icellr
Single (i) Cell R package (iCellR) is an interactive R package to work with high-throughput single cell sequencing technologies (i.e scRNA-seq, scVDJ-seq, scATAC-seq, CITE-Seq and Spatial Transcriptomics (ST)).
Science Score: 23.0%
This score indicates how likely this project is to be science-related based on various indicators:
-
○CITATION.cff file
-
○codemeta.json file
-
○.zenodo.json file
-
✓DOI references
Found 4 DOI reference(s) in README -
✓Academic publication links
Links to: biorxiv.org, scholar.google, pubmed.ncbi, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, nature.com -
○Committers with academic emails
-
○Institutional organization owner
-
○JOSS paper metadata
-
○Scientific vocabulary similarity
Low similarity (9.9%) to scientific vocabulary
Keywords
Repository
Single (i) Cell R package (iCellR) is an interactive R package to work with high-throughput single cell sequencing technologies (i.e scRNA-seq, scVDJ-seq, scATAC-seq, CITE-Seq and Spatial Transcriptomics (ST)).
Statistics
- Stars: 122
- Watchers: 12
- Forks: 19
- Open Issues: 13
- Releases: 10
Topics
Metadata Files
README.md
iCellR
iCellR is an interactive R package to work with high-throughput single cell sequencing technologies (i.e scRNA-seq, scVDJ-seq, scATAC-seq, CITE-Seq and Spatial Transcriptomics (ST)).
Maintainer: Alireza Khodadadi-Jamayran
News (April 2021): Use iCellR version 1.6.4 for scATAC-seq and Spatial Transcriptomics (ST). Use the i.score function for scoring (scoring cells based on gene signatures) methods (i.e. tirosh, mean, sum, gsva, ssgsea, zscore and plage).
News (July 2020): See iCellR version 1.5.5 with new cell cycle analysis for G0, G1S, G2M, M, G1M and S phase, Pseudotime Abstract KNetL map (PAK map) and gene-gene correlations. See below for how to.
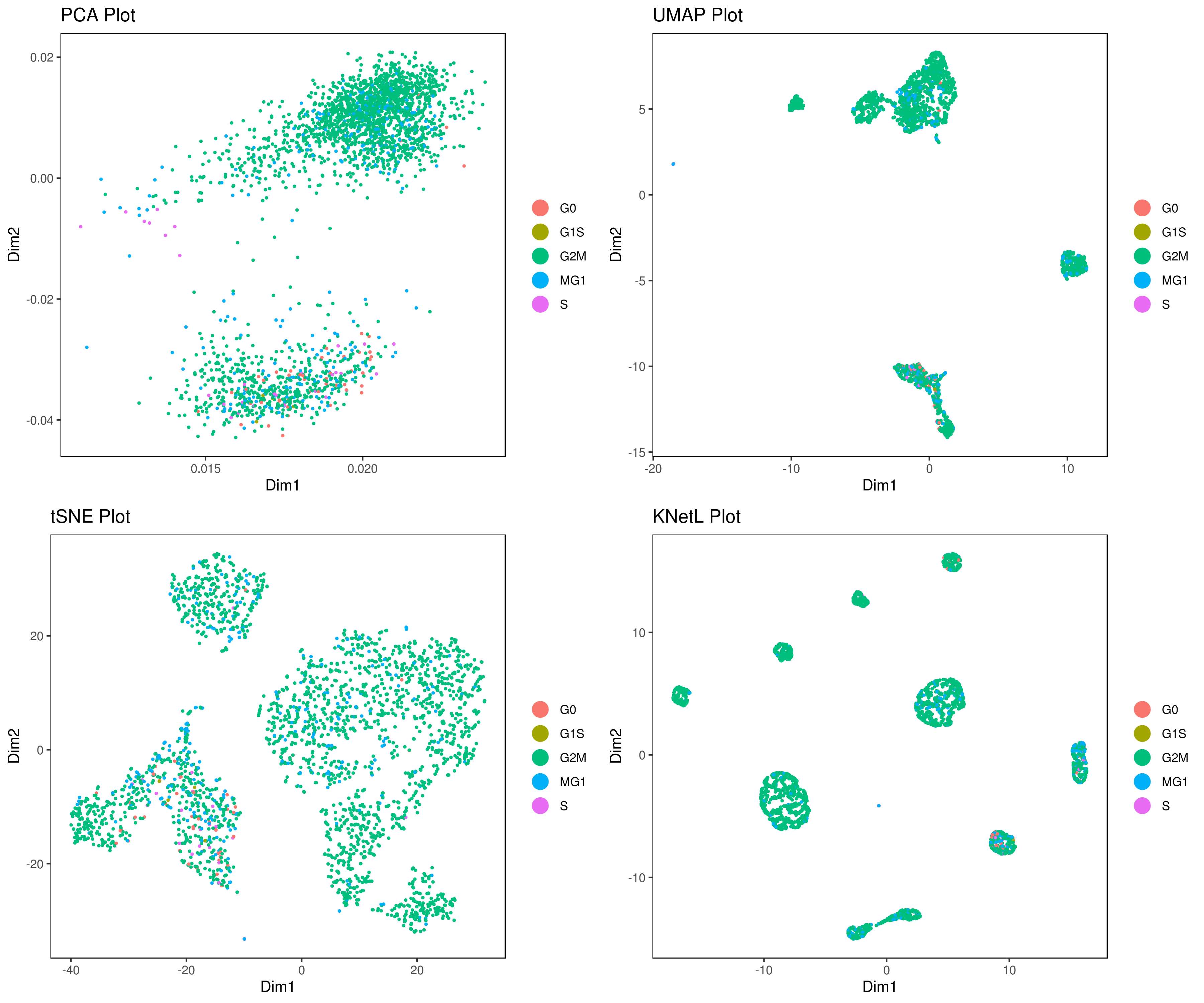
News (May 2020): see our dimensionality reduction called KNetL map  (pronounced like "nettle"). KNetL map is capable of zooming and shows a lot more details compared to tSNE and UMAP.
(pronounced like "nettle"). KNetL map is capable of zooming and shows a lot more details compared to tSNE and UMAP.
News (April 2020): see our imputation/coverage correction (CC) and batch alignment (CCCA and CPCA) methods. More databases added for cell type prediction (ImmGen and MCA).
- Tutorial: example 1 code and results (based on KNetL map
 )
) - Tutorial: example 2 code and results (based on CPCA batch alignment and KNetL map
 )
) - Link to a video tutorial for CITE-Seq and scRNA-Seq analysis: Video
- All you need to know about KNetL map: Video
- Link to manual Manual and Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN).
iCellR Viewer (web GUI app): https://compbio.nyumc.org/icellr/
If you are using FlowJo or SeqGeq, they have made plugins for iCellR and other single cell tools: https://www.flowjo.com/exchange/#/ (list of all plugins) and https://www.flowjo.com/exchange/#/plugin/profile?id=34 (iCellR plugin). SeqGeq DE tutorial
For citing iCellR use this PMID: 34353854
iCellR publications: PMID: 35660135 (scRNA-seq/KNetL) PMID: 35180378 (CITE-seq/KNetL), PMID: 34911733 (i.score and cell ranking), PMID: 34963055 (scRNA-seq), PMID 31744829 (scRNA-seq), PMID: 31934613 (bulk RNA-seq from TCGA), PMID: 32550269 (scVDJ-seq), PMID: 34135081, PMID: 33593073, PMID: 34634466, PMID: 35302059, PMID: 34353854
Single (i) Cell R package (iCellR)






How to install iCellR
```r
Install from CRAN
install.packages("iCellR")
Install from github
library(devtools)
install_github("rezakj/iCellR")
or
git clone https://github.com/rezakj/iCellR.git
R
install.packages('iCellR/', repos = NULL, type="source")
```
Download a sample data
- Download and unzip a publicly available sample PBMC scRNA-Seq data.
```r
set your working directory
setwd("/your/download/directory")
save the URL as an object
sample.file.url = "https://cf.10xgenomics.com/samples/cell/pbmc3k/pbmc3kfilteredgenebcmatrices.tar.gz"
download the file
download.file(url = sample.file.url, destfile = "pbmc3kfilteredgenebcmatrices.tar.gz", method = "auto")
unzip the file.
untar("pbmc3kfilteredgenebcmatrices.tar.gz") ``` more data available here: https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/
How to use iCellR for analyzing scRNA-seq data

To run a test sample follow these steps:
- Go to the R environment load the iCellR package and the PBMC sample data that you downloaded.
```r library("iCellR") my.data <- load10x("filteredgenebc_matrices/hg19/")
This directory includes; barcodes.tsv, genes.tsv/features.tsv and matrix.mtx files
Data could be zipped or unzipped.
if your data is in a csv or tsv format read it like this example
my.data <- read.delim("CITE-SeqsampleRNA.tsv.gz",header=TRUE)
if your data is in a h5 format read it like this example
library(hdf5r)
data <- load.h5("filteredfeaturebc_matrix.h5")
```
To see the help page for each function use question mark as:
r
?load10x
- Aggregate data
Conditions in iCellR are set or shown in the column names of the data and are separated by an underscore "_" sign. Let's say you want to merge multiple datasets (data frames/matrices) into one file and run iCellR in aggregate mode (all samples together). You can do so using "data.aggregation" function. Here’s an example: I divided this sample into four datasets and then aggregated them into one matrix. Here we are assuming you have four samples (e.g. WT,KO,Ctrl,KD). In this way, iCellR will know you have 4 samples for the rest of the analysis (e.g. batch alignment, plots, DE, etc.).
```r dim(my.data)
[1] 32738 2700
divide your sample into three samples for this example
sample1 <- my.data[1:900] sample2 <- my.data[901:1800] sample3 <- my.data[1801:2300] sample4 <- my.data[2301:2700]
merge all of your samples to make a single aggregated file.
my.data <- data.aggregation(samples = c("sample1","sample2","sample3","sample4"), condition.names = c("WT","KO","Ctrl","KD")) ```
- Check the head of your file.
```r
here is how the head of the first 2 cells in the aggregated file looks like.
head(my.data)[1:2]
WTAAACATACAACCAC-1 WTAAACATTGAGCTAC-1
A1BG 0 0
A1BG.AS1 0 0
A1CF 0 0
A2M 0 0
A2M.AS1 0 0
as you see the header has the conditions now
```
- Make an object of class iCellR.
```r my.obj <- make.obj(my.data) my.obj
,--. ,-----. ,--.,--.,------.
--'' .--./ ,---. | || || .--. '
,--.| | | .-. :| || || '--'.'
| |' '--'\ --. | || || |
--' -----'----'--'--'`--' '--'
An object of class iCellR version: 1.6.0 Raw/original data dimentions (rows,columns): 32738,2700 Data conditions in raw data: Ctrl,KD,KO,WT (500,400,900,900) Row names: A1BG,A1BG.AS1,A1CF ... Columns names: WTAAACATACAACCAC.1,WTAAACATTGAGCTAC.1,WT_AAACATTGATCAGC.1 ...
QC stats performed:FALSE, PCA performed:FALSE Clustering performed:FALSE, Number of clusters:0 tSNE performed:FALSE, UMAP performed:FALSE, DiffMap performed:FALSE Main data dimensions (rows,columns): 0,0 Normalization factors:,... Imputed data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0
######## scVDJ-seq
VDJ data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## CITE-seq
ADT raw data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT main data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT columns names:... ADT row names:...
######## scATAC-seq
ATAC raw data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ATAC main data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ATAC columns names:... ATAC row names:...
######## Spatial
Spatial data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
##### iCellR object
```
- Perform some QC
r
my.obj <- qc.stats(my.obj)
- Plot QC
By default all the plotting functions would create interactive html files unless you set this parameter: interactive = FALSE.
```r
plot UMIs, genes and percent mito all at once and in one plot.
you can make them individually as well, see the arguments ?stats.plot.
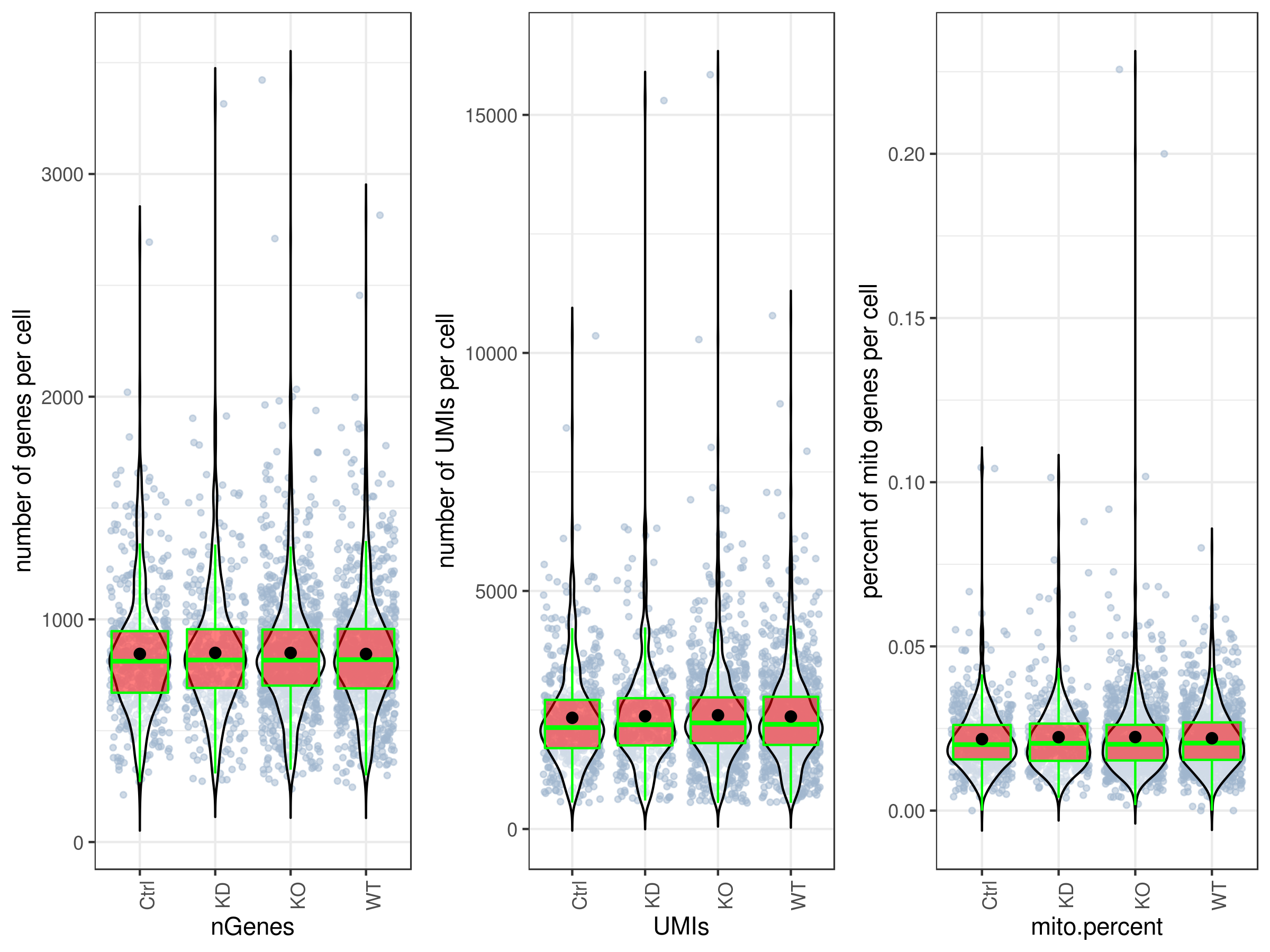
stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "three.in.one", out.name = "UMI-plot", interactive = FALSE, cell.color = "slategray3", cell.size = 1, cell.transparency = 0.5, box.color = "red", box.line.col = "green") ```
```r
Scatter plots
stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "point.mito.umi", out.name = "mito-umi-plot") stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "point.gene.umi", out.name = "gene-umi-plot") ```


- Filter cells.
iCellR allows you to filter based on library sizes (UMIs), number of genes per cell, percent mitochondrial content, one or more genes, and cell ids.
