https://github.com/ermshaua/claspy
ClaSPy: A Python package for time series segmentation.
Science Score: 36.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
○.zenodo.json file
-
✓DOI references
Found 2 DOI reference(s) in README -
○Academic publication links
-
✓Committers with academic emails
1 of 2 committers (50.0%) from academic institutions -
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (12.7%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
ClaSPy: A Python package for time series segmentation.
Basic Info
Statistics
- Stars: 118
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 7
- Open Issues: 0
- Releases: 0
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
ClaSPy: A Python package for time series segmentation
Time series segmentation (TSS) tries to partition a time series (TS) into semantically meaningful segments. It's an important unsupervised learning task applied to large, real-world sensor signals for human inspection, change point detection or as preprocessing for classification and anomaly detection. This python library is the official implementation of the accurate and domain-agnostic TSS algorithm ClaSP.
Installation
You can install ClaSPy with PyPi:
python -m pip install claspy
Usage: univariate time series
Let's first import the ClaSP algorithm and univariate TS data from the "Time Series Segmentation Benchmark" (TSSB) to demonstrate its utility.
```python3
from claspy.segmentation import BinaryClaSPSegmentation from claspy.dataloader import loadtssb_dataset ```
As an example, we choose the Cricket data set that contains motions of different umpire signals captured as wrist acceleration. ClaSP should automatically detect semantic changes between signals and deduce their segmentation. It is parameter-free, so we just need to pass the time series as a numpy array.
