mdance
MDANCE is a flexible n-ary clustering package for all applications.
Science Score: 67.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 5 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: biorxiv.org, acs.org -
○Academic email domains
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (14.8%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
MDANCE is a flexible n-ary clustering package for all applications.
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: mqcomplab
- License: mit
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://mdance.readthedocs.io
- Size: 62.5 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 69
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 9
- Open Issues: 0
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
MDANCE (Molecular Dynamics Analysis with N-ary Clustering Ensembles) is a flexible n-ary clustering package that provides a set of tools for clustering Molecular Dynamics trajectories. The package is written in Python and an extension of the n-ary similarity framework. The package is designed to be modular and extensible, allowing for the addition of new clustering algorithms and similarity metrics.
Menu
Installation
bash
$ pip install mdance
To check for proper installation, run the following command:
```python
import mdance mdance.version ```
Background
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations are a powerful tool for studying the dynamics of biomolecules. However, the analysis of MD trajectories is challenging due to the large amount of data generated. Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning approach to group similar frames into clusters. The clustering results can be used to reveal the structure of the data, identify the most representative structures, and to study the dynamics of the system.
Clustering Algorithms
NANI
🪄NANI🪄the first installment of MDANCE
k-Means N-Ary Natural Initiation (NANI) is an algorithm for selecting initial centroids for k-Means clustering. NANI is an extension of the k-Means++ algorithm. NANI stratifies the data to high density region and perform diversity selection on top of the it to select the initial centroids. This is a deterministic algorithm that will always select the same initial centroids for the same dataset and improve on k-means++ by reducing the number of iterations required to converge and improve the clustering quality.
Example Usage:
```python
from mdance.cluster.nani import KmeansNANI data = np.load('data.npy') N = 4 mod = KmeansNANI(data, nclusters=N, metric='MSD', Natoms=1) initiators = mod.initiatekmeans() initiators = initiators[:N] kmeans = KMeans(N, init=initiators, ninit=1, randomstate=None) kmeans.fit(data) ``` <a target="blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/mqcomplab/MDANCE/blob/main/tutorials/MDANCE.ipynb">

A tutorial is available for NANI here.
For more information on the NANI algorithm, please refer to the NANI paper.
eQual
eQual is a O(N) clustering algorithm that use the radial threshold to grow the cluster to maximize similarity between members in a cluster. It is an extension of the Radial Threshold Clustering algorithm (Daura and Oscar Conchillo-Solé). eQual has improved with new seed selection methods and tie-breaking criteria.
A tutorial is available for eQual here.
For more information on the eQual algorithm, please refer to the eQual preprint.
SHINE

Pathway Analysis SHINE!
Sampling Hierarchical Intrinsic N-ary Ensembles (SHINE) is a hierarchical clustering tool for pathway analysis. This can be particularly useful if you want to identical the dominant pathway(s) of your enhanced sampling simulations.
A tutorial is available for SHINE here.
For more information on the SHINE algorithm, please refer to the SHINE preprint.
HELM
HELM is a hierarchical agglomerative clustering algorithm that uses the n-ary similarity to merge clusters at each level. It transformed from the traditional hierarchical clustering algorithm to be more efficient and scalable turning a $O(N^2)$ algorithm to $O(N)$. It specializes in recognizing dominant conformations within an ensemble and is often used alongside NANI to achieve a balance between efficiency and precision.
A tutorial is available for HELM here.
Clustering Postprocessing
PRIME