```r my.obj <- cell.filter(my.obj, min.mito = 0, max.mito = 0.05, min.genes = 200, max.genes = 2400, min.umis = 0, max.umis = Inf)
[1] "cells with min mito ratio of 0 and max mito ratio of 0.05 were filtered."
[1] "cells with min genes of 200 and max genes of 2400 were filtered."
[1] "No UMI number filter"
[1] "No cell filter by provided gene/genes"
[1] "No cell id filter"
[1] "filters_set.txt file has beed generated and includes the filters set for this experiment."
more examples
my.obj <- cell.filter(my.obj, filter.by.gene = c("RPL13","RPL10")) # filter our cell having no counts for these genes
my.obj <- cell.filter(my.obj, filter.by.cell.id = c("WT_AAACATACAACCAC.1")) # filter our cell cell by their cell ids.
chack to see how many cells are left.
dim(my.obj@main.data)
[1] 32738 2637
``` - Down sampling
This step is optional and is for having the same number of cells for each condition.
```r
optional
my.obj <- down.sample(my.obj)
[1] "From"
[1] "Data conditions: Ctrl,KO,WT (877,877,883)"
[1] "to"
[1] "Data conditions: Ctrl,KO,WT (877,877,877)"
```
- Normalize data
You have a few options to normalize your data based on your study. You can also normalize your data using tools other than iCellR and import your data to iCellR. We recommend "ranked.glsf" normalization for most single cell studies. This normalization is great for fixing matrixes with lots of zeros and because it's geometric it will reduce some of batch differences in the library sizes, as long as all the data is aggregated into one file (to aggregate your data see "aggregating data" section above). GLSF stands for Geometric Library Size Factor, this is very similar to the normalization done by DESeq2 and the ranked part would take the sum of the top most expressed genes as your library size instead of the full LB size which is to help resduce some of the drop out effects on normalization.
```r my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "ranked.glsf", top.rank = 500) # best for scRNA-Seq
more examples
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "ranked.deseq", top.rank = 500)
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "deseq") # best for bulk RNA-Seq
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "global.glsf") # best for bulk RNA-Seq
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "rpm", rpm.factor = 100000) # best for bulk RNA-Seq
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "spike.in", spike.in.factors = NULL)
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "no.norm") # if the data is already normalized
```
- Perform second QC (optioal)
```r
my.obj <- qc.stats(my.obj,which.data = "main.data")
stats.plot(my.obj,
plot.type = "all.in.one",
out.name = "UMI-plot",
interactive = F,
cell.color = "slategray3",
cell.size = 1,
cell.transparency = 0.5,
box.color = "red",
box.line.col = "green",
back.col = "white")
```
- Scale data (optional)
iCellR does not need this step as it scales the data when they need to be scaled on the fly; like for plotting or running PCA. This is because, it is important to use the untransformed data for differential expression analysis to calculate the accurate/true fold changes. If you run this function the scaled data will "not" replace the main data and instead will be saved in different data slot in the object.
```r
my.obj <- data.scale(my.obj)
```
- Gene stats
```r my.obj <- gene.stats(my.obj, which.data = "main.data")
head(my.obj@gene.data[order(my.obj@gene.data$numberOfCells, decreasing = T),])
genes numberOfCells totalNumberOfCells percentOfCells meanExp
30303 TMSB4X 2637 2637 100.00000 38.55948
3633 B2M 2636 2637 99.96208 45.07327
14403 MALAT1 2636 2637 99.96208 70.95452
27191 RPL13A 2635 2637 99.92416 32.29009
27185 RPL10 2632 2637 99.81039 35.43002
27190 RPL13 2630 2637 99.73455 32.32106
SDs condition
30303 7.545968e-15 all
3633 2.893940e+01 all
14403 7.996407e+01 all
27191 2.783799e+01 all
27185 2.599067e+01 all
27190 2.661361e+01 all
```
- Make a gene model for clustering
This function will help you find a good number of genes to use for running PCA.
```r
See model plot
make.gene.model(my.obj, my.out.put = "plot", dispersion.limit = 1.5, base.mean.rank = 1500, no.mito.model = T, mark.mito = T, interactive = F, out.name = "gene.model")
Write the gene model data into the object
my.obj <- make.gene.model(my.obj, my.out.put = "data", dispersion.limit = 1.5, base.mean.rank = 1500, no.mito.model = T, mark.mito = T, interactive = F, out.name = "gene.model")
head(my.obj@gene.model)
"ACTB" "ACTG1" "ACTR3" "AES" "AIF1" "ALDOA"
get html plot (optional)
make.gene.model(my.obj, my.out.put = "plot",
dispersion.limit = 1.5,
base.mean.rank = 1500,
no.mito.model = T,
mark.mito = T,
interactive = T,
out.name = "plot4_gene.model")
``` To view an the html interactive plot click on this links: Dispersion plot

- Perform Principal component analysis (PCA)
Note: skip this step if you plan to do batch correction. For batch correction (sample alignment/harmonization/integration) see the sections; CPCA, CCCA, MNN or anchor alignment.
```r
If you run PCA (run.pca) there would be no batch alignment but if you run CPCA (using iba function) this would perform batch alignment and PCA after batch alignment. Example for batch alignment using iba function:
my.obj <- iba(my.obj,dims = 1:30, k = 10,ba.method = "CPCA", method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model)
run PCA in case no batch alignment is necessary
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj, method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model,data.type = "main")
opt.pcs.plot(my.obj)
2 round PCA (optional)
This is to find top genes in the first 10 PCs and re-run PCA for better clustering.
This is optional and might not be good in some cases
length(my.obj@gene.model)
683
my.obj <- find.dim.genes(my.obj, dims = 1:10,top.pos = 20, top.neg = 20) # (optional)
length(my.obj@gene.model)
211
second round PC
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj, method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model,data.type = "main")
```

- Perform other dimensionality reductions (tSNE, UMAP, KNetL, PHATE, destiny, diffusion maps)
We recommend tSNE, UMAP and KNetL. KNetL is fundamentally more powerful.
```r
tSNE
my.obj <- run.pc.tsne(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
UMAP
my.obj <- run.umap(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
KNetL (for lager than 5000 cell use a zoom of about 400)
Because knetl has a very high resolution it's best to use a dim of 20 (this usually works best for most data)
my.obj <- run.knetl(my.obj, dims = 1:20, zoom = 110) # (Important note!) don't forget to set the zoom in the right range
#################### IMPORTANT DISCLAIMER NOTE
*** KNetL map is very dynamic with zoom and dims! ***
*** Therefore it needs to be adjusted! ***
For data with less than 1000 cells use a zoom of about 5-50.
For data with 1000-5000 cells use a zoom of about 50-200.
For data with 5000-10000 cells use a zoom of about 100-300.
For data with 10000-30000 cells use a zoom of about 200-500.
For data with more than 30000 cells use a zoom of about 400-600.
zoom 400 is usually good for big data but adjust for intended resolution.
Lower number for zoom in and higher for zoom out (its reverse).
dims = 1:20 is generally good for most data.
other parameters are best as default.
Just like a microscope, you need to zoom to see the intended amount of details.
Here we use a zoom of 100 or 110 but this might not be ideal for your data.
example: # my.obj <- run.knetl(my.obj, dims = 1:20, zoom = 400)
Because knetl has a very high resolution it's best to use a dim of 20 (this usually works best for most data)
diffusion map
this requires python packge phate or bioconductor R package destiny
How to install destiny
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("destiny")
How to install phate
pip install --user phate
Install phateR version 2.9
wget https://cran.r-project.org/src/contrib/Archive/phateR/phateR_0.2.9.tar.gz
install.packages('phateR/', repos = NULL, type="source")
or
library(devtools)
install_version("phateR", version = "0.2.9", repos = "http://cran.us.r-project.org")
optional
library(destiny)
my.obj <- run.diffusion.map(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
or
library(phateR)
my.obj <- run.diffusion.map(my.obj, dims = 1:10, method = "phate")
```
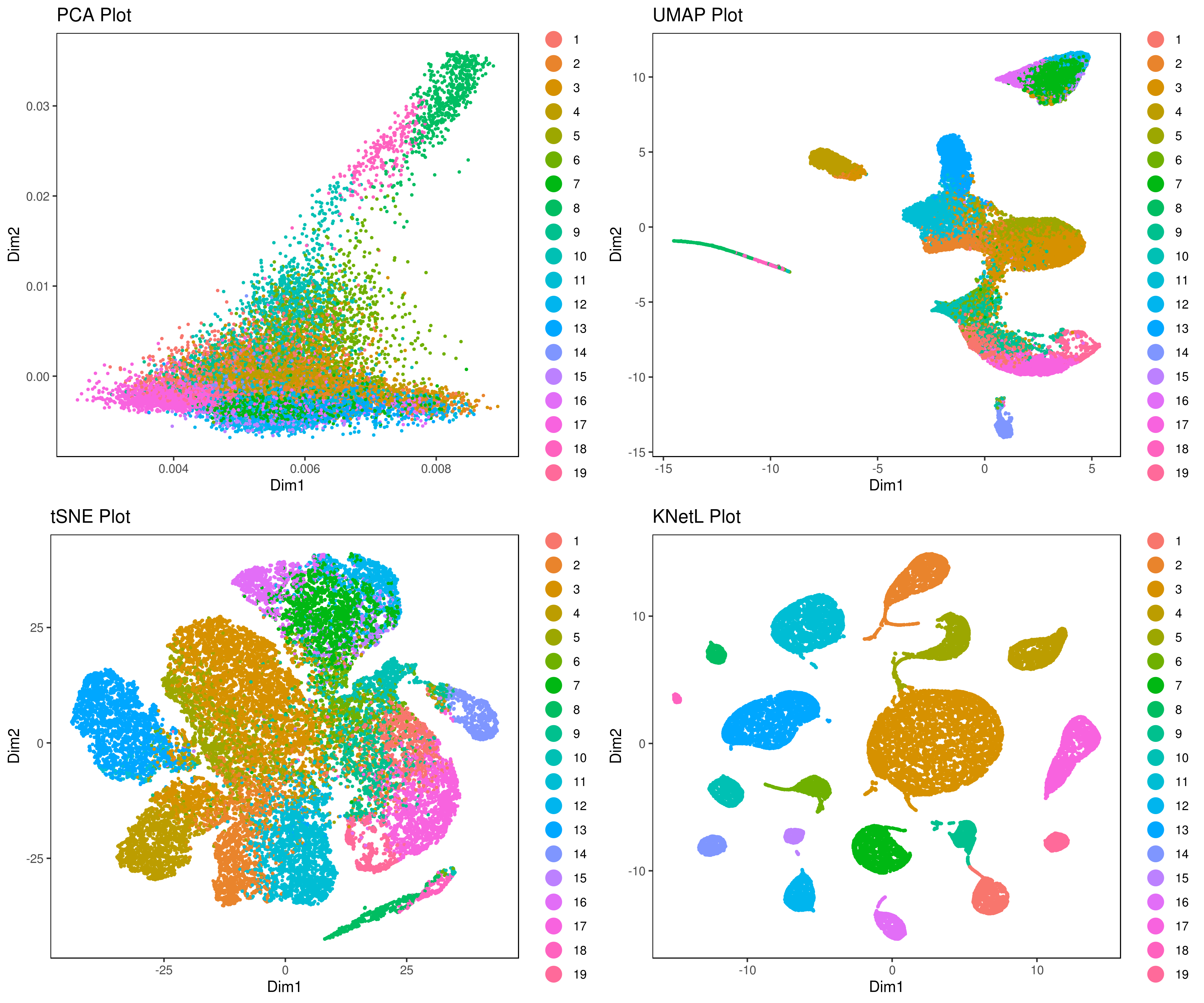
- Visualizing the results of dimensionality reductions before clustering (optional)
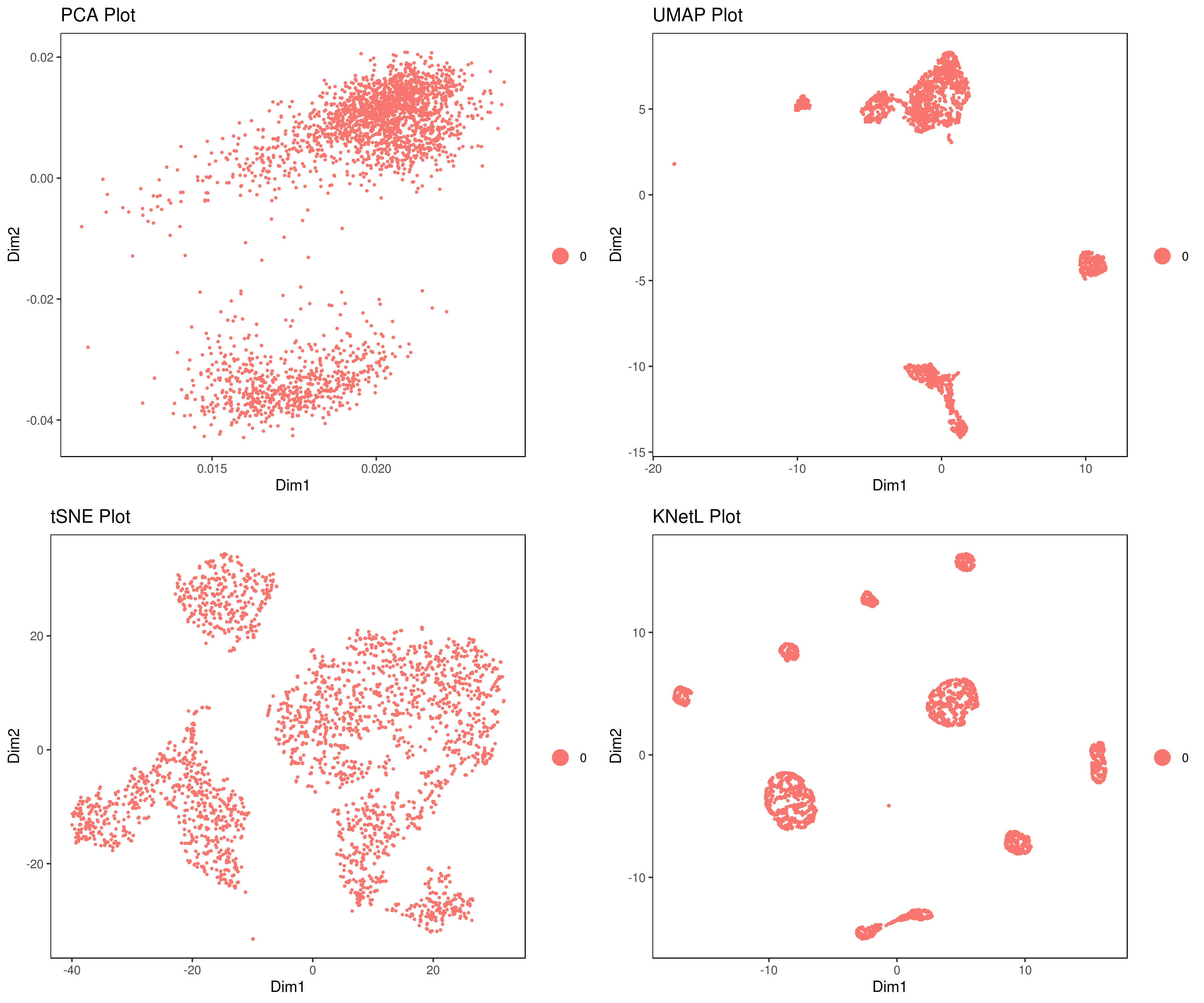
```r A= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",interactive = F) B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F) C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F) D= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F)
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) ```
Clustering
We provide three functions to run the clustering method of your choice:
1- iclust (** recommended):
Faster and optimized for iCellR. This function takes PCA, UMAP or tSNE, Destiny (diffusion map), PHATE or KNetL map as input. This function is using Louvain algorithm for clustering a graph made using KNN. Similar to PhenoGraph (Levine et al., Cell, 2015) however instead of Jaccard similarity values we use distance (euclidean by default) values for the weights.