```python3
dataset, windowsize, truecps, timeseries = loadtssbdataset(names=("CricketX",)).iloc[0,:] clasp = BinaryClaSPSegmentation() clasp.fitpredict(time_series) [ 712 1281 1933 2581] ```
ClaSP is fully interpretable to human inspection. It creates a score profile (between 0 and 1) that estimates the probability of a "change point" in a TS, where one segment transitions into another. We visualize the segmentation and compare it to the pre-defined human annotation.
python3
clasp.plot(gt_cps=true_cps, heading="Segmentation of different umpire cricket signals", ts_name="ACC", file_path="segmentation_example.png")
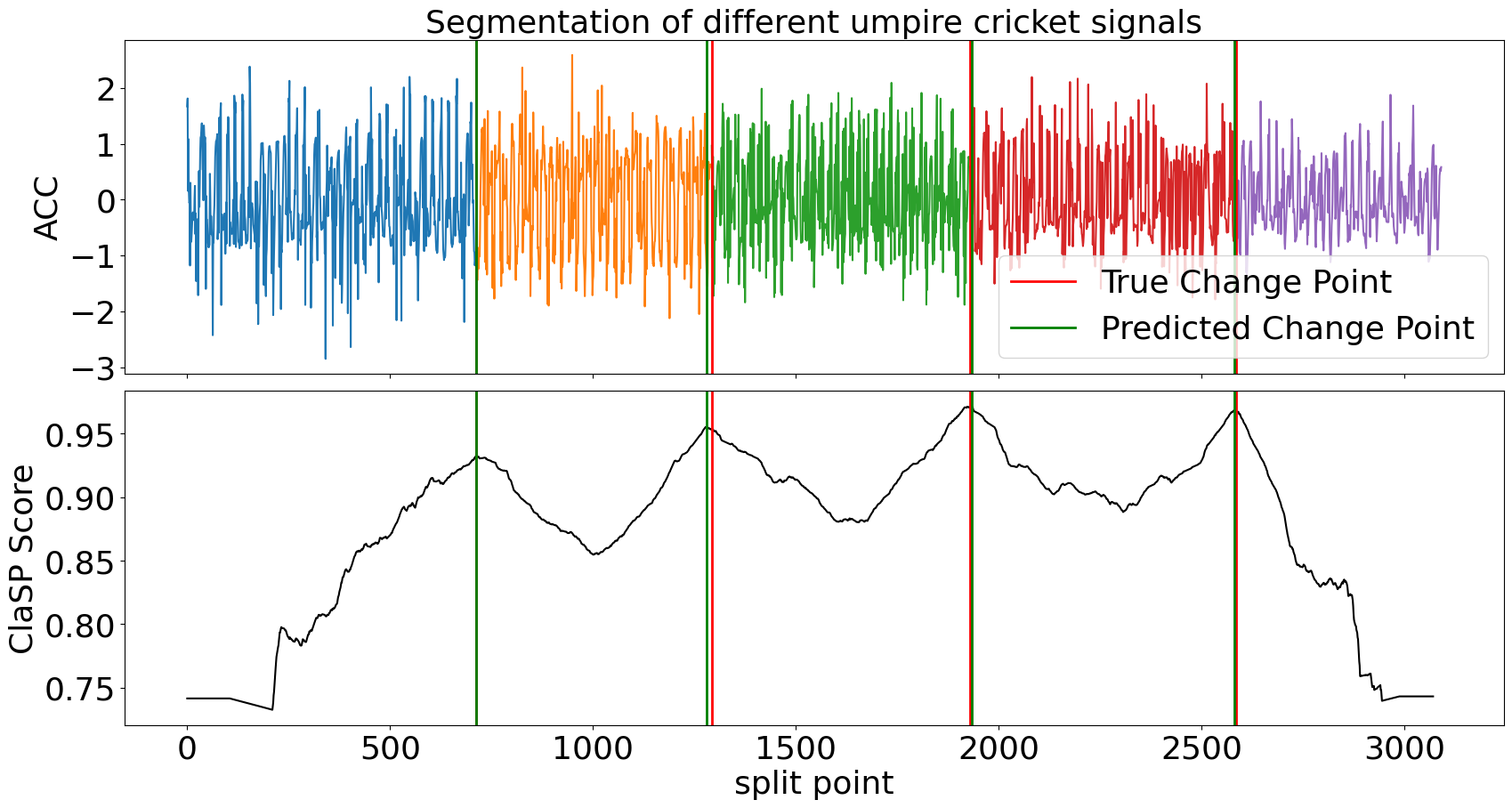
ClaSP accurately detects the number and location of changes in the motion sequence (compare green vs red lines) that infer its segmentation (the different-coloured subsequences). It is carefully designed to do this fully autonomously. However, if you have domain-specific knowledge, you can utilize it to guide and improve the segmentation. See its parameters for more information.
Usage: multivariate time series
Now, let's import multivariate TS data from the "Human Activity Segmentation Challenge" to show how ClaSP handles it.
```python3
from claspy.dataloader import loadhas_dataset ``` In this example, we use a motion routine from a student getting on, riding, and getting of a train. The multivariate TS consists of acceleration and magnetometer readings from a smartphone. We pass the time series as a 2-dimensional numpy array to ClaSP.
```python3
dataset, windowsize, truecps, labels, timeseries = loadhasdataset().iloc[107, :] clasp = BinaryClaSPSegmentation() clasp.fitpredict(time_series) [ 781 8212 9287 14468] ```
We visualize the segmentation and compare it to the ground truth annotation.
