of HyperDbg and its features in the documentation. Here's a top-level diagram that shows how HyperDbg works:
Scripts
You can write your scripts to automate your debugging journey. HyperDbg has a powerful, fast, and entirely kernel-side implemented script engine.
Contributing
Contributing to HyperDbg is super appreciated. We have made a list of potential tasks that you might be interested in contributing towards.
If you want to contribute to HyperDbg, please read the Contribution Guide.
License
HyperDbg, and all its submodules and repos, unless a license is otherwise specified, are licensed under GPLv3 LICENSE.
Dependencies are licensed by their own.
Owner
- Name: HyperDbg
- Login: HyperDbg
- Kind: organization
- Website: https://hyperdbg.org
- Twitter: HyperDbg
- Repositories: 41
- Profile: https://github.com/HyperDbg
Next Generation Debugger, Dynamic Binary Analyzer, and System Introspection Tool
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 30
- Release event: 10
- Issues event: 32
- Watch event: 472
- Delete event: 31
- Issue comment event: 46
- Push event: 170
- Pull request event: 91
- Fork event: 58
Last Year
- Create event: 30
- Release event: 10
- Issues event: 32
- Watch event: 472
- Delete event: 31
- Issue comment event: 46
- Push event: 170
- Pull request event: 91
- Fork event: 58
Committers
Last synced: 9 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| SinaKarvandi | m****i@y****m | 1,924 |
| Moammad97 | m****7@g****m | 124 |
| Behrooz Abbassi | B****i@o****m | 67 |
| xmaple555 | x****5@g****m | 40 |
| Abbas-MG | a****g@g****m | 38 |
| AleeAmini | a****z@g****m | 33 |
| Admin | 2****1@q****m | 30 |
| Björn Ruytenberg | b****n@b****l | 17 |
| gmh5225 | 2****7@q****m | 15 |
| ahmed | 6****e | 12 |
| semenov_gv | G****k@y****u | 12 |
| Matthijs Lavrijsen | m****i@g****m | 7 |
| Sinaei | s****i@g****m | 6 |
| Saleh | m****d@e****r | 4 |
| Thiago | 4****r | 3 |
| Sariaki | k****o@g****m | 3 |
| gmh | g****h | 3 |
| jianxq@163.com | j****q@1****m | 2 |
| Christian Zimmerer | c****i@p****e | 2 |
| gavinl1b0 | 7****9@q****m | 2 |
| Shtan7 | d****a@g****m | 2 |
| angel_killah | a****h | 2 |
| botao | 7****4@q****m | 2 |
| xorrsp | 9****p | 1 |
| Maladiy | M****y | 1 |
| SinaKarvandi | m****i@e****m | 1 |
| Tumpes | e****i@g****m | 1 |
| wxwywz | 8****0@p****m | 1 |
| reo | r****o@r****m | 1 |
| momo5502 | m****n@g****m | 1 |
| and 10 more... | ||
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 81
- Total pull requests: 115
- Average time to close issues: 3 months
- Average time to close pull requests: about 6 hours
- Total issue authors: 41
- Total pull request authors: 25
- Average comments per issue: 6.69
- Average comments per pull request: 0.24
- Merged pull requests: 102
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 11
- Pull requests: 73
- Average time to close issues: about 1 month
- Average time to close pull requests: about 7 hours
- Issue authors: 7
- Pull request authors: 15
- Average comments per issue: 1.55
- Average comments per pull request: 0.12
- Merged pull requests: 61
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- SinaKarvandi (13)
- wuhao13 (12)
- xSanx (8)
- ddkwork (7)
- ghost (7)
- kqikz (5)
- DarkerSquirrel (3)
- m853ax (3)
- vxcute (2)
- sjzbwdiy (2)
- w58850 (2)
- zero-168 (2)
- louwangzhiyuY (2)
- prnuimeer (2)
- Mack5443 (2)
Pull Request Authors
- SinaKarvandi (115)
- Abbas-MG (20)
- ddkwork (11)
- xmaple555 (10)
- BjornRuytenberg (9)
- GermanAizek (6)
- Shtan7 (4)
- CokeTree3 (4)
- Mattiwatti (3)
- halbGefressen (3)
- Sal3h (3)
- BehroozAbbassi (3)
- binophism (2)
- kqikz (2)
- ZhouZiY (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- actions/download-artifact v2 composite
- actions/upload-artifact v2 composite
- microsoft/setup-msbuild v1.0.2 composite
- softprops/action-gh-release v1 composite
- thedoctor0/zip-release master composite