2- run.phenograph:
R implementation of the PhenoGraph algorithm. Rphenograph wrapper (Levine et al., Cell, 2015).
3- run.clustering:
In this function we provide a variety of many other options for you to explore the data with different flavours of clustering and indexing methods. Choose any combinations from the table below.
| clustering methods | distance methods | indexing methods | | ------------- | ------------- | ------------- | | ward.D, ward.D2, single, complete, average, mcquitty, median, centroid, kmeans| euclidean, maximum, manhattan, canberra, binary, minkowski or NULL | kl, ch, hartigan, ccc, scott, marriot, trcovw, tracew, friedman, rubin, cindex, db, silhouette, duda, pseudot2, beale, ratkowsky, ball, ptbiserial, gap, frey, mcclain, gamma, gplus, tau, dunn, hubert, sdindex, dindex, sdbw |
Conventionally people cluster based on PCA data (usually first 10 dimensions) however you have the option of choosing tSNE, UMAP and KNetL map dimensions as well. If you have adjusted your KNetL map and are confident about the results we recommend clustering based on KNetL map.
This is one of the harder parts of the analysis and sometimes you need to adjust your clustering based on marker genes. This means you might need to merge some clusters, gate (see our cell gating tools) or try different sensitivities to find more or less communities.
```r
clustering based on KNetL
my.obj <- iclust(my.obj, sensitivity = 150, data.type = "knetl")
clustering based on PCA
my.obj <- iclust(my.obj, sensitivity = 150, data.type = "pca", dims=1:10)
play with k to get the clusters right. Usually 150 is good.
more examples
clustering based on PCA
my.obj <- iclust(my.obj,
dist.method = "euclidean",
sensitivity = 100,
dims = 1:10,
data.type = "pca")
or
run.phenograph
my.obj <- run.phenograph(my.obj,k = 100,dims = 1:10)
or
run.clustering
my.obj <- run.clustering(my.obj,
clust.method = "kmeans",
dist.method = "euclidean",
index.method = "silhouette",
max.clust = 25,
min.clust = 2,
dims = 1:10)
If you want to manually set the number of clusters, and not used the predicted optimal number, set the minimum and maximum to the number you want:
my.obj <- run.clustering(my.obj,
clust.method = "ward.D",
dist.method = "euclidean",
index.method = "ccc",
max.clust = 8,
min.clust = 8,
dims = 1:10)
more examples
my.obj <- run.clustering(my.obj,
clust.method = "ward.D",
dist.method = "euclidean",
index.method = "kl",
max.clust = 25,
min.clust = 2,
dims = 1:10)
```
- Visualize data clustering results
```r
