dbscan
Theoretically Efficient and Practical Parallel DBSCAN
Science Score: 46.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
○.zenodo.json file
-
✓DOI references
Found 4 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: arxiv.org, acm.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
1 of 6 committers (16.7%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (16.1%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
Theoretically Efficient and Practical Parallel DBSCAN
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: wangyiqiu
- License: mit
- Language: C++
- Default Branch: master
- Homepage: https://sites.google.com/view/yiqiuwang/dbscan
- Size: 339 KB
Statistics
- Stars: 89
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 18
- Open Issues: 4
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
Theoretically-Efficient and Practical Parallel DBSCAN
Overview
This repository hosts fast parallel DBSCAN clustering code for low dimensional Euclidean space. The code automatically uses the available threads on a parallel shared-memory machine to speedup DBSCAN clustering. It stems from a paper presented in SIGMOD'20: Theoretically Efficient and Practical Parallel DBSCAN.
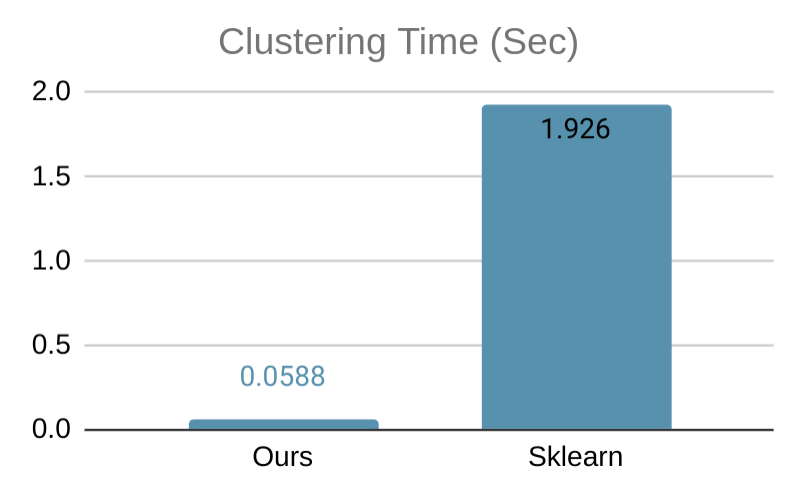
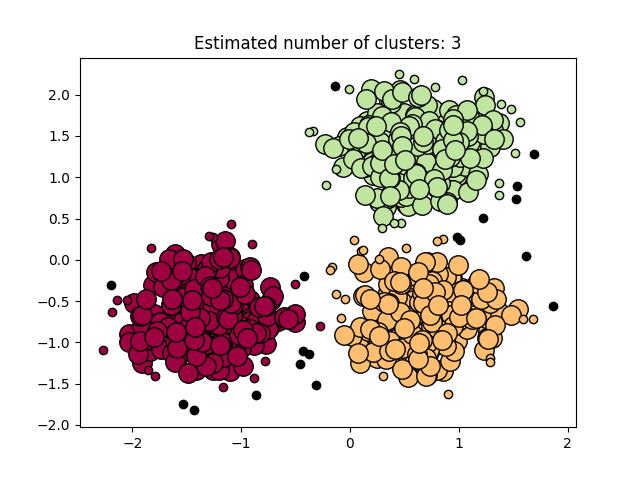
Our software on 1 thread is on par with all serial state-of-the-art DBSCAN packages, and provides additional speedup via multi-threading. Below, we show a simple benchmark comparing our code with the DBSCAN implementation of Sklearn, tested on a 6-core computer with 2-way hyperthreading using a 2-dimensional data set with 50000 data points, where both implementation uses all available threads. Our implementation is more than 32x faster. We also show a visualization of the clustering result on a smaller data set.
Data sets with dimensionality 2 - 20 are supported by default, which can be modified by modifying DBSCAN_MIN_DIMS and DBSCAN_MAX_DIMS in the source code.
