https://github.com/cerlymarco/tspiral
A python package for time series forecasting with scikit-learn estimators.
Science Score: 13.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
✓codemeta.json file
Found codemeta.json file -
○.zenodo.json file
-
○DOI references
-
○Academic publication links
-
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (10.7%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
A python package for time series forecasting with scikit-learn estimators.
Basic Info
Statistics
- Stars: 161
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 19
- Open Issues: 0
- Releases: 2
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
tspiral
A python package for time series forecasting with scikit-learn estimators.
tspiral is not a library that works as a wrapper for other tools and methods for time series forecasting. tspiral directly provides scikit-learn estimators for time series forecasting. It leverages the benefit of using scikit-learn syntax and components to easily access the open source ecosystem built on top of the scikit-learn community. It easily maps a complex time series forecasting problems into a tabular supervised regression task, solving it with a standard approach.
Overview
tspiral provides 4 optimized forecasting techniques:
- Recursive Forecasting
Lagged target features are combined with exogenous regressors (if provided) and lagged exogenous features (if specified). A scikit-learn compatible regressor is fitted on the whole merged data. The fitted estimator is called iteratively to predict multiple steps ahead.
Which in a compact way we can summarize in:
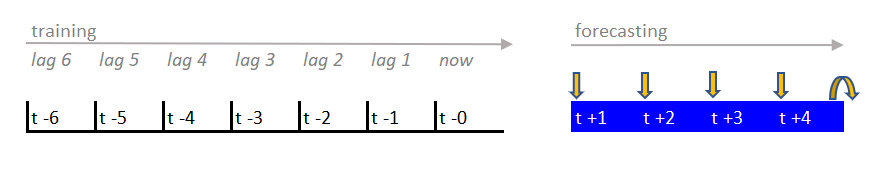
- Direct Forecasting
A scikit-learn compatible regressor is fitted on the lagged data for each time step to forecast.
Which in a compact way we can summarize in:
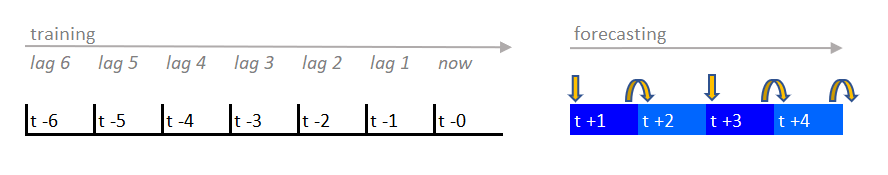
It's also possible to mix recursive and direct forecasting by predicting directly some future horizons while using recursive on the remaining.
- Stacking Forecasting
Multiple recursive time series forecasters are fitted and combined on the final portion of the training data with a meta-learner.
- Rectified Forecasting
Multiple direct time series forecasters are fitted and combined on the final portion of the training data with a meta-learner.
GLOBAL and MULTIVARIATE time series forecasting are natively supported for all the forecasting methods available. For GLOBAL forecasting, use the groups parameter to specify the column of the input data that contains the group identifiers. For MULTIVARIATE forecasting, pass a target with multiple columns when calling fit.
Installation
shell
pip install --upgrade tspiral
The module depends only on NumPy, Pandas, and Scikit-Learn (>=0.24.2). Python 3.6 or above is supported.
Media
- How to Improve Recursive Time Series Forecasting
- Time Series Forecasting with Feature Selection: Why you may need it
- Forecast Time Series with Missing Values: Beyond Linear Interpolation
- Time Series Forecasting with Conformal Prediction Intervals: Scikit-Learn is All you Need
- Hitting Time Forecasting: The Other Way for Time Series Probabilistic Forecasting
- Hitchhiker’s Guide to MLOps for Time Series Forecasting with Sklearn
Usage
Recursive Forecasting
python import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge from tspiral.forecasting import ForecastingCascade timesteps = 400 e = np.random.normal(0,1, (timesteps,)) y = np.concatenate([ 2*np.sin(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, 2*np.cos(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, ]) X = [[0]]*timesteps+[[1]]*timesteps model = ForecastingCascade( Ridge(), lags=range(1,24+1), groups=[0], ).fit(X, y) forecasts = model.predict([[0]]*80+[[1]]*80)Direct Forecasting
python import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge from tspiral.forecasting import ForecastingChain timesteps = 400 e = np.random.normal(0,1, (timesteps,)) y = np.concatenate([ 2*np.sin(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, 2*np.cos(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, ]) X = [[0]]*timesteps+[[1]]*timesteps model = ForecastingChain( Ridge(), n_estimators=24, lags=range(1,24+1), groups=[0], ).fit(X, y) forecasts = model.predict([[0]]*80+[[1]]*80)Stacking Forecasting
python import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor from tspiral.forecasting import ForecastingStacked timesteps = 400 e = np.random.normal(0,1, (timesteps,)) y = np.concatenate([ 2*np.sin(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, 2*np.cos(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, ]) X = [[0]]*timesteps+[[1]]*timesteps model = ForecastingStacked( [Ridge(), DecisionTreeRegressor()], test_size=24*3, lags=range(1,24+1), groups=[0], ).fit(X, y) forecasts = model.predict([[0]]*80+[[1]]*80)Rectified Forecasting
python import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor from tspiral.forecasting import ForecastingRectified timesteps = 400 e = np.random.normal(0,1, (timesteps,)) y = np.concatenate([ 2*np.sin(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, 2*np.cos(np.arange(timesteps)*(2*np.pi/24))+e, ]) X = [[0]]*timesteps+[[1]]*timesteps model = ForecastingRectified( [Ridge(), DecisionTreeRegressor()], n_estimators=24*3, test_size=24*3, lags=range(1,24+1), groups=[0], ).fit(X, y) forecasts = model.predict([[0]]*80+[[1]]*80)
More examples in the notebooks folder.
Owner
- Name: Marco Cerliani
- Login: cerlymarco
- Kind: user
- Location: Milan, Italy
- Website: https://www.linkedin.com/in/marco-cerliani-b0bba714b/
- Repositories: 6
- Profile: https://github.com/cerlymarco
Statistician Hacker & Data Scientist
GitHub Events
Total
- Watch event: 1
Last Year
- Watch event: 1
Committers
Last synced: 9 months ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| cerlymarco | 3****o | 20 |
| marco.cerliani | m****i@a****u | 3 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 9 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 3
- Total pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: about 2 months
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Total issue authors: 3
- Total pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 1.0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 0
- Pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 0
- Pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- Sandy4321 (1)
- jorisparet (1)
- liuwenfeng93 (1)
Pull Request Authors
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- pypi 45 last-month
- Total dependent packages: 1
- Total dependent repositories: 1
- Total versions: 8
- Total maintainers: 1
pypi.org: tspiral
A python package for time series forecasting with scikit-learn estimators.
- Homepage: https://github.com/cerlymarco/tspiral
- Documentation: https://tspiral.readthedocs.io/
- License: MIT
-
Latest release: 0.3.0
published about 2 years ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- numpy *
- scikit-learn >=0.24.2
- scipy *