plot clusters (in the figures below clustering is done based on KNetL)
example: # my.obj <- iclust(my.obj, k = 150, data.type = "knetl")
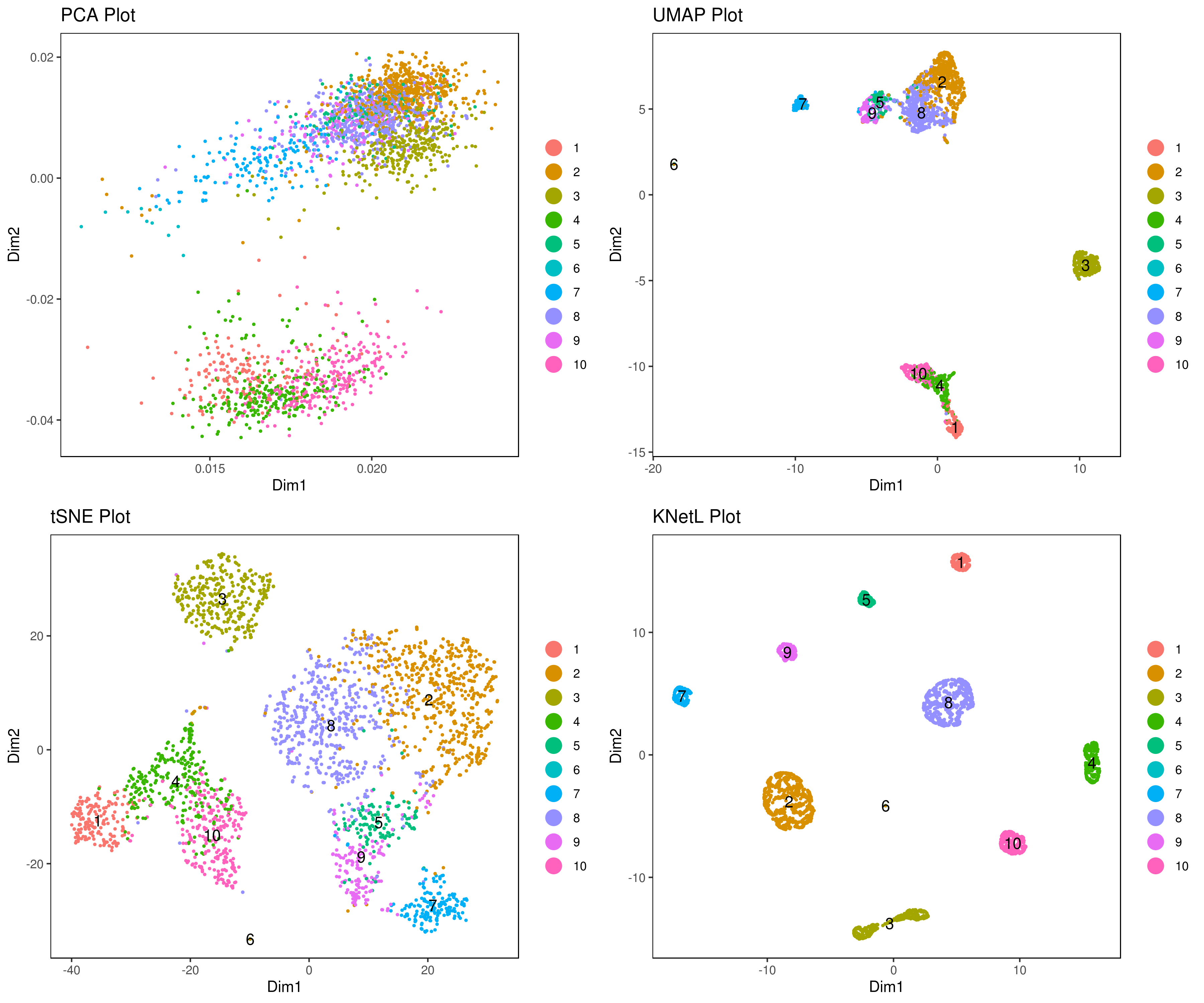
A <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) B <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) C <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) D <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T)
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) ```
- Re-numbering clusters based on their distances, this is so that the are more in consecutive order (optional)
This is visually helpful to look at your heatmap after finding marker genes and can help you decide which clusters need to be merged and adjusted.
```r
my.obj <- clust.ord(my.obj,top.rank = 500, how.to.order = "distance")
my.obj <- clust.ord(my.obj,top.rank = 500, how.to.order = "random")
A= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) D= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T)
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) ```
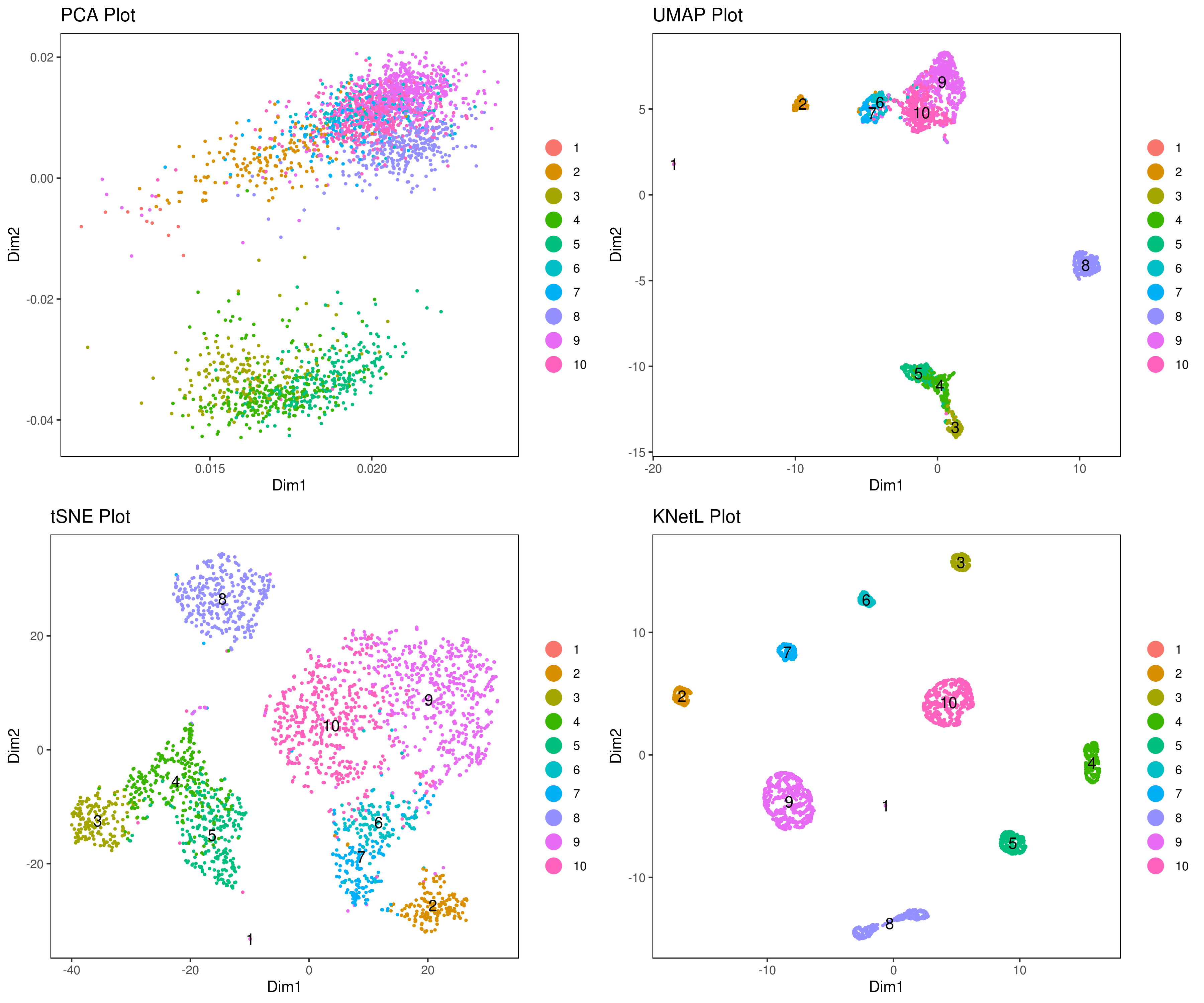
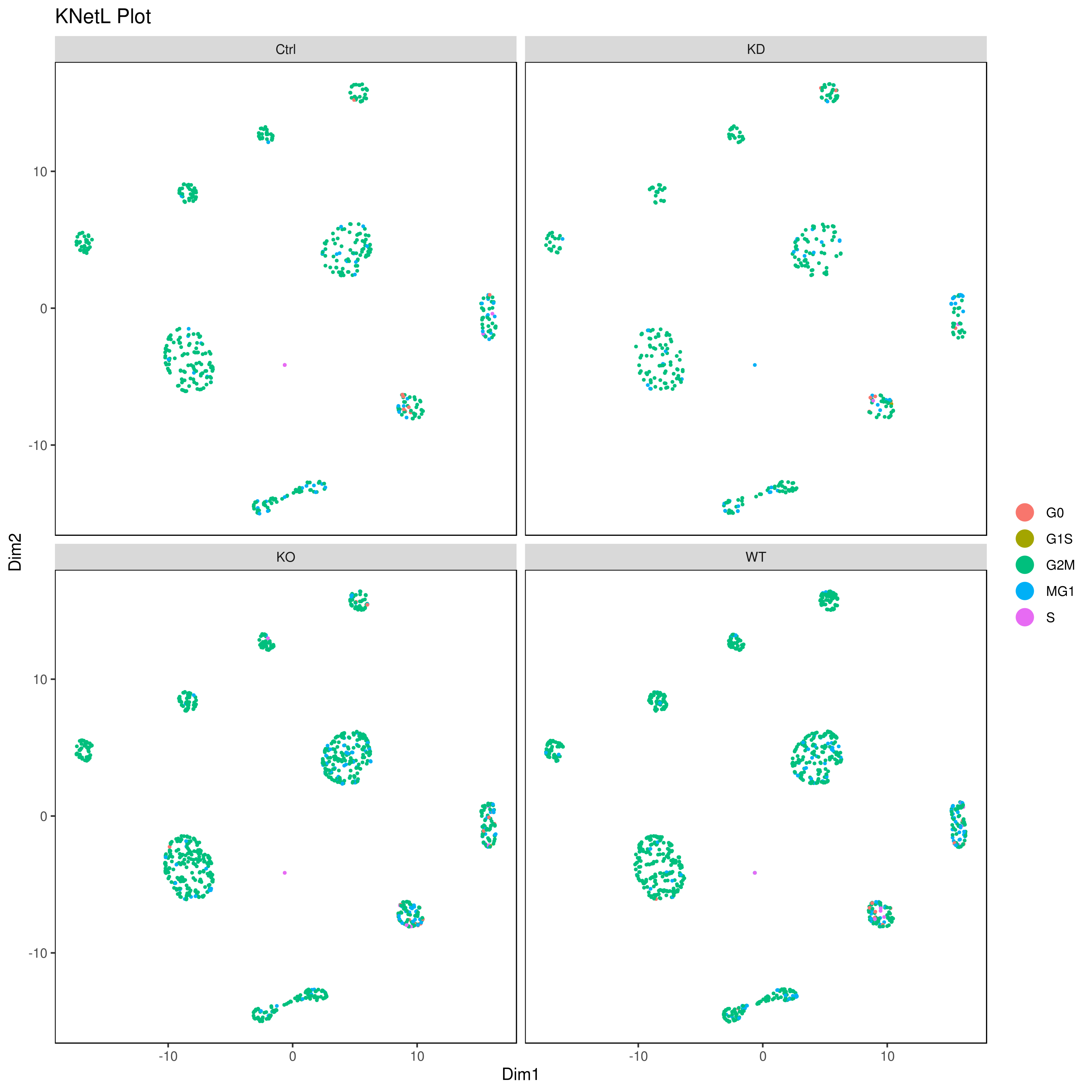
- Look at conditions
```r
conditions
A <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",col.by = "conditions",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5) B <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",col.by = "conditions",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5) C <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",col.by = "conditions",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5) D <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",col.by = "conditions",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5)
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D)
or
png('AllCondsclustsknetl.png', width = 16, height = 8, units = 'in', res = 300) cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 0.1, plot.type = "knetl", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", cell.transparency = 1, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F,cond.facet = T) dev.off()
```
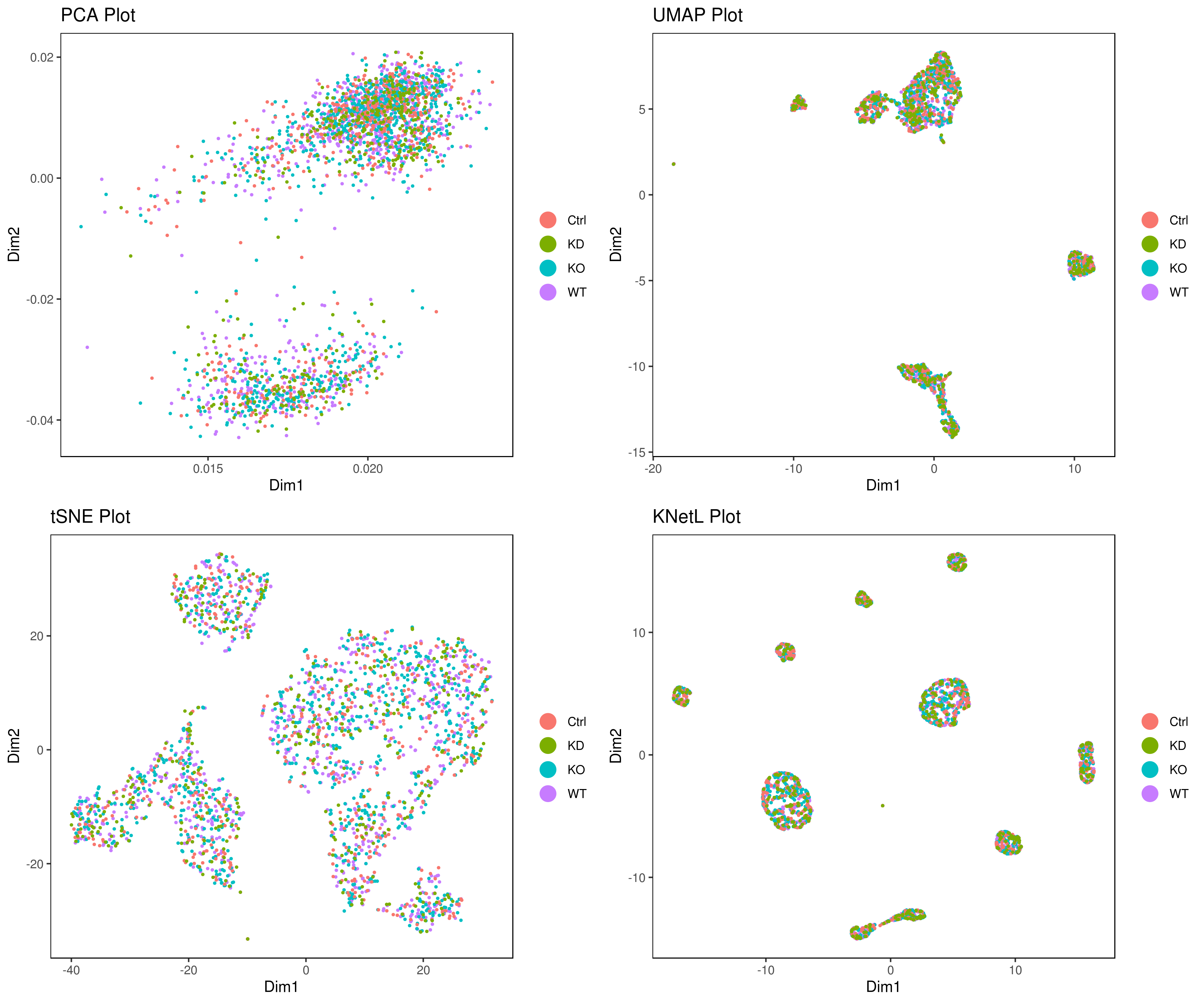
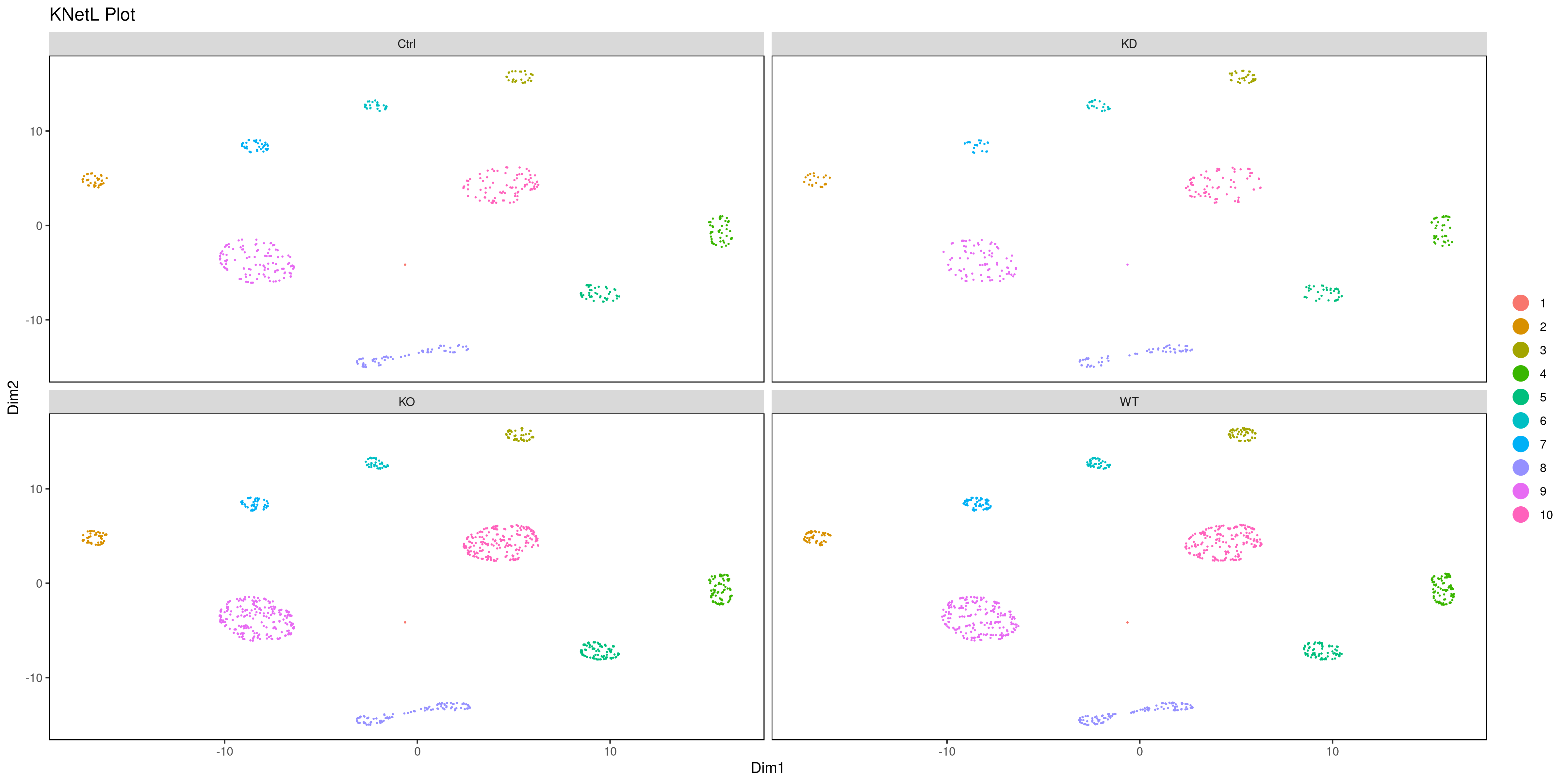
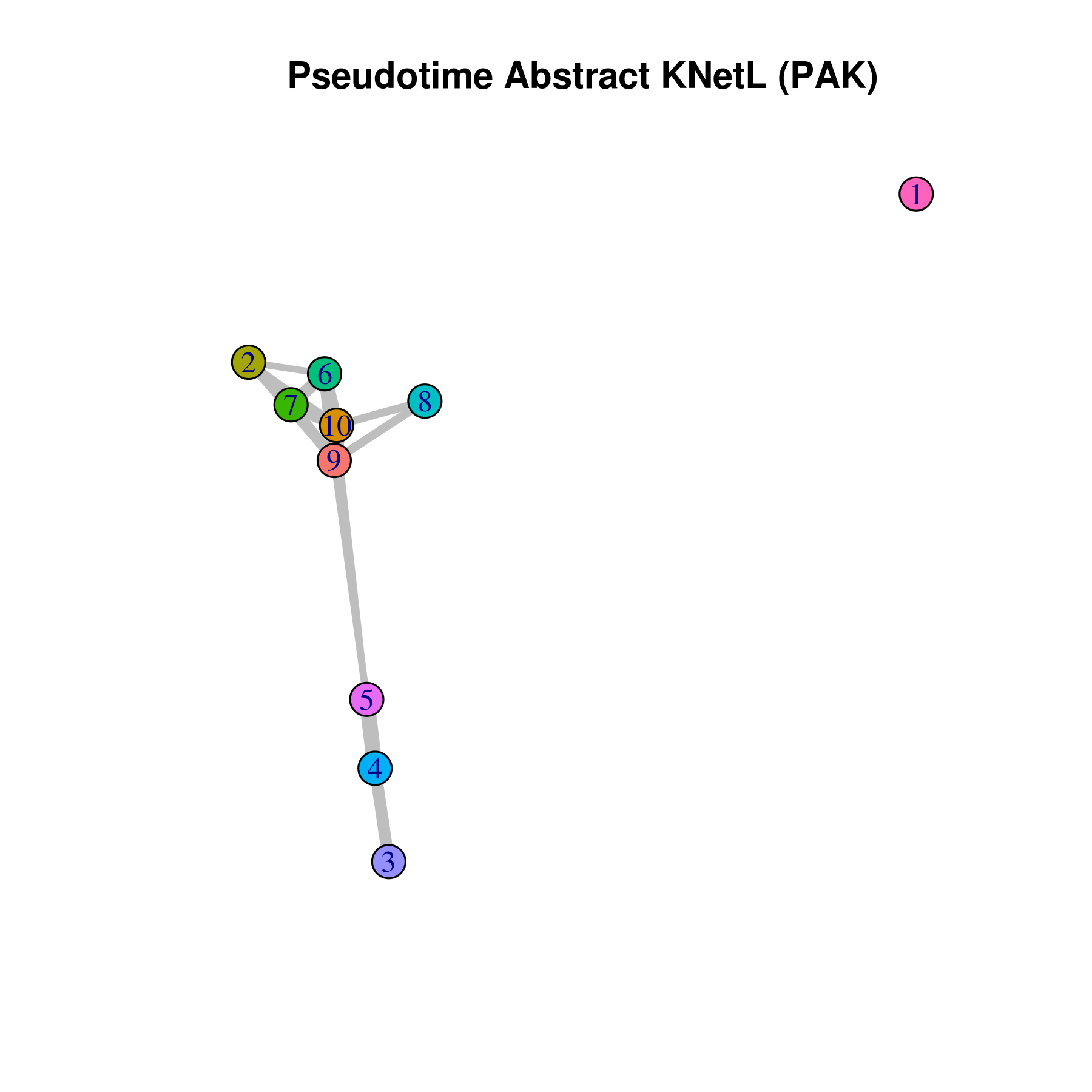
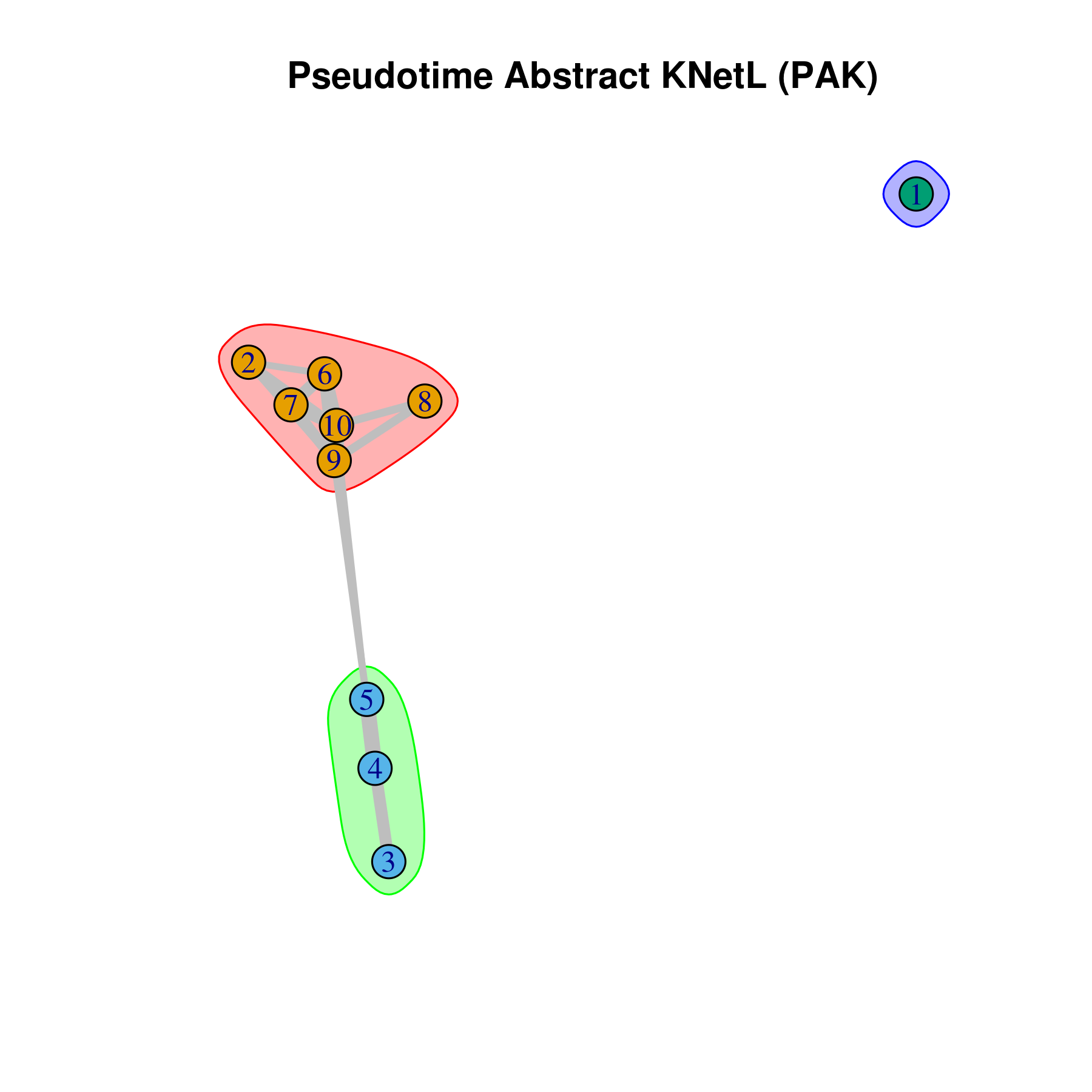
- Pseudotime Abstract KNetL map (PAK map)
This is very helpful to see the distances or similarities between different communities. The shorter and thicker the lines/links (rubber bands) are the more similar the communities. The nodes are the clusters and the edges or links are the distance between them.