python3
clasp.plot(gt_cps=true_cps, heading=f"Segmentation of activity routine: {', '.join(labels)}", ts_name="ACC", font_size=18, file_path="multivariate_segmentation_example.png")
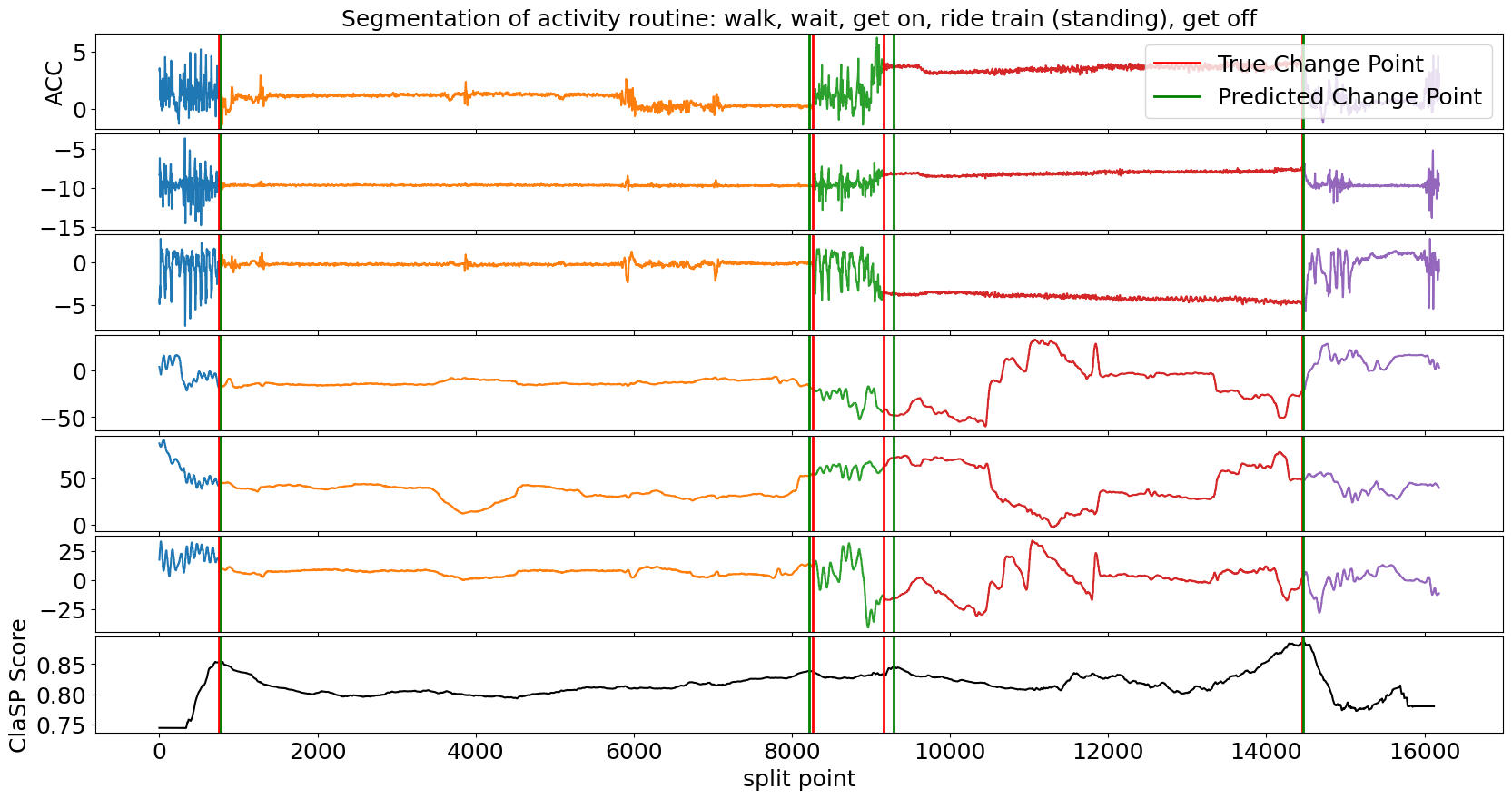
Also in the multivariate case, ClaSP correctly determines the number und location of activities in the routine. It is built to extract information from all TS channels to guide the segmentation. To ensure high performance, only provide necessary TS dimensions to ClaSP.
Usage: streaming time series
We also provide a streaming implementation of ClaSP that can segment ongoing time series streams or very large data archives in real-time (few thousand observations per second).
```python3
from claspy.streaming.segmentation import StreamingClaSPSegmentation ```
In our example, we simulate an ongoing ECG time series stream and use ClaSP to detect the transition between normal heartbeats and a myocardial infarction as soon as possible. We use a sliding window of 1k data points and update ClaSP with every data point.
