planetMagFields
planetMagFields: A Python package for analyzing and plotting planetary magnetic field data - Published in JOSS (2024)
Science Score: 100.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
✓CITATION.cff file
Found CITATION.cff file -
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 12 DOI reference(s) in README and JOSS metadata -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: joss.theoj.org, zenodo.org -
✓Committers with academic emails
2 of 5 committers (40.0%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
✓JOSS paper metadata
Published in Journal of Open Source Software
Keywords
Scientific Fields
Repository
Routines to plot and analyze magnetic fields of planets in our solar system
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: AnkitBarik
- License: gpl-3.0
- Language: Python
- Default Branch: main
- Homepage: https://ankitbarik.github.io/planetMagFields/
- Size: 26.6 MB
Statistics
- Stars: 42
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 9
- Open Issues: 1
- Releases: 11
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
planetMagFields
Software to easily access and analyze information about magnetic fields of planets in our solar system and visualize them in both 2D and 3D.
Code contribution and reporting issues
Prerequisites
planetMagFields requires NumPy, Matplotlib and SciPy. Other than that, the following external libraries are used for a few different functions:
- 2D plotting for map projections other than Hammer : Cartopy library
- Potential extrapolation: SHTns library
- Writing vts files for 3D visualisation: PyEVTK library
Installation
planetMagFields can be installed in a few different ways:
Using pip
planetMagFields is available on PyPI and can be installed with
bash
$ python3 -m pip install planetMagFields
Using setup.py
You can also use setup.py to install planetMagFields:
```bash
$ git clone https://github.com/AnkitBarik/planetMagFields $ cd planetMagFields $ pytho3 setup.py install --user ```
Or using pip:
```bash
$ git clone https://github.com/AnkitBarik/planetMagFields $ cd planetMagFields $ python3 -m pip install . --user ```
Using PYTHONPATH
Download the package from the GitHub repository and add it
to PYTHONPATH:
```bash
$ git clone https://github.com/AnkitBarik/planetMagFields $ export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:/path/to/planetMagFields ```
Features and examples
The Planet class
This gives access to all the relevant properties of a planet and has methods to plot
the field and write a vts file for 3D visualization. Usage:
python
from planetmagfields import Planet
p = Planet(name='earth',datDir='planetmagfields/data/')
This displays the some information about the planet
bash
Planet: Earth
l_max = 13
Dipole tilt (degrees) = -9.410531
and gives access to variables associated with the planet such as:
p.lmax: maximum spherical harmonic degree till which data is availablep.glm,p.hlm: the Gauss coefficientsp.Br: computed radial magnetic field at surfacep.dipTheta: dipole tilt with respect to the rotation axisp.dipPhi: dipole longitude ( in case zero longitude is known, applicable to Earth )p.idx: indices to get values of Gauss coefficientsp.model: the magnetic field model used. Available models can be obtained using theget_modelsfunction. Selects the latest available model when unspecified.
Example using IPython:
```python In [1]: from planetmagfields import Planet
In [2]: p = Planet(name='jupiter',model='jrm09') Planet: Jupiter Model: jrm09 l_max = 10 Dipole tilt (degrees) = 10.307870
In [3]: p.glm[p.idx[2,0]] # g20 Out[3]: 11670.4
In [4]: p.hlm[p.idx[4,2]] # h42 Out[4]: 27811.2 ```
2D and 3D visualizations
planetMagFields can be used to produce both 2D and 3D visualizations of a planetary field.
While doing so, it also provides the option of potential extrapolation using the SHTns
library. Two examples are shown below: Earth's surface field and a 3D visualization of Jupiter's field using
Paraview. This is done by writing a .vts file using the PyEVTK
library.
