https://github.com/sanity/pav.rs
An implementation of the Pair Adjacent Violators algorithm for isotonic regression in Rust
Science Score: 49.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
✓.zenodo.json file
Found .zenodo.json file -
✓DOI references
Found 1 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: wiley.com -
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (10.2%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
An implementation of the Pair Adjacent Violators algorithm for isotonic regression in Rust
Basic Info
- Host: GitHub
- Owner: sanity
- Language: Rust
- Default Branch: master
- Homepage: https://crates.io/crates/pav_regression
- Size: 99.6 KB
Statistics
- Stars: 10
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
Pair Adjacent Violators for Rust
Overview
An implementation of the Pair Adjacent Violators algorithm for isotonic regression. Note this algorithm is also known as "Pool Adjacent Violators".
What is "Isotonic Regression" and why should I care?
Imagine you have two variables, x and y, and you don't know the relationship between them, but you know that if x increases then y will increase, and if x decreases then y will decrease. Alternatively it may be the opposite, if x increases then y decreases, and if x decreases then y increases.
Examples of such isotonic or monotonic relationships include:
- x is the pressure applied to the accelerator in a car, y is the acceleration of the car (acceleration increases as more pressure is applied)
- x is the rate at which a web server is receiving HTTP requests, y is the CPU usage of the web server (server CPU usage will increase as the request rate increases)
- x is the price of an item, and y is the probability that someone will buy it (this would be a decreasing relationship, as x increases y decreases)
These are all examples of an isotonic relationship between two variables, where the relationship is likely to be more complex than linear.
So we know the relationship between x and y is isotonic, and let's also say that we've been able to collect data about actual x and y values that occur in practice.
What we'd really like to be able to do is estimate, for any given x, what y will be, or alternatively for any given y, what x would be required.
But of course real-world data is noisy, and is unlikely to be strictly isotonic, so we want something that allows us to feed in this raw noisy data, figure out the actual relationship between x and y, and then use this to allow us to predict y given x, or to predict what value of x will give us a particular value of y. This is the purpose of the pair-adjacent-violators algorithm.
...and why should I care?
Using the examples I provide above:
- A self-driving car could use it to learn how much pressure to apply to the accelerator to give a desired amount of acceleration
- An autoscaling system could use it to help predict how many web servers they need to handle a given amount of web traffic
- A retailer could use it to choose a price for an item that maximizes their profit (aka "yield optimization")
Isotonic regression in online advertising
If you have an hour to spare, and are interested in learning more about how online advertising works - you should check out this lecture that I gave in 2015 where I explain how we were able to use pair adjacent violators to solve some fun problems.
A picture is worth a thousand words
Here is the relationship that PAV extracts from some very noisy input data where there is an increasing relationship between x and y:
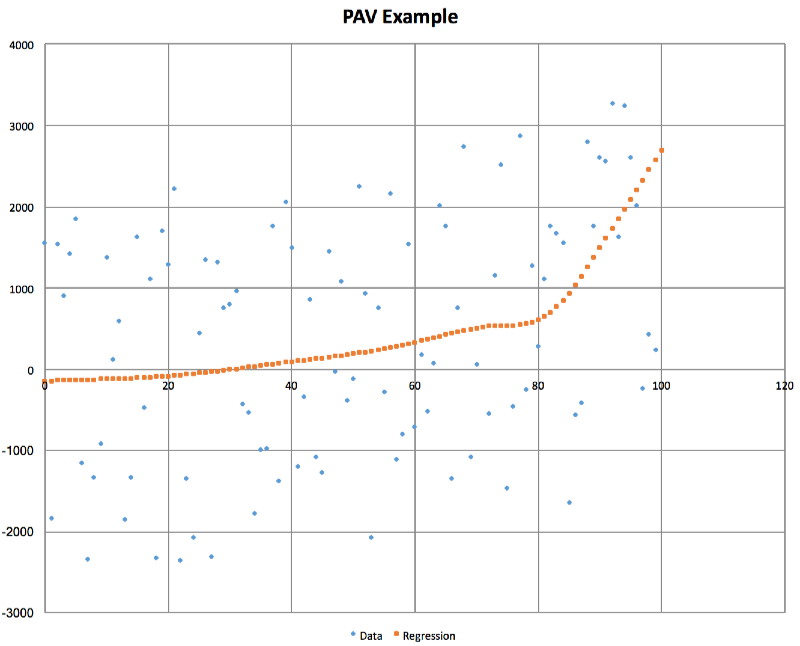
Features
- Smart linear interpolation between points and extrapolation outside the training data domain
- Fairly efficient implementation without compromizing code readability
- Will intelligently extrapolate to compute y for values of x greater or less than those used to build the PAV model
Usage example
```rust use pav_regression::pav::{IsotonicRegression, Point};
// ..
let points = &[
Point::new(0.0, 1.0),
Point::new(1.0, 2.0),
Point::new(2.0, 1.5),
];
let regression = IsotonicRegression::new_ascending(points);
assert_eq!(
regression.interpolate(1.5), 1.75
);
```
For more examples please see the unit tests.
License
Released under the LGPL version 3 by Ian Clarke.
See also
- An earlier implementation of PAV for Kotlin/JVM by the same author: https://github.com/sanity/pairAdjacentViolators
Owner
- Name: Ian Clarke
- Login: sanity
- Kind: user
- Location: Austin TX
- Company: @freenet
- Website: http://blog.locut.us/
- Twitter: sanity
- Repositories: 53
- Profile: https://github.com/sanity
Degree in CS & AI. Creator of freenet.org, kweb.io, 33mail.com.
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 1
- Watch event: 1
- Pull request event: 1
- Fork event: 1
Last Year
- Issues event: 1
- Watch event: 1
- Pull request event: 1
- Fork event: 1
Committers
Last synced: over 1 year ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Ian Clarke | g****b@i****m | 58 |
| Ian Clarke | i****e@g****m | 46 |
| Ian Clarke | s****y | 24 |
| Ian Clarke | i****n@l****s | 1 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 3
- Total pull requests: 1
- Average time to close issues: 10 months
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Total issue authors: 2
- Total pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0.67
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 0
- Pull requests: 1
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 0
- Pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- sanity (2)
- Puumanamana (1)
Pull Request Authors
- anchpop (1)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- cargo 35,551 total
- Total dependent packages: 1
- Total dependent repositories: 3
- Total versions: 26
- Total maintainers: 1
crates.io: pav_regression
The pair adjacent violators algorithm for isotonic regression
- Homepage: https://github.com/sanity/pav.rs
- Documentation: https://docs.rs/pav_regression/
- License: LGPL-3.0-or-later
-
Latest release: 0.5.2
published over 1 year ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- actions/checkout v2 composite
- rand 0.8.5 development
- ordered-float 3.6.0
- serde 1.0.159
- thiserror 1.0