```python3
dataset, windowsize, truecps, timeseries = loadtssbdataset(names=("ECG200",)).iloc[0, :] clasp = StreamingClaSPSegmentation(ntimepoints=1000)
for idx, value in enumerate(timeseries): clasp.update(value) if idx >= clasp.nwarmup and clasp.predict() != 0: break ```
For the first 1k data points, ClaSP "warms up", which means that it learns internal parameters from the data. Thereafter, we can query its predict method to find the last change point, e.g. to alert the user in real-time. In this example we wait for the first change point to occur and then inspect the sliding window.
python3
clasp.plot(heading="Detection of myocardial infarction in ECG stream", stream_name="ECG", file_path=f"streaming_segmentation_example.png")
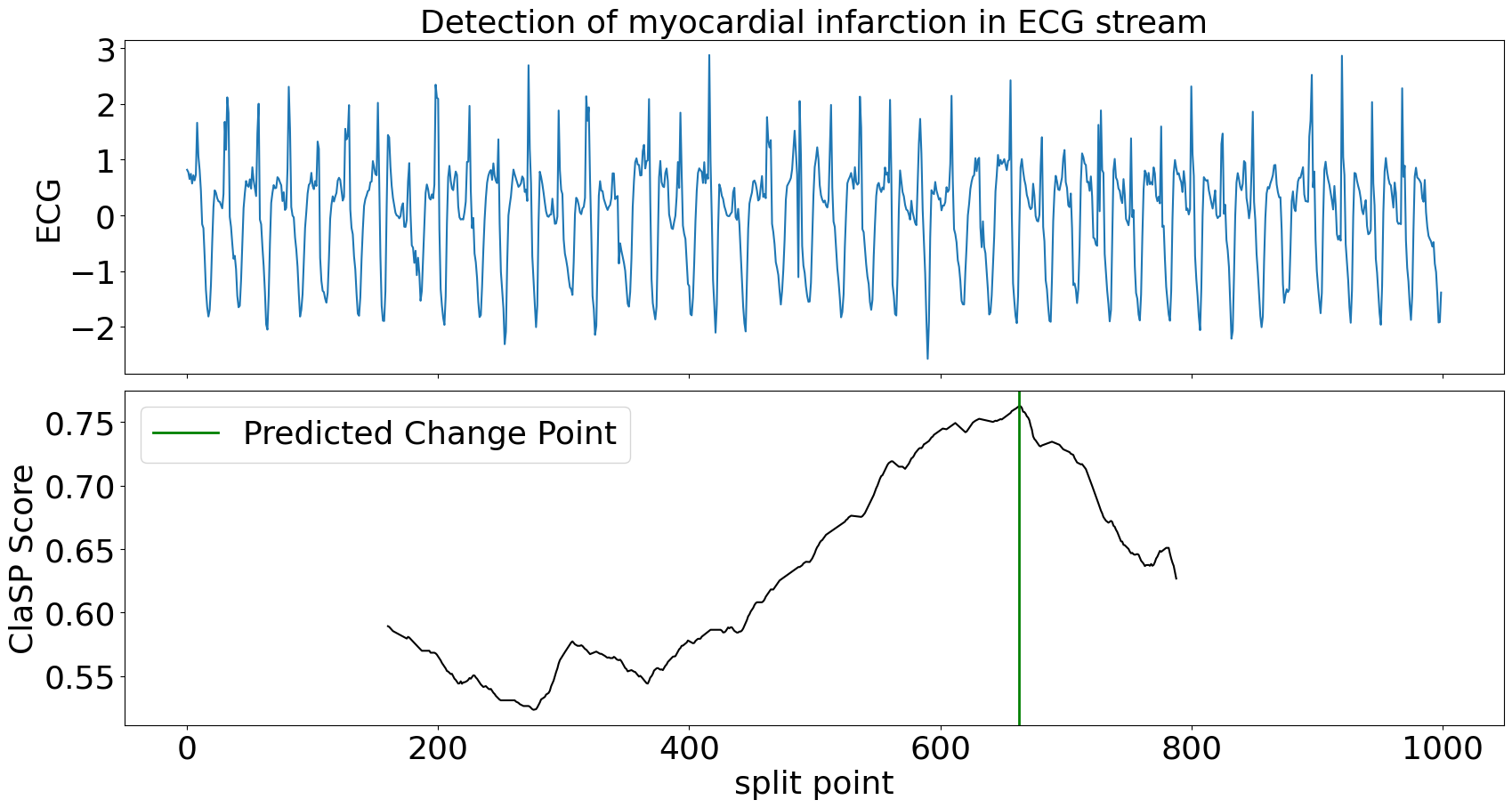
ClaSP needs circa 300 data points to accurately detect the change in heart beats. After the alert, it can be continued to be updated to detect more changes in the future. ClaSP is designed to automatically expel old data from its sliding window, efficiently use memory and run indefinitely. See this tutorial for more information.