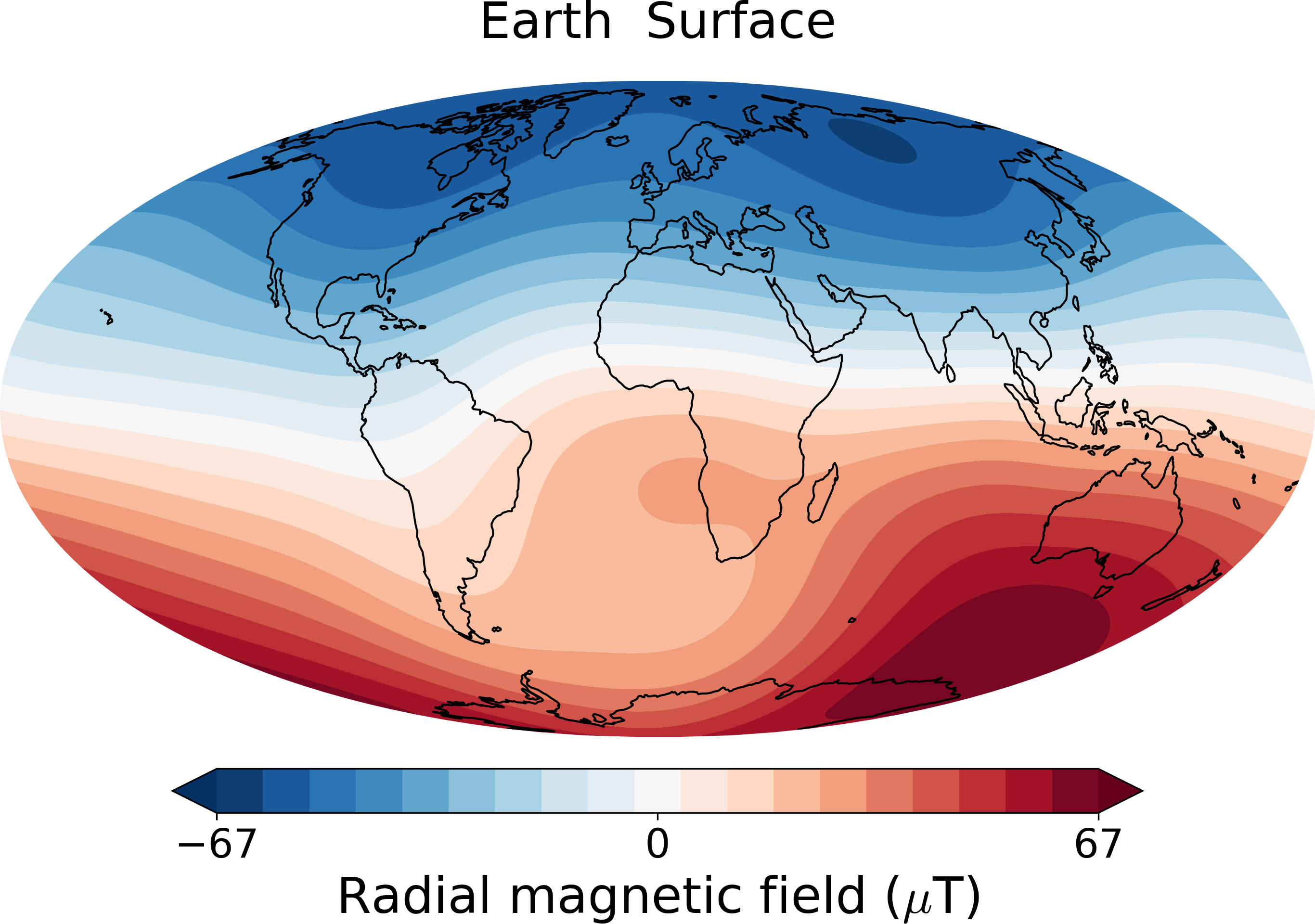
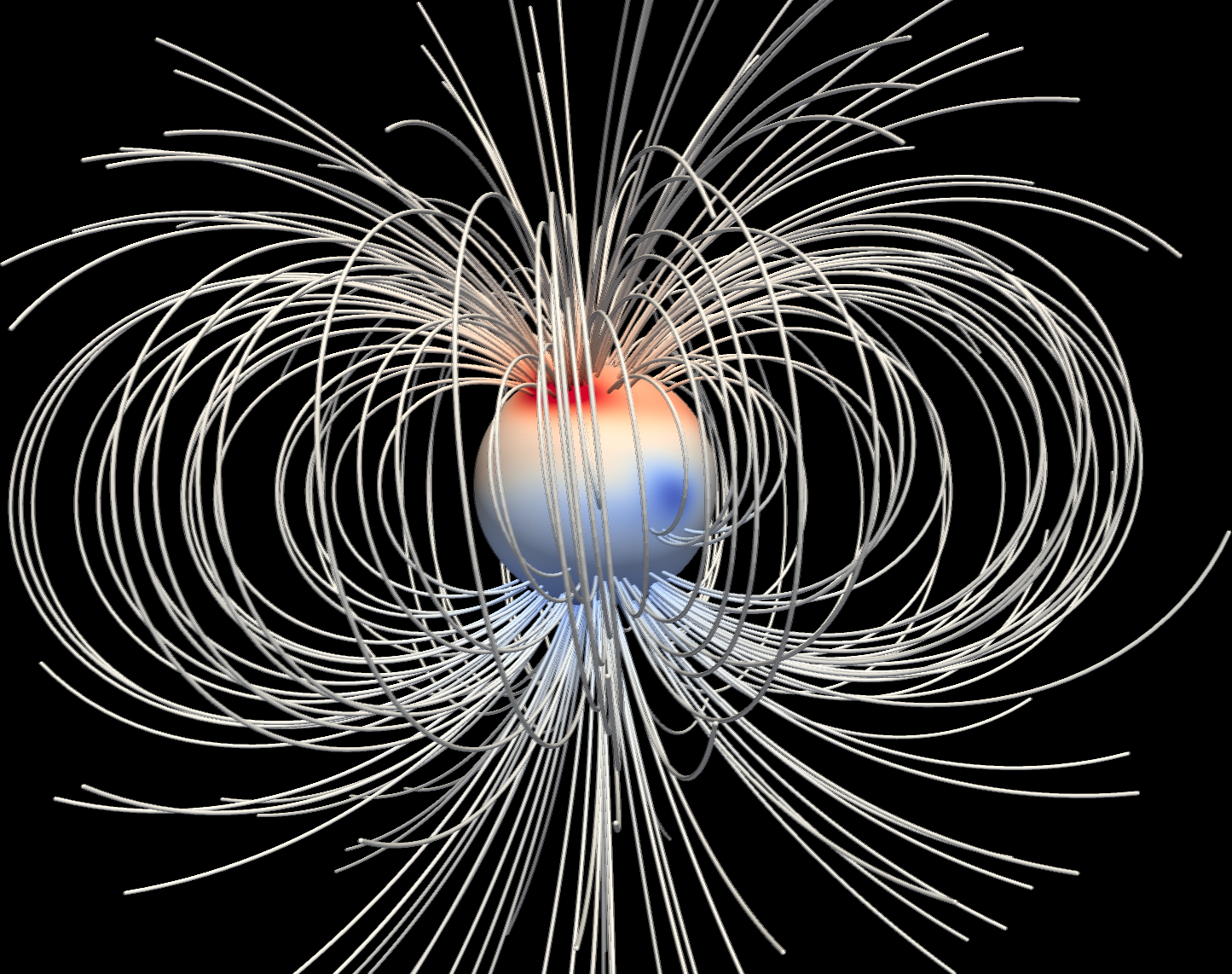
Jupyter notebook
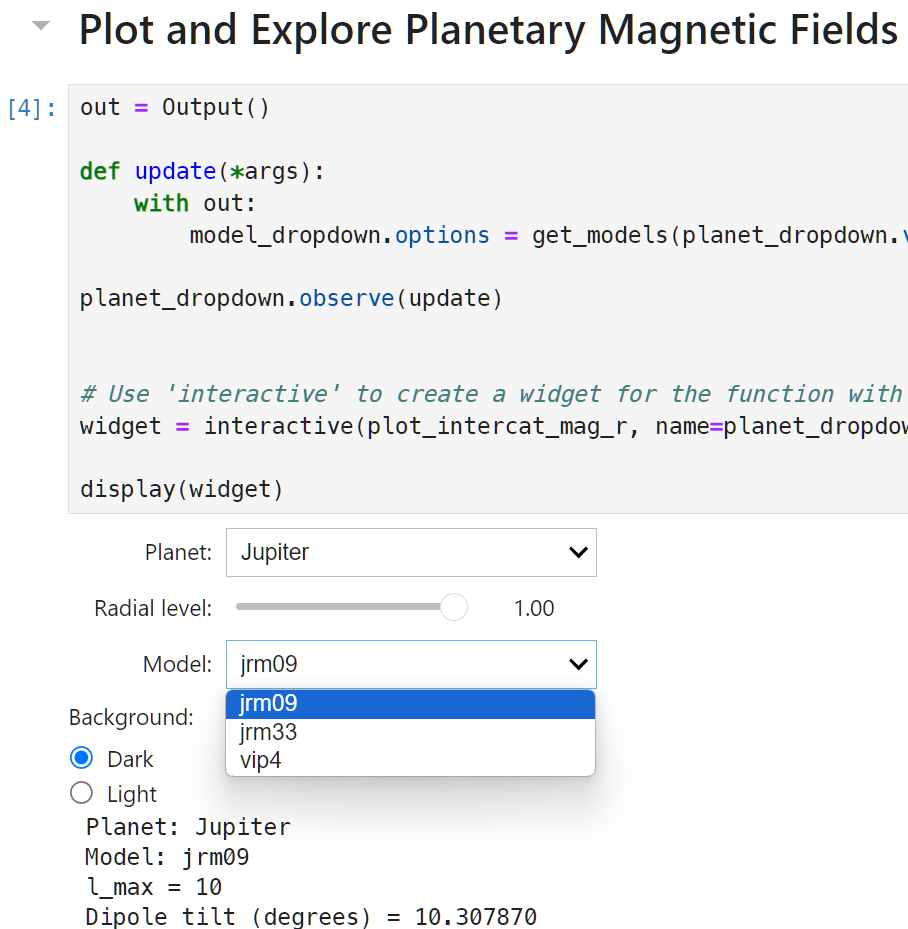
For quick and easy visualization we include a Jupyter notebook with a binder link (see badge at the top). This makes use of Jupyter widgets to provide dropdown lists of planets and available magnetic field models for each as well as a slider for radial level, as shown below
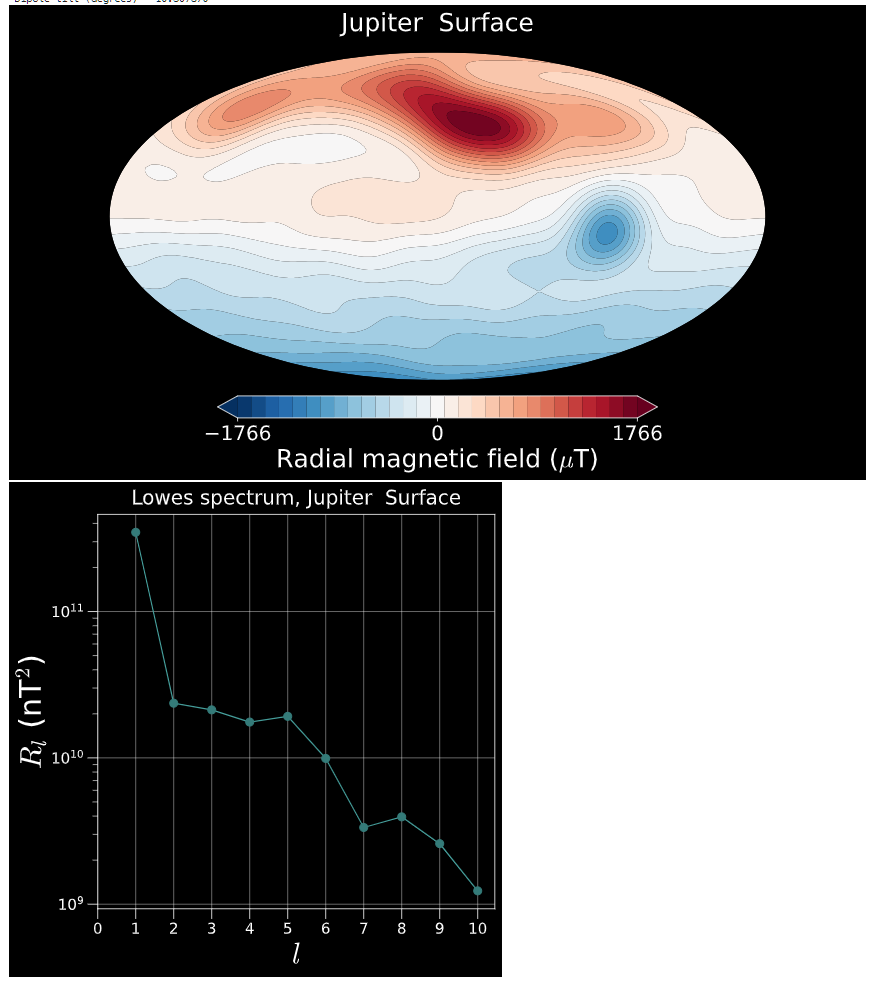
This plots the radial magnetic field at the chosen radial level and the corresponding magnetic field spectrum,
Documentation
Full list of features with examples as well as the magnetic field models used are described in detail in the documentation, available here: https://ankitbarik.github.io/planetMagFields/
Code contribution and reporting issues
planetMagFields is an open source project and anyone is welcome to contribute to it. If you wish to contribute to this project, please follow the guidelines below:
- Please make sure the tests pass before opening a pull request.
- Please follow Python PEP-8 guidelines when it comes to code style.
- If you wish to add new data file, please name it following the convention
<planet>_<model>.dat, whereplanetandmodeldenote the names of the planet and the magnetic field model being used. See thedatadirectory for examples. - If you implement a new feature or data source, please update the documentation accordingly.
Please report any bugs or other issues through GitHub Issues.