Tutorial
Option 1: Use the Python binding
There are two ways to install it:
- Install it using PyPI:
pip3 install --user dbscan(you can find the wheels here). - To build from scratch for testing:
pip3 install -e .from the project root directory.
An example for using the Python module is provided in example.py. It generates the clustering example above.
Python API
from dbscan import DBSCAN
labels, core_samples_mask = DBSCAN(X, eps=0.3, min_samples=10)
Input
X: A 2-D Numpy array containing the input data points. The first dimension ofXis the number of data pointsn, and the second dimension is the data set dimensionality (the maximum supported dimensionality is 20).eps: The epsilon parameter (default 0.5).min_samples: The minPts parameter (default 5).
Output
labels: A lengthnNumpy array (dtype=np.int32) containing cluster IDs of the data points, in the same ordering as the input data. Noise points are given a pseudo-ID of-1.core_samples_mask: A lengthnNumpy array (dtype=np.bool) masking the core points, in the same ordering as the input data.
We provide a complete example below that generates a toy data set, computes the DBSCAN clustering, and visualizes the result as shown in the plot above.
``` import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
Generate sample data
centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]] X, labelstrue = makeblobs(nsamples=750, centers=centers, clusterstd=0.4, randomstate=0) X = StandardScaler().fittransform(X)
Compute DBSCAN
direct call of the C API:
from dbscan import DBSCAN labels, coresamplesmask = DBSCAN(X, eps=0.3, min_samples=10)
OR calling our sklearn API:
from dbscan import sklDBSCAN as DBSCAN
db = DBSCAN(eps=0.3, min_samples=10).fit(X)
coresamplesmask = np.zeroslike(db.labels, dtype=bool)
coresamplesmask[db.coresampleindices_] = True
labels = db.labels_
Plot result
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
nclusters = len(set(labels)) - (1 if -1 in labels else 0) nnoise = list(labels).count(-1)
Black removed and is used for noise instead.
uniquelabels = set(labels) colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(each) for each in np.linspace(0, 1, len(uniquelabels))] for k, col in zip(uniquelabels, colors): if k == -1: # Black used for noise. col = [0, 0, 0, 1] classmembermask = (labels == k) xy = X[classmembermask & coresamplesmask] plt.plot(xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1], 'o', markerfacecolor=tuple(col), markeredgecolor='k', markersize=14) xy = X[classmembermask & ~coresamplesmask] plt.plot(xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1], 'o', markerfacecolor=tuple(col), markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6) plt.title('Estimated number of clusters: %d' % nclusters_) plt.show() ```
Option 2: Use the binary executable
Compile and run the program:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
cd executable
make -j # this will take a while
./dbscan -eps 0.1 -minpts 10 -o clusters.txt <data-file>
The <data-file> can be any CSV-like point data file, where each line contains a data point -- see an example here. The data file can be either with or without header. The cluster output clusters.txt will contain a cluster ID on each line (other than the first-line header), giving a cluster assignment in the same ordering as the input file. A noise point will have a cluster ID of -1.
Option 3: Include directly in your own C++ program
Create your own caller header and source file by instantiating the DBSCAN template function in "dbscan/algo.h".
dbscan.h:
```c++
template
// equivalent to // int DBSCAN(intT n, floatT PF[n][dim], double epsilon, intT minPts, bool coreFlagOut[n], intT coreFlag[n], intT cluster[n]) // if C++ syntax was a little more flexible
template<> int DBSCAN<3>(int n, double* PF, double epsilon, int minPts, bool* coreFlagOut, int* coreFlag, int* cluster); ```
dbscan.cpp: ```c++
include "dbscan/algo.h"
include "dbscan.h"
```
Calling the instantiated function:
c++
int n = ...; // number of data points
double data[n][3] = ...; // data points
int labels[n]; // label ids get saved here
bool core_samples[n]; // a flag determining whether or not the sample is a core sample is saved here
{
int ignore[n];
DBSCAN<3>(n, (void*)data, 70, 100, core_samples, ignore, labels);
}
Doing this will only compile the function for the number of dimensions that you want, which saves on compilation time.