Examples
Checkout the following Jupyter notebooks that show applications of the ClaSPy package:
- ClaSP evaluation on the "Time Series Segmentation Benchmark" (TSSB)
- ClaSP results for the "Human Activity Segmentation Challenge"
- Hyper-parameter Tuning and Configuration of ClaSP
- Window Size Selection for Unsupervised Time Series Analytics
- Segmentation of Streaming Time Series and Large Data Archives
Citation
The ClaSPy package is actively maintained, updated and intended for application. If you use ClaSP in your scientific publication, we would appreciate the following citation:
@article{clasp2023,
title={ClaSP: parameter-free time series segmentation},
author={Arik Ermshaus and Patrick Sch{\"a}fer and Ulf Leser},
journal={Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery},
year={2023},
}
Todos
Here are some of the things we would like to add to ClaSPy in the future:
- Future research related to ClaSP
- Example and application Jupyter notebooks
- More documentation and tests
If you want to contribute, report bugs, or need help applying ClaSP for your application, feel free to reach out.
Owner
- Name: Arik Ermshaus
- Login: ermshaua
- Kind: user
- Location: Berlin, Germany
- Company: Humboldt University
- Twitter: ermshaua
- Repositories: 3
- Profile: https://github.com/ermshaua
PhD student at WBI, Humboldt University, Berlin. Interested in time series analytics, big data processing and machine learning.
GitHub Events
Total
- Create event: 1
- Release event: 1
- Issues event: 13
- Watch event: 44
- Issue comment event: 17
- Push event: 8
- Fork event: 2
Last Year
- Create event: 1
- Release event: 1
- Issues event: 13
- Watch event: 44
- Issue comment event: 17
- Push event: 8
- Fork event: 2
Committers
Last synced: about 2 years ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Arik Ermshaus | e****a@i****e | 32 |
| Arik Ermshaus | a****s@g****m | 3 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 18
- Total pull requests: 1
- Average time to close issues: 28 days
- Average time to close pull requests: 1 minute
- Total issue authors: 15
- Total pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 2.44
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 8
- Pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: 7 days
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 6
- Pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 1.88
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- sssaha (2)
- DanielaFe7-personal (2)
- agardiman (2)
- mheskett (1)
- jfcann (1)
- lucamcwood (1)
- jixuan1989 (1)
- aceg00 (1)
- voloddia (1)
- kageazusa (1)
- Andreasbirch (1)
- brandon-hastings (1)
- kikatuso (1)
- weihuang-cs (1)
Pull Request Authors
- tmb2k01 (2)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 269 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 1
- Total dependent repositories: 1
- Total versions: 18
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: claspy
- Homepage: https://github.com/ermshaua/claspy
- Documentation: https://claspy.readthedocs.io/
- License: BSD 3-Clause License Copyright (c) 2023, Arik Ermshaus Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. 3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission. THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
-
Latest release: 0.2.7
published 7 months ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- matplotlib >=3.3
- numba >=0.53
- numpy >=1.21.0,<1.25
- pandas >=1.1.0,<1.6.0
- scikit-learn >=0.24.0,<1.3.0
- scipy <2.0.0,>=1.2.0
- statsmodels >=0.13.5
- daproli >=0.22
- matplotlib >=3.3
- numba >=0.53
- numpy >=1.21.0,<1.25
- pandas >=1.1.0,<1.6.0
- scikit-learn >=0.24.0,<1.3.0
- scipy <2.0.0,>=1.2.0
- setuptools >=65.6.3
- statsmodels >=0.13.5
- toml >=0.10.2
- tomli >=2.0.1