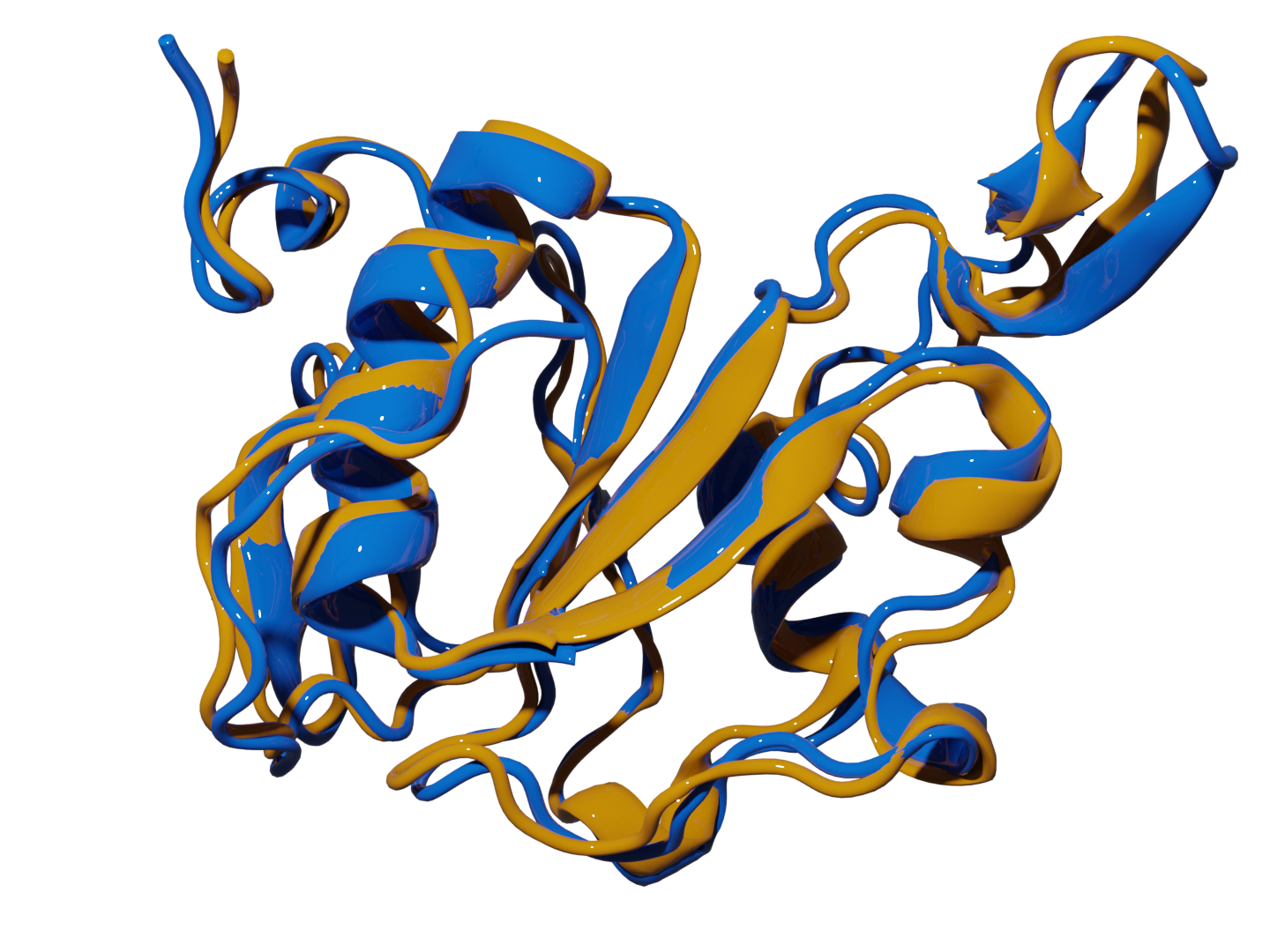
🪄 Predict Protein Structure with Precision 🪄
|
Protein Retrieval via Integrative Molecular Ensembles (PRIME) is a novel algorithm that predicts the native structure of a protein from simulation or clustering data. These methods perfectly mapped all the structural motifs in the studied systems and required unprecedented linear scaling. |
|
A tutorial is available for PRIME here.
For more information on the PRIME algorithm, please refer to the PRIME paper.
Notes
Research contained in this package was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under award number R35GM150620.
Collab or Contribute?! Please! Don't hesitate to reach out!
Owner
- Name: mqcomplab
- Login: mqcomplab
- Kind: organization
- Email: ramirandaq@gmail.com
- Location: United States of America
- Twitter: GroupQuintana
- Repositories: 1
- Profile: https://github.com/mqcomplab
MQ Lab software and projects
Citation (CITATION.bib)
@article{chen_k-means_2024,
title = {k-{Means} {NANI}: {An} {Improved} {Clustering} {Algorithm} for {Molecular} {Dynamics} {Simulations}},
issn = {1549-9618},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.4c00308},
doi = {10.1021/acs.jctc.4c00308},
journal = {Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation},
author = {Chen, Lexin and Roe, Daniel R. and Kochert, Matthew and Simmerling, Carlos and Miranda-Quintana, Ramón Alain},
month = jun,
year = {2024},
note = {Publisher: American Chemical Society},
}
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 4
- Watch event: 25
- Delete event: 1
- Issue comment event: 3
- Push event: 36
- Pull request event: 27
- Fork event: 5
- Create event: 5
Last Year
- Issues event: 4
- Watch event: 25
- Delete event: 1
- Issue comment event: 3
- Push event: 36
- Pull request event: 27
- Fork event: 5
- Create event: 5
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 3
- Total pull requests: 11
- Average time to close issues: 2 days
- Average time to close pull requests: about 8 hours
- Total issue authors: 3
- Total pull request authors: 4
- Average comments per issue: 0.67
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 9
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 3
- Pull requests: 11
- Average time to close issues: 2 days
- Average time to close pull requests: about 8 hours
- Issue authors: 3
- Pull request authors: 4
- Average comments per issue: 0.67
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 9
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- lexin-chen (2)
- nbruciaferri (1)
- KSUN63 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- lexin-chen (59)
- PhiMykah (2)
- bryllewoody (1)
- wilzzw (1)
- helmutcarter (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 242 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 18
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: mdance
a flexible n-ary clustering package for all applications.
- Homepage: https://github.com/mqcomplab/MDANCE
- Documentation: https://mdance.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
- License: MIT License
-
Latest release: 0.3.7
published 10 months ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- mdance >=0.2.8
- sphinx ==7.1.2
- sphinx-gallery ==0.16.0
- sphinx-rtd-theme ==1.3.0rc1
- MDAnalysis >= 2.0.0
- numpy >= 1.20.0
- scikit-learn >= 0.24.0
- shapeGMMTorch >= 1.0.0
- torch >= 2.2.2