```r pseudotime.knetl(my.obj,interactive = F,cluster.membership = F,conds.to.plot = NULL)
with memberships
pseudotime.knetl(my.obj,interactive = F,cluster.membership = T,conds.to.plot = NULL)
intractive plot
pseudotime.knetl(my.obj,interactive = T) ```
- Average expression per cluster
```r
for all cunditions
my.obj <- clust.avg.exp(my.obj, conds.to.avg = NULL)
for one cundition
my.obj <- clust.avg.exp(my.obj, conds.to.avg = "WT")
for two cundition
my.obj <- clust.avg.exp(my.obj, conds.to.avg = c("WT","KO"))
head(my.obj@clust.avg)
gene cluster1 cluster2 cluster3 cluster4 cluster_5
1 A1BG 0 0.034248447 0.029590643 0.076486590 0.090270833
2 A1BG.AS1 0 0.000000000 0.006274854 0.019724138 0.004700000
3 A1CF 0 0.000000000 0.000000000 0.000000000 0.000000000
4 A2M 0 0.006925466 0.003614035 0.000000000 0.000000000
5 A2M.AS1 0 0.056155280 0.000000000 0.005344828 0.006795833
6 A2ML1 0 0.000000000 0.000000000 0.000000000 0.000000000
cluster6 cluster7 cluster8 cluster9 cluster_10
1 0.074360294 0.07623494 0.04522321 0.088735057 0.065292818
2 0.000000000 0.00000000 0.01553869 0.013072698 0.013550645
3 0.000000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.000000000 0.000000000
4 0.000000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.001810985 0.003200737
5 0.008191176 0.06227108 0.00000000 0.011621971 0.012837937
6 0.000000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.000000000 0.000000000
```
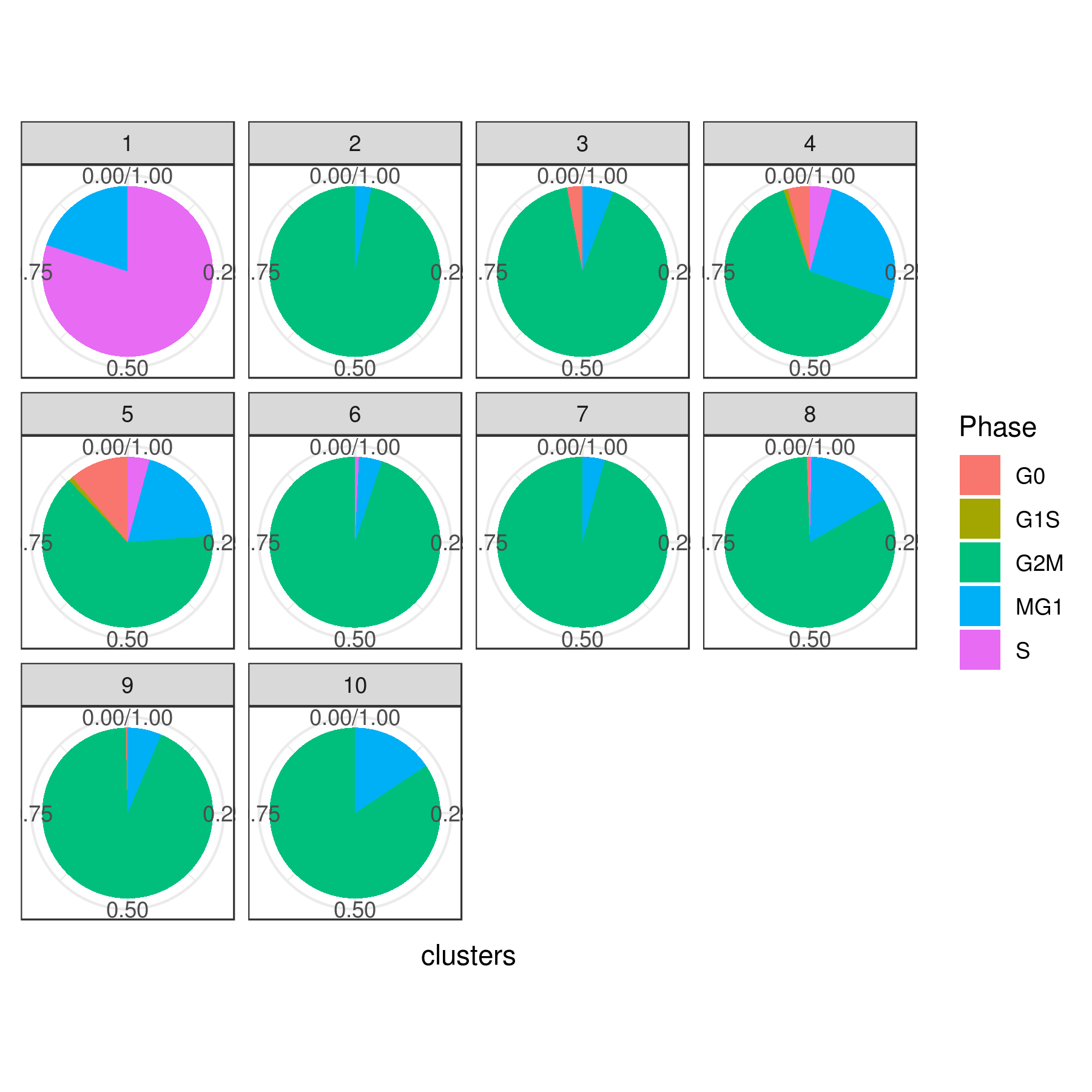
- Cell cycle prediction
Tirosh scoring method Tirosh, et. al. 2016 (default) or coverage is used to calculate G0, G1S, G2M, M, G1M and S phase score. The gene lists for G0, G1S, G2M, M, G1M and S phase are chosen from previously published article Xue, et.al 2020
NOTE: These genes work best for cancer cells. You can use a different gene set for each category (G0, G1S, G2M, M, G1M and S).
```r
old method
my.obj <- cc(my.obj, s.genes = s.phase, g2m.genes = g2m.phase)
new method
G0 <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'G0.txt', package = 'iCellR')) G1S <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'G1S.txt', package = 'iCellR')) G2M <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'G2M.txt', package = 'iCellR')) M <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'M.txt', package = 'iCellR')) MG1 <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'MG1.txt', package = 'iCellR')) S <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'S.txt', package = 'iCellR'))
Tirosh scoring method (recomanded)
my.obj <- cell.cycle(my.obj, scoring.List = c("G0","G1S","G2M","M","MG1","S"), scoring.method = "tirosh")
Coverage scoring method (recomanded)