You can also include the "dbscan/capi.h" and define your own DBSCAN_MIN_DIMS and DBSCAN_MAX_DIMS macros the same way the Python extension uses it. The function exported has the following signature.
c++
extern "C" int DBSCAN(int dim, int n, double* PF, double epsilon, int minPts, bool* coreFlag, int* cluster);
Right now, the only two files that are guaranteed to remain in the C/C++ API are "dbscan/algo.h" and "dbscan/capi.h" and the functions named DBSCAN within.
Citation
If you use our work in a publication, we would appreciate citations:
@inproceedings{wang2020theoretically,
author = {Wang, Yiqiu and Gu, Yan and Shun, Julian},
title = {Theoretically-Efficient and Practical Parallel DBSCAN},
year = {2020},
isbn = {9781450367356},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3318464.3380582},
doi = {10.1145/3318464.3380582},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2020 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data},
pages = {2555–2571},
numpages = {17},
keywords = {parallel algorithms, spatial clustering, DBScan},
location = {Portland, OR, USA},
series = {SIGMOD ’20}
}
Owner
- Name: Yiqiu Wang
- Login: wangyiqiu
- Kind: user
- Company: MIT
- Website: https://sites.google.com/view/yiqiuwang
- Repositories: 2
- Profile: https://github.com/wangyiqiu
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 6
- Issues event: 6
- Watch event: 17
- Delete event: 6
- Member event: 1
- Issue comment event: 8
- Push event: 17
- Pull request event: 4
- Pull request review event: 5
- Pull request review comment event: 4
- Fork event: 2
Last Year
- Create event: 6
- Issues event: 6
- Watch event: 17
- Delete event: 6
- Member event: 1
- Issue comment event: 8
- Push event: 17
- Pull request event: 4
- Pull request review event: 5
- Pull request review comment event: 4
- Fork event: 2
Committers
Last synced: over 2 years ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Yiqiu Wang | y****g@i****m | 32 |
| Yiqiu Wang | y****k@g****m | 26 |
| anivegesana | a****a@g****m | 9 |
| Iurii Ivanov | i****i@p****o | 6 |
| anivegesana | a****a@b****m | 2 |
| Yiqiu Wang | y****w@m****u | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 17
- Total pull requests: 12
- Average time to close issues: 7 months
- Average time to close pull requests: 7 days
- Total issue authors: 15
- Total pull request authors: 4
- Average comments per issue: 3.24
- Average comments per pull request: 3.83
- Merged pull requests: 11
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 4
- Pull requests: 7
- Average time to close issues: 7 months
- Average time to close pull requests: 2 days
- Issue authors: 4
- Pull request authors: 2
- Average comments per issue: 0.25
- Average comments per pull request: 0.43
- Merged pull requests: 6
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- william-silversmith (2)
- amir-keramatian (2)
- chi2liu (1)
- sleeplessTLV (1)
- nikisalli (1)
- ShJacub (1)
- zp-yang (1)
- kevinjohncutler (1)
- adamwawrzynski (1)
- shteren1 (1)
- mcmingchang (1)
- sun11 (1)
- detrin (1)
- jacksongoode (1)
- mohammedsalah98 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- John-194 (5)
- anivegesana (4)
- skbill84 (2)
- iurii-provizio (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 11,944 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 1
- Total dependent repositories: 2
- Total versions: 9
- Total maintainers: 2
pypi.org: dbscan
Theoretically efficient and practical parallel DBSCAN
- Homepage: https://github.com/wangyiqiu/dbscan-python
- Documentation: https://dbscan.readthedocs.io/
- License: MIT
-
Latest release: 1.0.0
published 8 months ago
Rankings
Maintainers (2)
Dependencies
- numpy >=
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/download-artifact v3 composite
- actions/upload-artifact v3 composite
- docker/setup-qemu-action v2 composite
- pypa/cibuildwheel v2.11.2 composite
- pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish v1.5.0 composite