Citing planetMagFields
If you're using planetMagFields for your work, please cite the JOSS paper:
Barik et al., (2024). planetMagFields: A Python package for analyzing and plotting planetary magnetic field data. Journal of Open Source Software, 9(97), 6677, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.06677
bibtex
@article{Barik2024,
doi = {10.21105/joss.06677},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.06677},
year = {2024},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
volume = {9},
number = {97},
pages = {6677},
author = {Barik, Ankit and Angappan, Regupathi},
title = {planetMagFields: A Python package for analyzing and plotting planetary magnetic field data},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software}
}
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Regupathi Angappan for motivating me to create this package, testing it and for writing the Jupyter notebook. I thank Jon Aurnou for testing it out and pointing out runtime errors. I would like to thank Thomas Gastine for comparing the plots with real data and pointing out a normalization error which has been fixed. Thanks a lot to Arthus for adding the setup.py.
Owner
- Name: Ankit Barik
- Login: AnkitBarik
- Kind: user
- Location: Baltimore, USA
- Company: Johns Hopkins University
- Twitter: MHDwizard
- Repositories: 10
- Profile: https://github.com/AnkitBarik
JOSS Publication
planetMagFields: A Python package for analyzing and plotting planetary magnetic field data
Tags
planetary science magnetic fields visualizationCitation (CITATION.cff)
# This CITATION.cff file was generated with cffinit.
# Visit https://bit.ly/cffinit to generate yours today!
cff-version: 1.2.0
title: planetMagFields
message: >-
If you use this software, please cite it using the
metadata from this file.
type: software
authors:
- given-names: Ankit
family-names: Barik
email: ankit.barik@gmail.com
affiliation: Johns Hopkins University
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5747-669X'
- given-names: Regupathi
family-names: Angappan
email: rangapp1@jhu.edu
orcid: 'https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6258-0659'
affiliation: Johns Hopkins University
identifiers:
- type: doi
value: 10.21105/joss.06677
description: JOSS paper
repository-code: 'https://github.com/AnkitBarik/planetMagFields'
url: 'https://ankitbarik.github.io/planetMagFields/'
abstract: >-
planetMagFields is a package that provides an easy
interface to plot and analyze planetary magnetic field
data.
keywords:
- planetary science
- magnetic fields
- planetary data
license: GPL-3.0
preferred-citation:
type: article
authors:
- family-names: "Barik"
given-names: "Ankit"
orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5747-669X"
- family-names: "Angappan"
given-names: "Regupathi"
orcid: "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6258-0659"
doi: "10.21105/joss.06677"
journal: "Journal of Open Source Software"
start: 6677
end: 6677
title: "planetMagFields: A Python package for analyzing and plotting planetary magnetic field data"
volume: 9
year: 2024
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 3
- Issues event: 2
- Release event: 3
- Watch event: 5
- Issue comment event: 2
- Push event: 49
- Pull request event: 2
- Fork event: 4
Last Year
- Create event: 3
- Issues event: 2
- Release event: 3
- Watch event: 5
- Issue comment event: 2
- Push event: 49
- Pull request event: 2
- Fork event: 4
Committers
Last synced: 7 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| AnkitBarik | a****k@g****m | 249 |
| Arthus | a****s@g****e | 6 |
| reguang | r****1@j****u | 1 |
| Dan F-M | f****y@g****m | 1 |
| Nathanael Schaeffer | n****r@c****r | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 9
- Total pull requests: 7
- Average time to close issues: 3 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 1 day
- Total issue authors: 6
- Total pull request authors: 3
- Average comments per issue: 2.89
- Average comments per pull request: 0.14
- Merged pull requests: 5
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 1
- Pull requests: 4
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: about 8 hours
- Issue authors: 1
- Pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0.0
- Average comments per pull request: 0.25
- Merged pull requests: 2
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- athulpg007 (4)
- arthus701 (2)
- MissKLKnowles (1)
- AlainPlattner (1)
- Menamonmon (1)
- AnkitBarik (1)
Pull Request Authors
- nschaeff (4)
- arthus701 (2)
- dfm (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 51 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 14
- Total maintainers: 2
pypi.org: planetmagfields
Routines to easily access information about magnetic fields of planets in our solar system and visualize them in both 2D and 3D
- Homepage: https://ankitbarik.github.io/planetMagFields/
- Documentation: https://planetmagfields.readthedocs.io/
- License: GNU General Public License v3 or later (GPLv3+)
-
Latest release: 1.5.8
published 8 months ago
Rankings
Maintainers (2)
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/upload-artifact v1 composite
- openjournals/openjournals-draft-action master composite
- matplotlib >=3
- numpy >=1.18
- scipy >=1.5.4
- matplotlib *
- numpy *
- scipy *
- actions/checkout v3 composite
- actions/setup-python v3 composite
- peaceiris/actions-gh-pages v3 composite
- actions/checkout v2 composite