my.obj <- cell.cycle(my.obj, scoring.List = c("G0","G1S","G2M","M","MG1","S"), scoring.method = "coverage")
plot cell cycle
A= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T,col.by = "cc") B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T, col.by = "cc") C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T, col.by = "cc") D= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T, col.by = "cc")
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D)
or
cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 0.5, plot.type = "knetl", col.by = "cc", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", cell.transparency = 1, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F,cond.facet = T)
Pie
clust.stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "pie.cc", interactive = F, conds.to.plot = NULL) dev.off()
bar
clust.stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "bar.cc", interactive = F, conds.to.plot = NULL) dev.off()
or per condition
clust.stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "pie.cc", interactive = F, conds.to.plot = "WT")
```
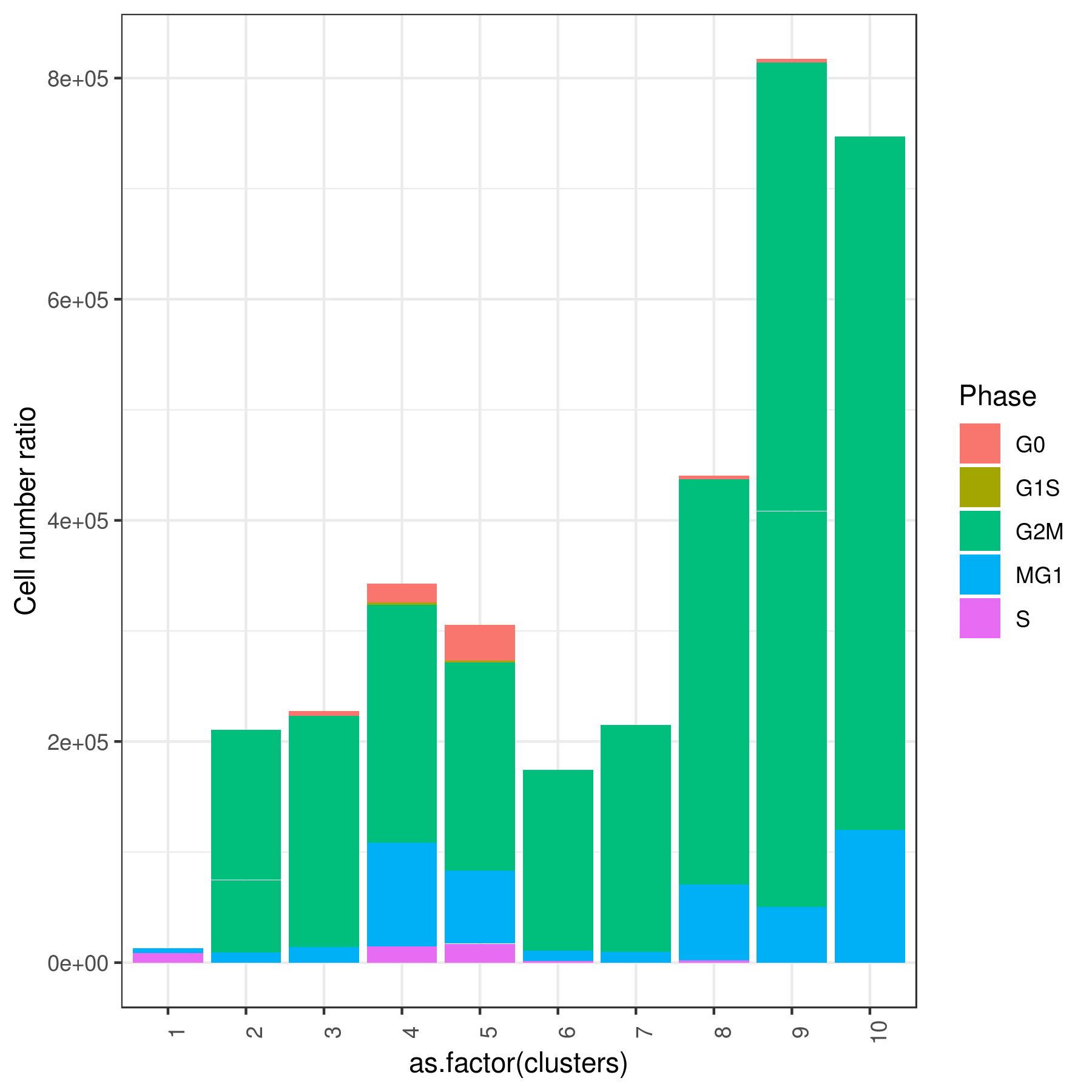
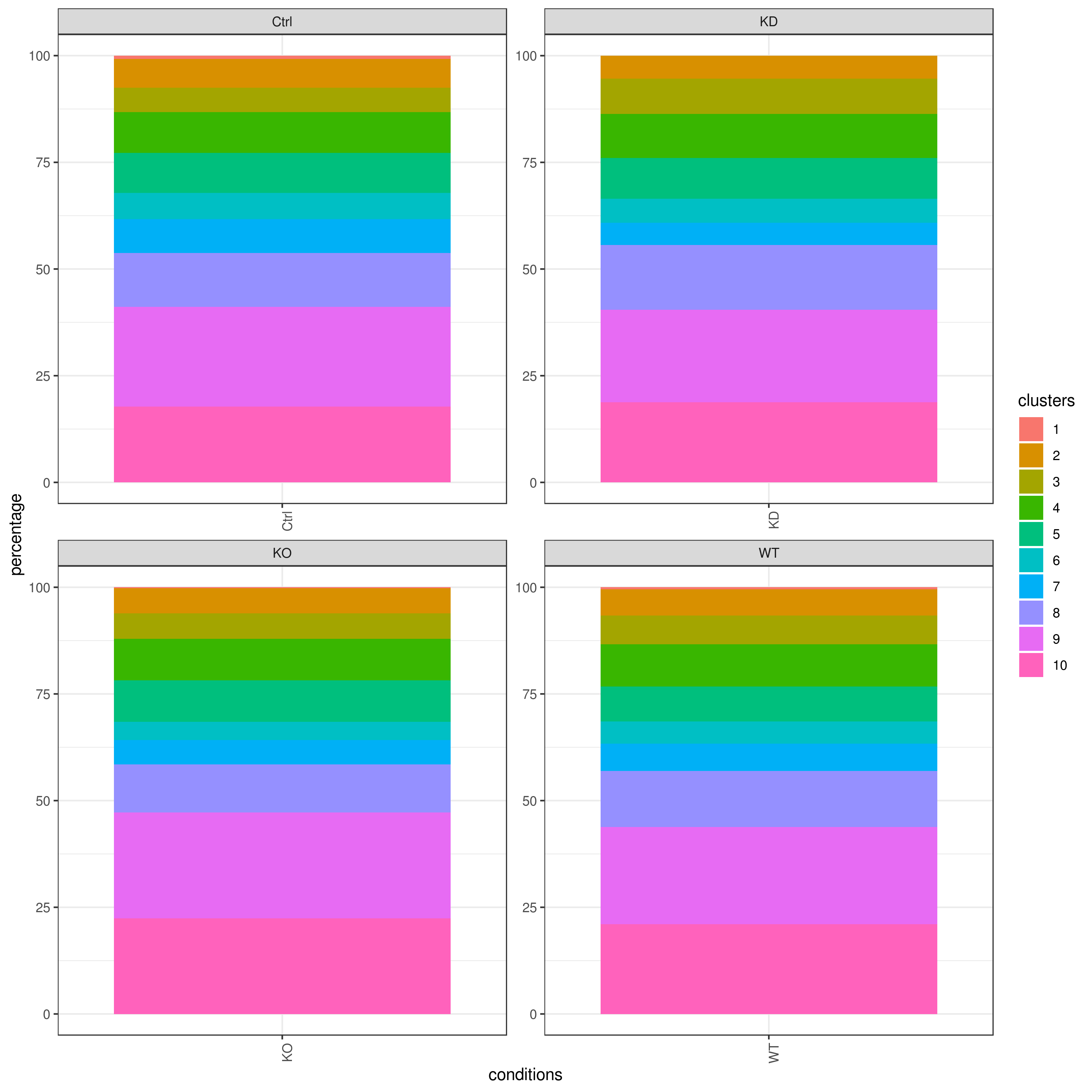
- Cell frequencies and proportions
```r clust.cond.info(my.obj, plot.type = "pie", normalize.ncell = TRUE, my.out.put = "plot", normalize.by = "percentage")
clust.cond.info(my.obj, plot.type = "bar", normalize.ncell = TRUE,my.out.put = "plot", normalize.by = "percentage")
clust.cond.info(my.obj, plot.type = "pie.cond", normalize.ncell = T, my.out.put = "plot", normalize.by = "percentage")
clust.cond.info(my.obj, plot.type = "bar.cond", normalize.ncell = T,my.out.put = "plot", normalize.by = "percentage")
my.obj <- clust.cond.info(my.obj) head(my.obj@my.freq)
conditions TC SF clusters Freq Norm.Freq percentage
1 Ctrl 491 1.265 1 4 3.162 0.81
2 Ctrl 491 1.265 11 32 25.296 6.52
3 Ctrl 491 1.265 8 114 90.119 23.22
4 Ctrl 491 1.265 5 43 33.992 8.76
5 Ctrl 491 1.265 2 33 26.087 6.72
6 Ctrl 491 1.265 9 86 67.984 17.52
```
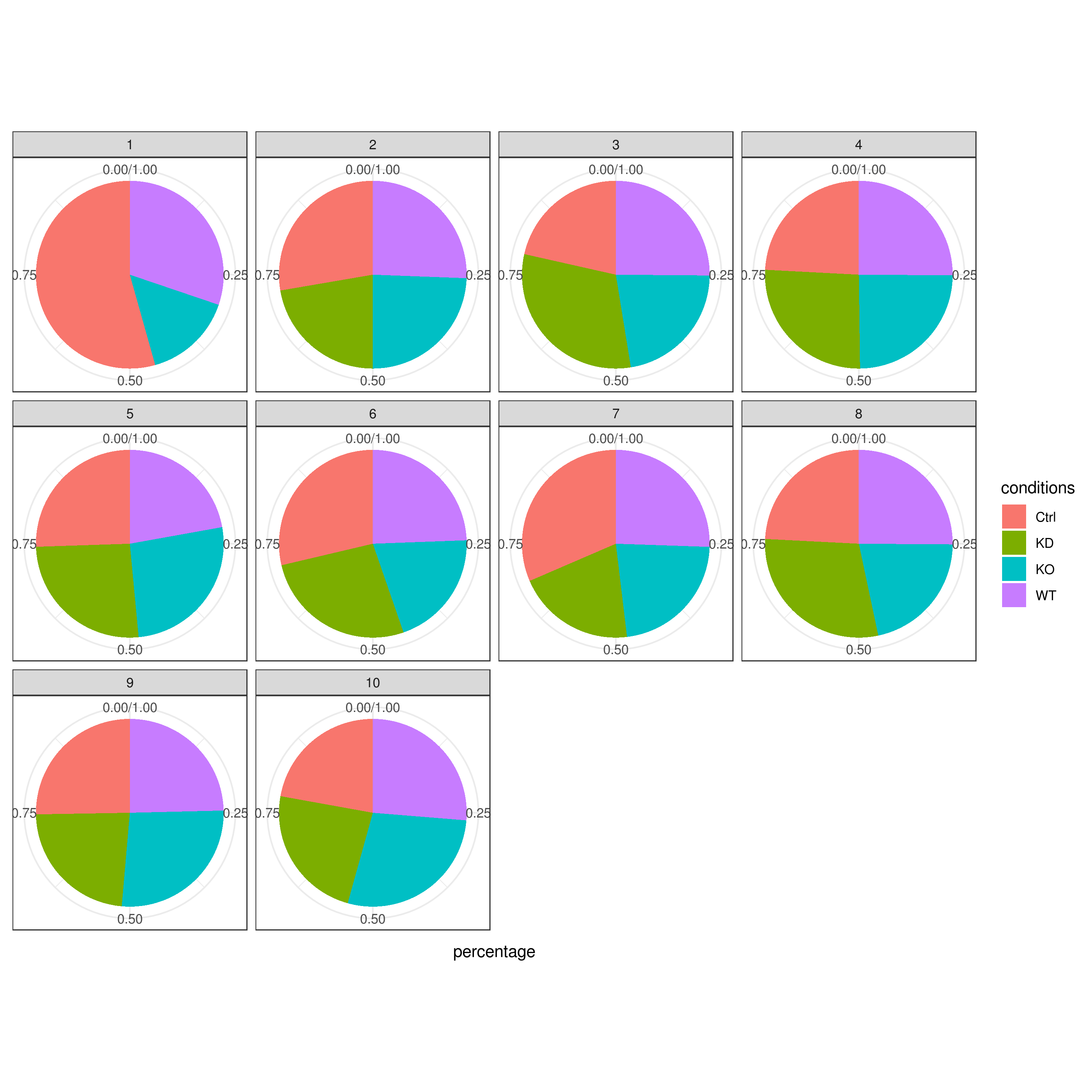
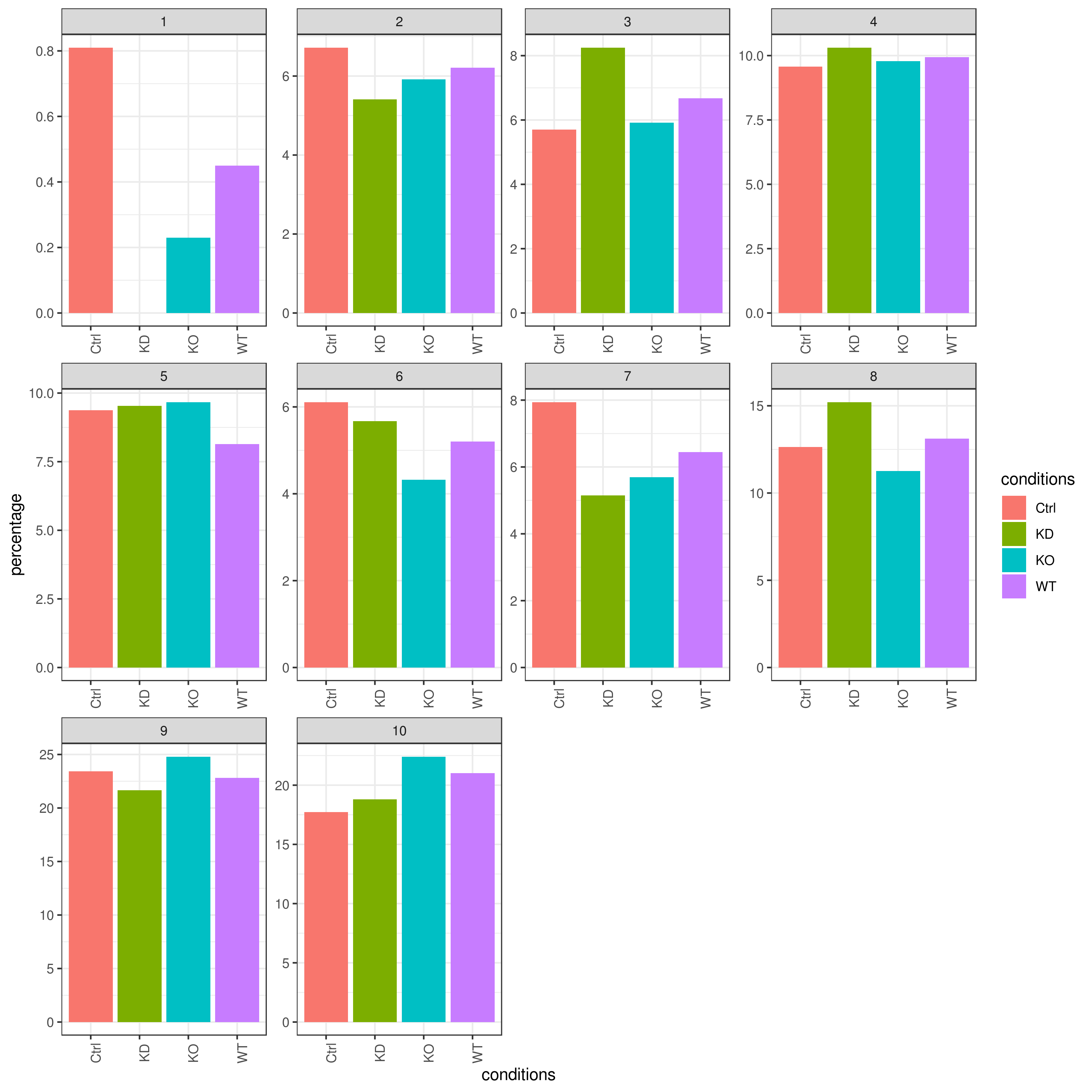
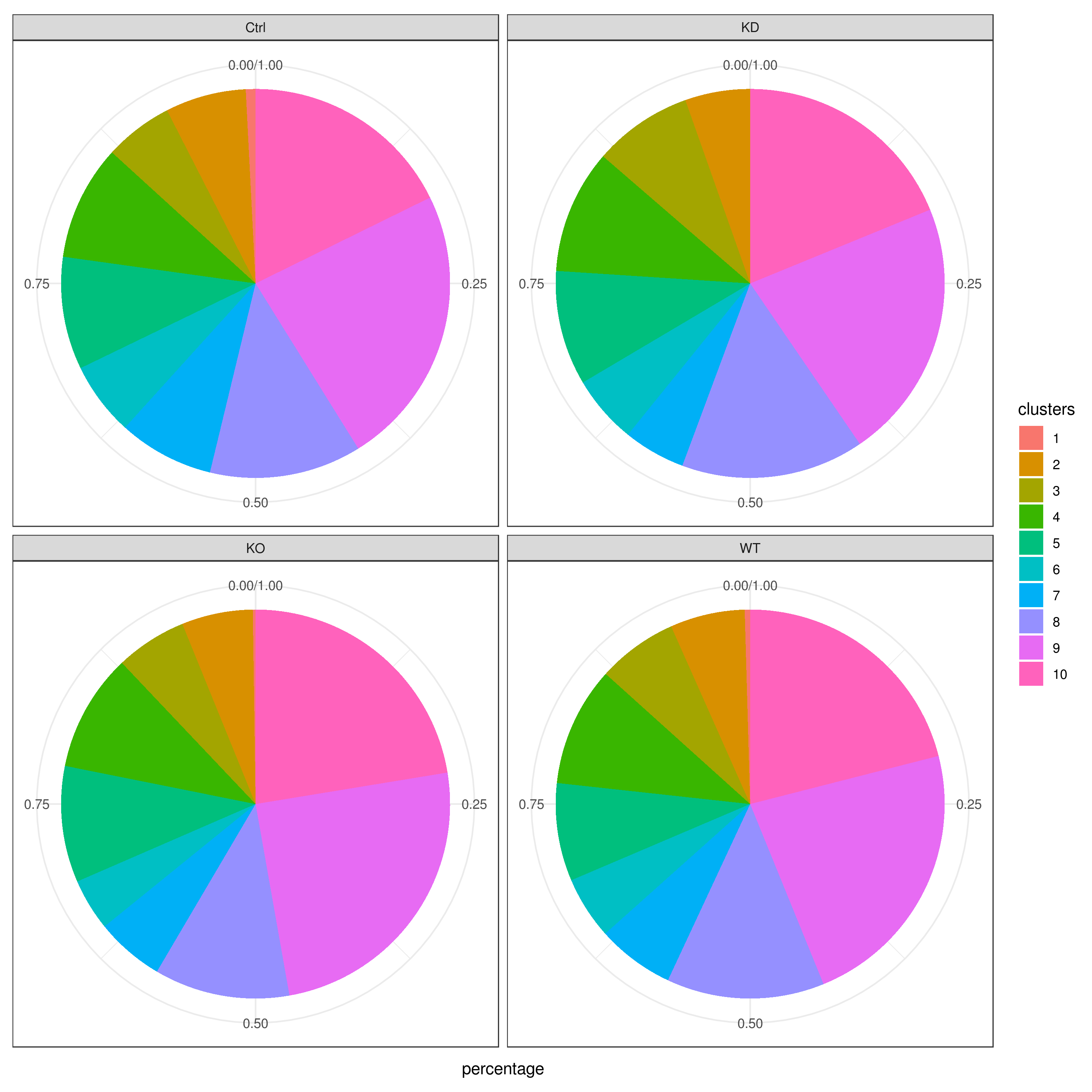
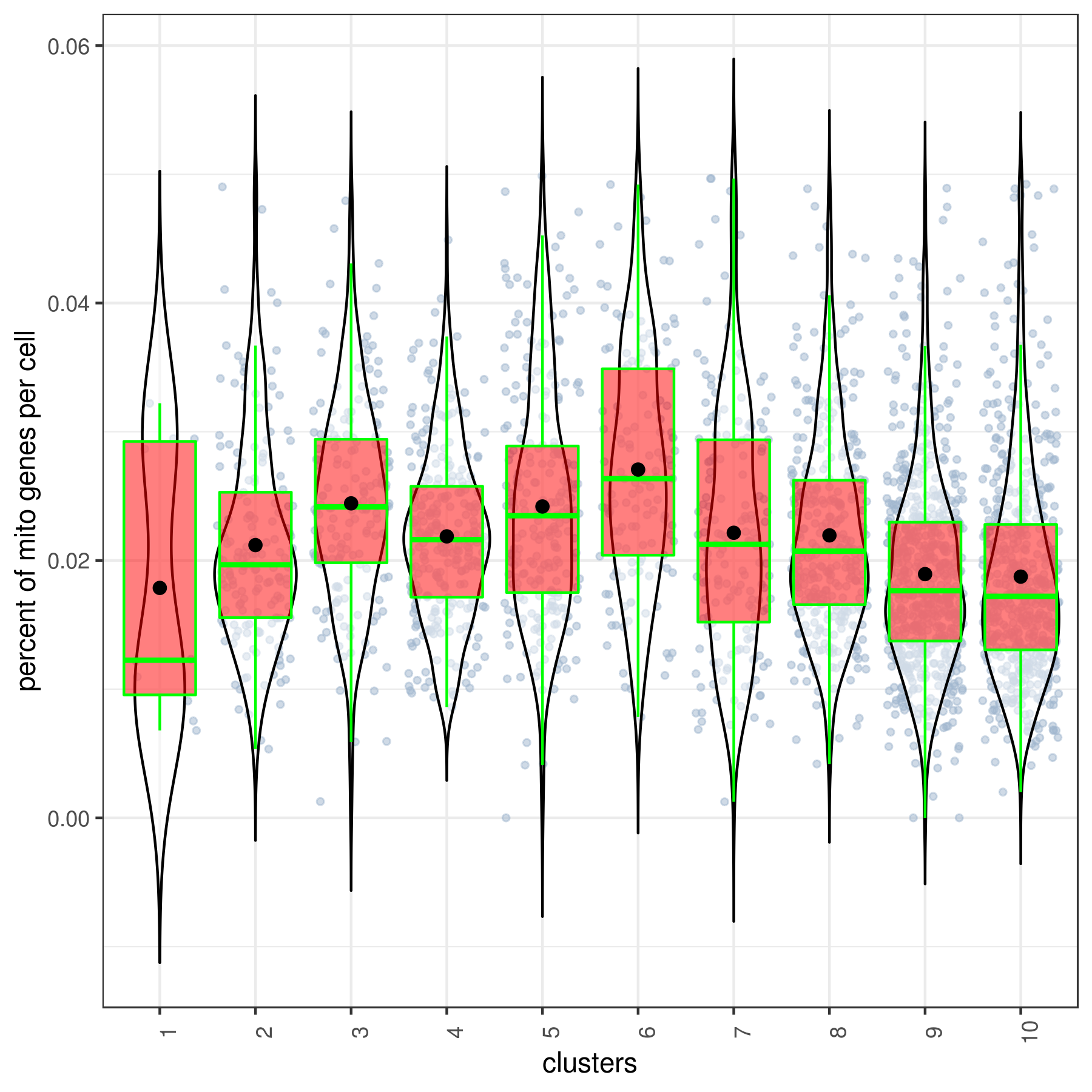
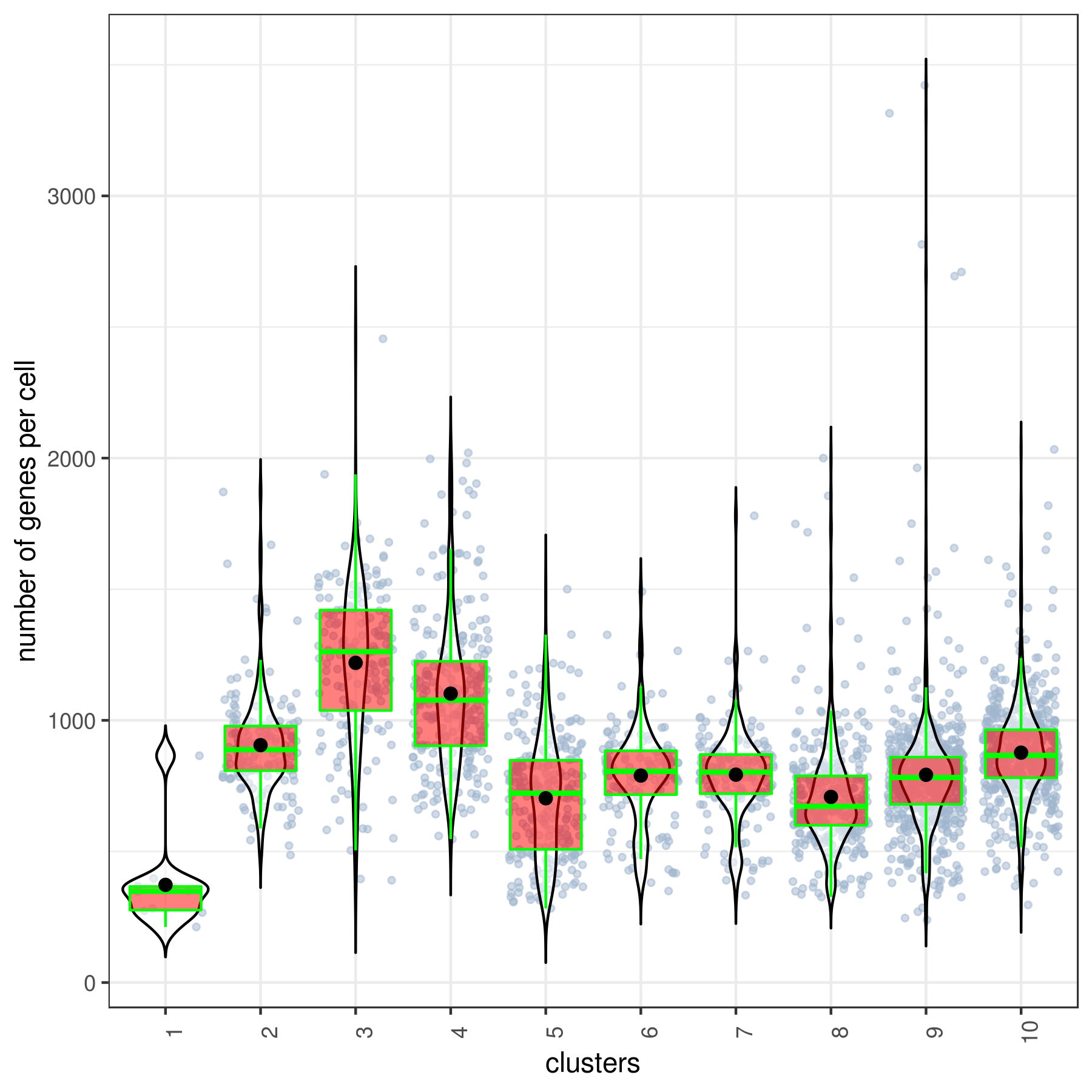
- Cluster QC
```r clust.stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "box.mito", interactive = F)
clust.stats.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "box.gene", interactive = F) ```
- Run data imputation
r
my.obj <- run.impute(my.obj, dims = 1:10, nn = 10, data.type = "pca")
- Save your object
r
save(my.obj, file = "my.obj.Robj")
- gene gene correlation
```r
impute more cells by increasing nn for better resulst.
my.obj <- run.impute(my.obj,dims = 1:10,data.type = "pca", nn = 50)
main data
A <- gg.cor(my.obj, interactive = F, gene1 = "GNLY", gene2 = "NKG7", conds = NULL, clusts = NULL, data.type = "main")
imputed data
B <- gg.cor(my.obj, interactive = F, gene1 = "GNLY", gene2 = "NKG7", conds = NULL, clusts = NULL, data.type = "imputed")
C <- gg.cor(my.obj, interactive = F, gene1 = "GNLY", gene2 = "NKG7", conds = NULL, clusts = c(3,2), data.type = "imputed")
imputed data
D <- gg.cor(my.obj, interactive = F, gene1 = "GNLY", gene2 = "NKG7", conds = c("WT"), clusts = NULL, data.type = "imputed")
grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) ```
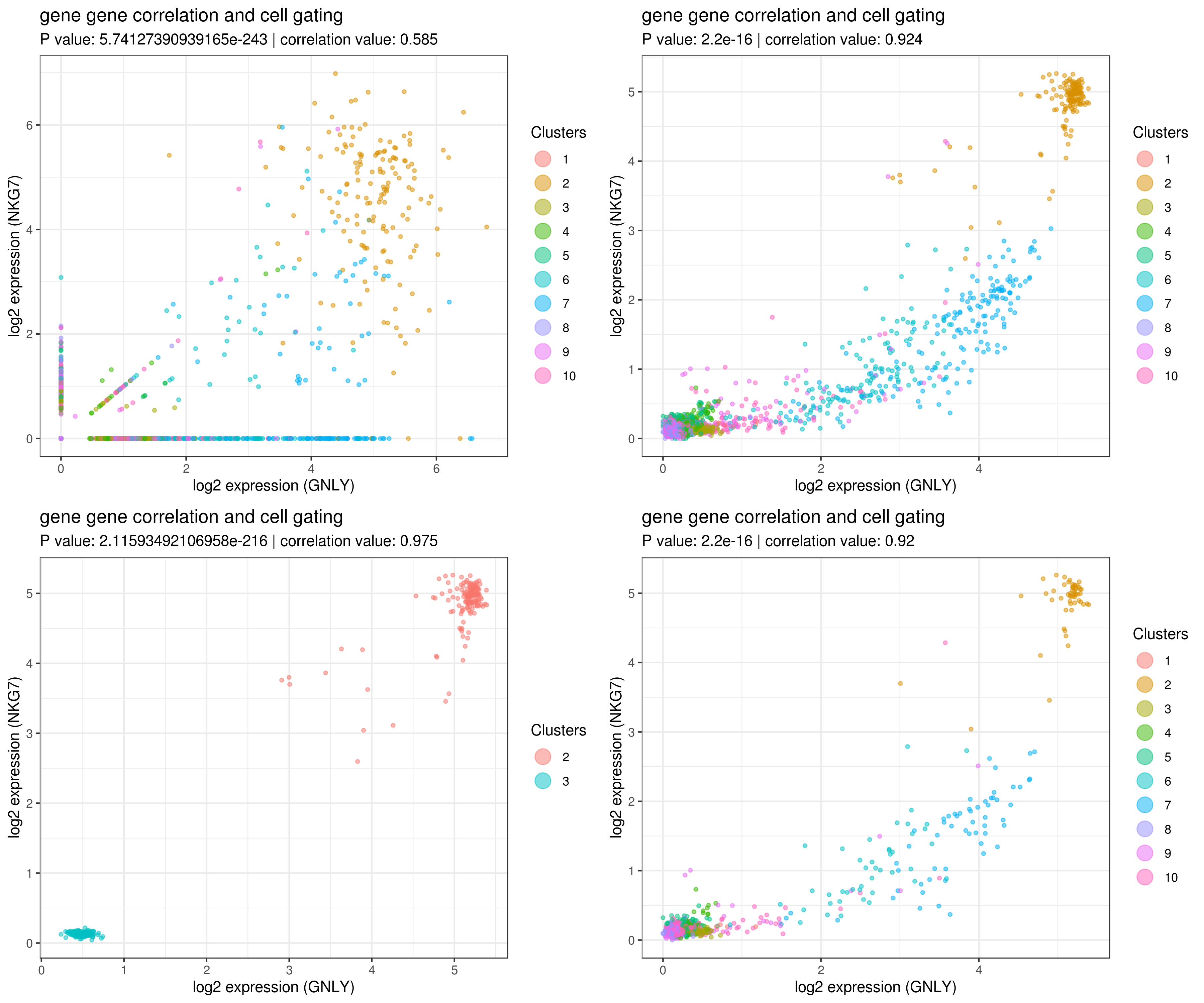
- Find marker genes
```r marker.genes <- findMarkers(my.obj, fold.change = 2, padjval = 0.1)
dim(marker.genes)
[1] 1070 17
head(marker.genes)
baseMean baseSD AvExpInCluster AvExpInOtherClusters foldChange
PPBP 0.8257760 12.144694 181.3945 0.1399852 1295.8120969
GPX1 1.3989591 4.344717 57.4034 1.1862571 48.3903523
CALM3 0.5469743 1.230942 10.7848 0.5080915 21.2260968
OAZ1 4.9077851 5.979586 46.7867 4.7487311 9.8524635
MYL6 3.0806167 3.562124 21.3690 3.0111584 7.0966045
CD74 8.5523704 13.359205 2.6120 8.5749316 0.3046088
log2FoldChange pval padj clusters gene cluster_1
PPBP 10.339641 1.586683e-06 0.014786300 1 PPBP 181.3945
GPX1 5.596648 1.107541e-07 0.001103775 1 GPX1 57.4034
CALM3 4.407767 2.098341e-06 0.019415953 1 CALM3 10.7848
OAZ1 3.300485 7.857814e-07 0.007464137 1 OAZ1 46.7867
MYL6 2.827129 1.296112e-06 0.012156230 1 MYL6 21.3690
CD74 -1.714970 9.505749e-06 0.083983296 1 CD74 2.6120
cluster2 cluster3 cluster4 cluster5 cluster6 cluster7
PPBP 0.0000000 0.1444327 0.2282912 0.0640625 0.01739706 0.1541084
GPX1 0.2424969 1.2218772 3.9292720 4.4329583 0.25663235 0.2712831
CALM3 0.6537205 0.8149415 0.6071034 0.5245625 0.44687500 0.5081867
OAZ1 3.2077826 12.2072339 8.6080077 10.8738208 2.71288971 3.6402289
MYL6 4.9660870 5.7945673 4.2813218 4.3046458 2.42854412 3.9030542
CD74 2.9385839 8.9848538 15.7646245 5.9454250 2.19555882 3.8323072
cluster8 cluster9 cluster_10
PPBP 0.02478274 0.3668433 0.01026335
GPX1 0.61210714 0.4635153 0.39311786
CALM3 0.22591369 0.5210339 0.48856538
OAZ1 3.67225595 2.3590420 2.53362063
MYL6 1.72344048 1.6460420 2.59901289
CD74 36.10877976 1.5638853 1.82587477
baseMean: average expression in all the cells
baseSD: Standard Deviation
AvExpInCluster: average expression in cluster number (see clusters)
AvExpInOtherClusters: average expression in all the other clusters
foldChange: AvExpInCluster/AvExpInOtherClusters
log2FoldChange: log2(AvExpInCluster/AvExpInOtherClusters)
pval: P value
padj: Adjusted P value
clusters: marker for cluster number
gene: marker gene for the cluster
the rest are the average expression for each cluster
```
- Heatmap
```r
find top genes
MyGenes <- top.markers(marker.genes, topde = 10, min.base.mean = 0.2,filt.ambig = F) MyGenes <- unique(MyGenes)
main data
heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters", conds.to.plot = NULL)
imputed data
heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters", data.type = "imputed", conds.to.plot = NULL)
sort cells and plot only one condition
heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters", data.type = "imputed", cell.sort = TRUE, conds.to.plot = c("WT"))
Pseudotime stile
heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "none", data.type = "imputed", cell.sort = TRUE)
intractive
heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = T, out.name = "heatmap_gg", cluster.by = "clusters")
````
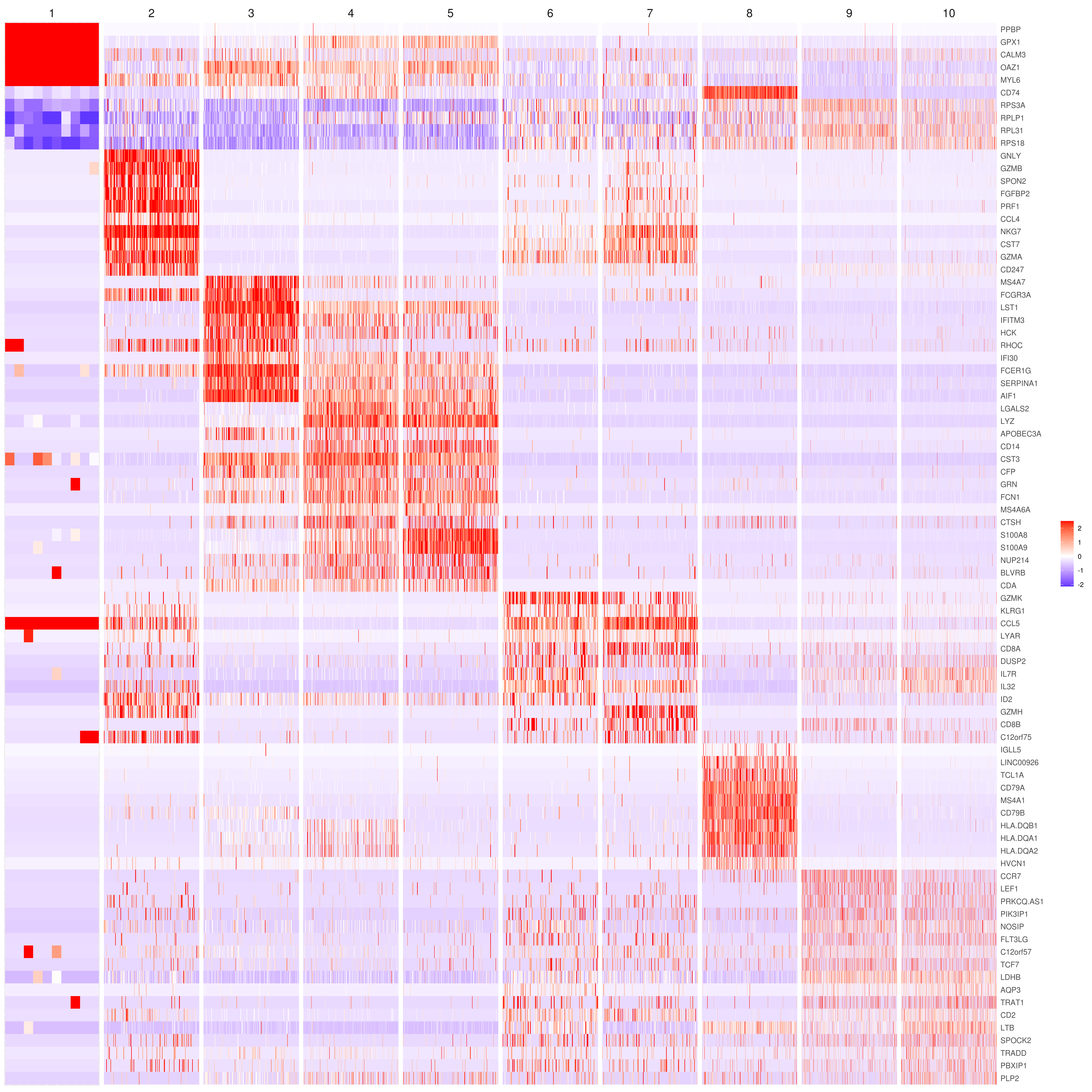
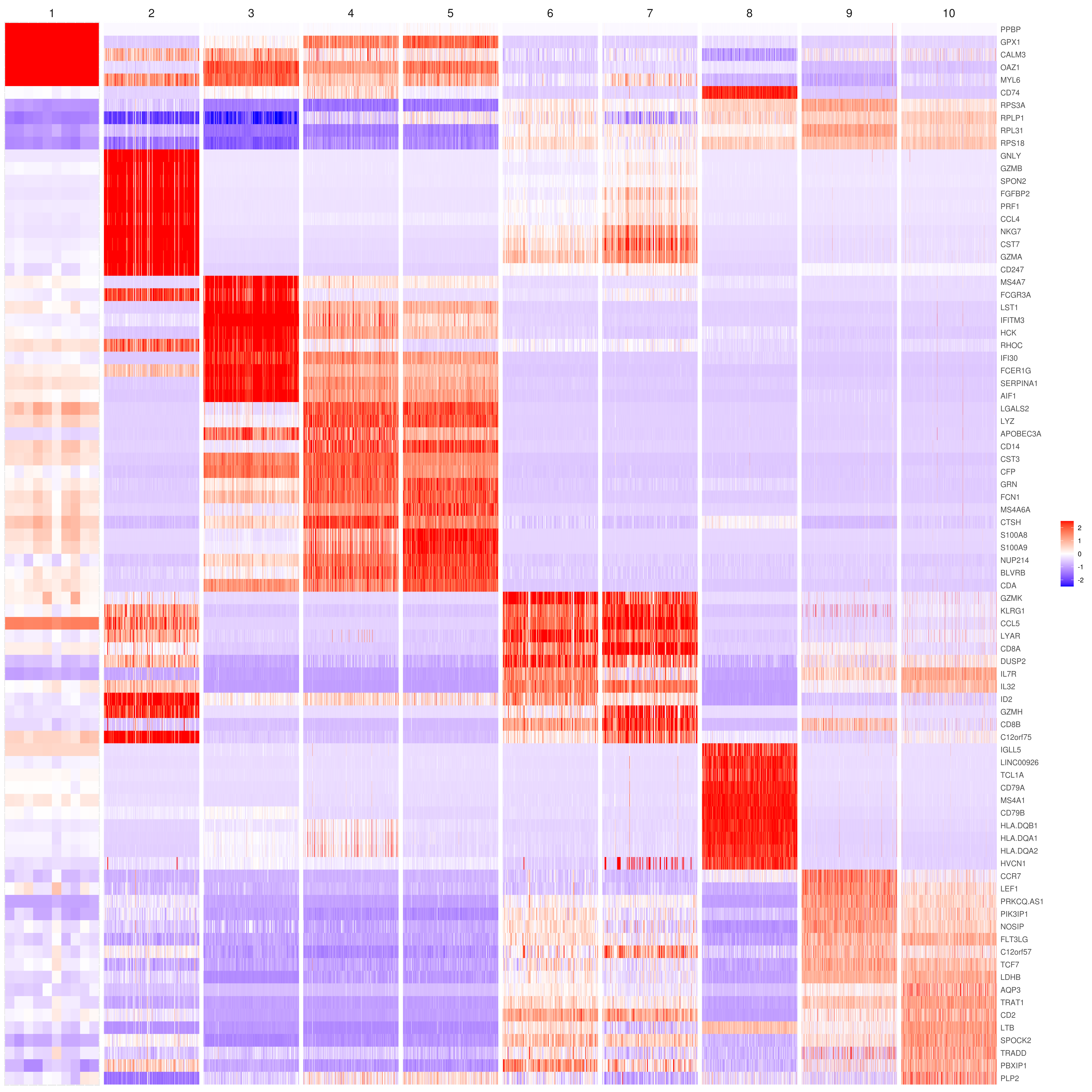
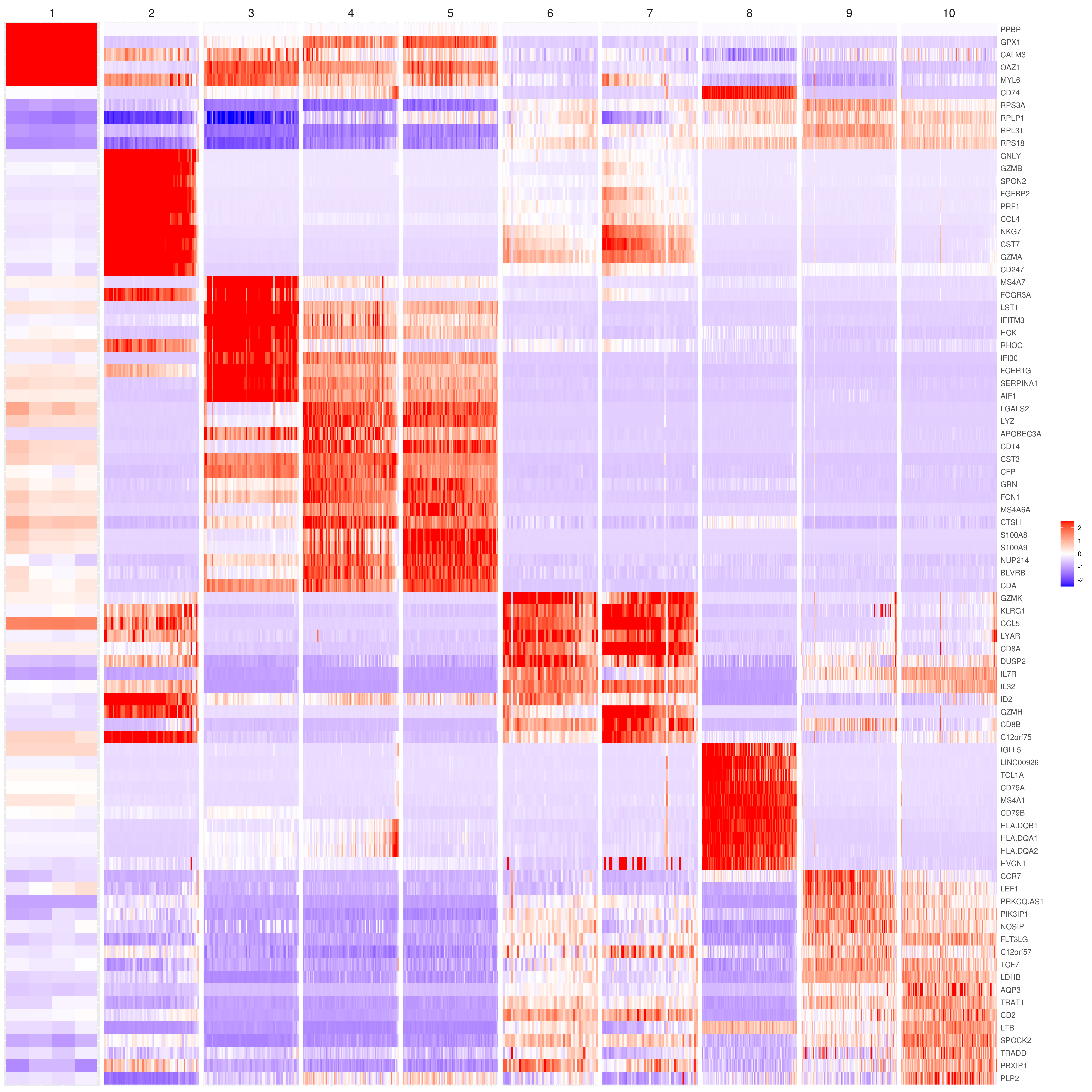
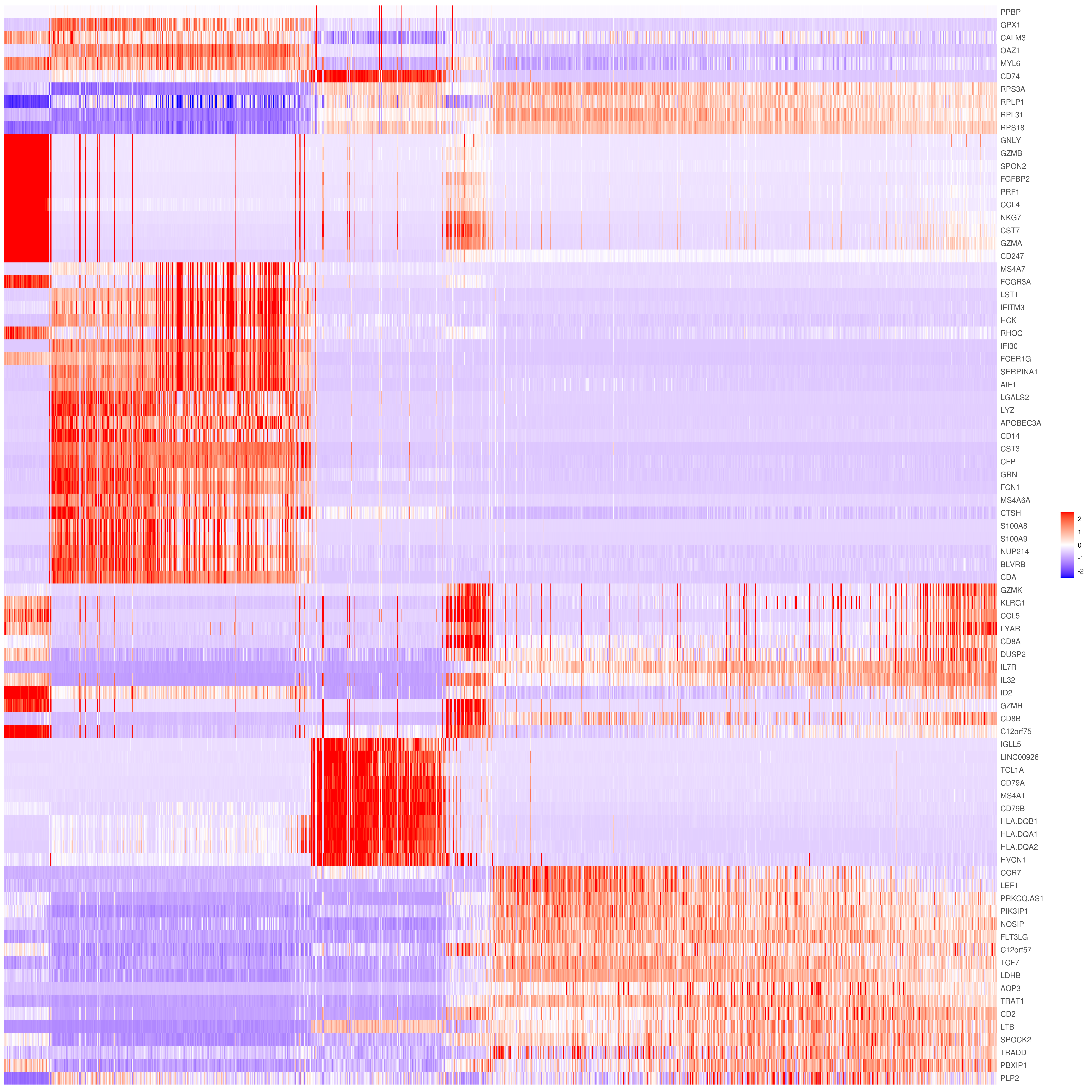
- Bubble heatmap
r
png('heatmap_bubble_gg_genes.png', width = 10, height = 20, units = 'in', res = 300)
bubble.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, conds.to.plot = NULL, size = "Percent.Expressed",colour = "Expression")
dev.off()
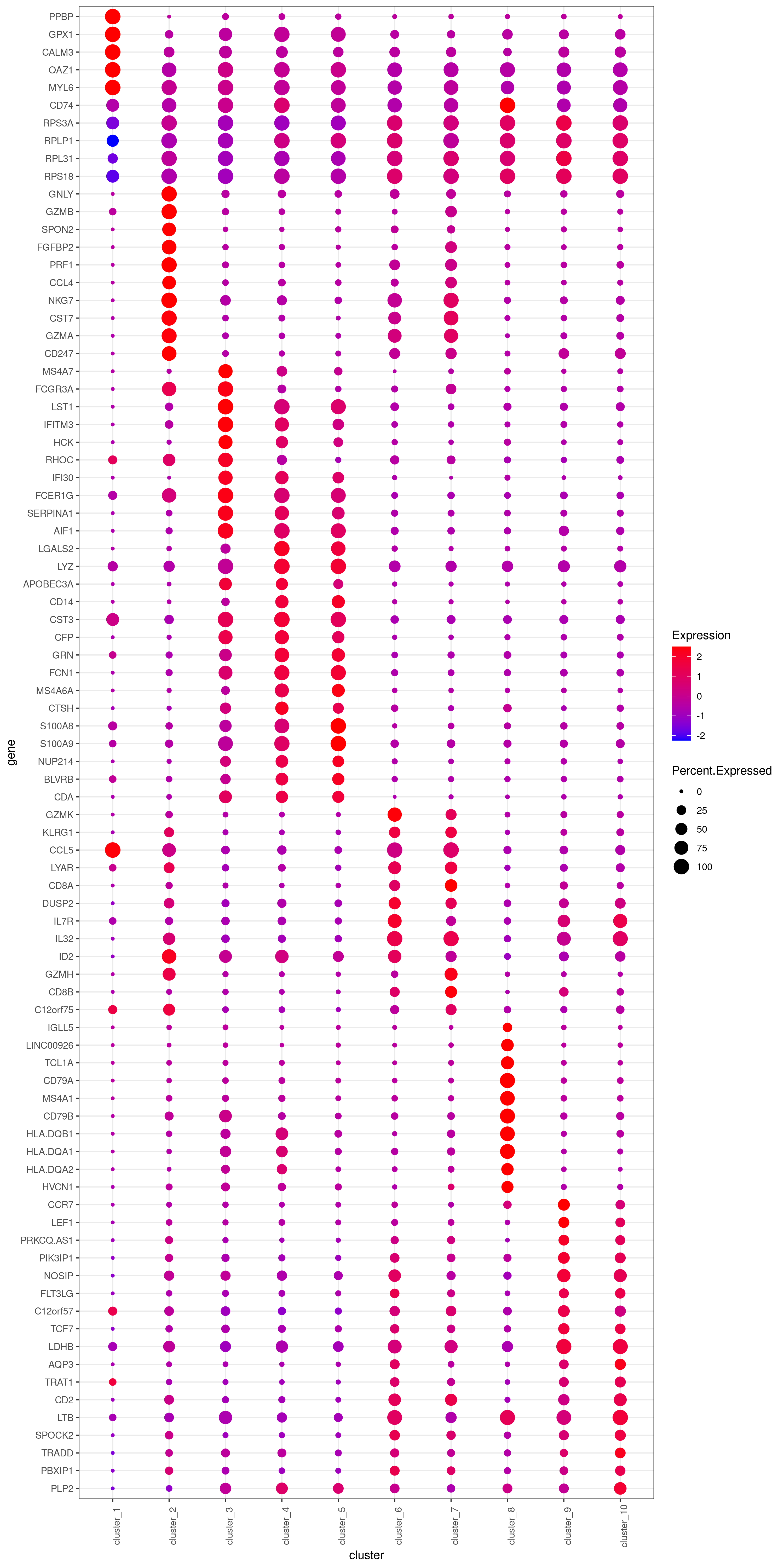
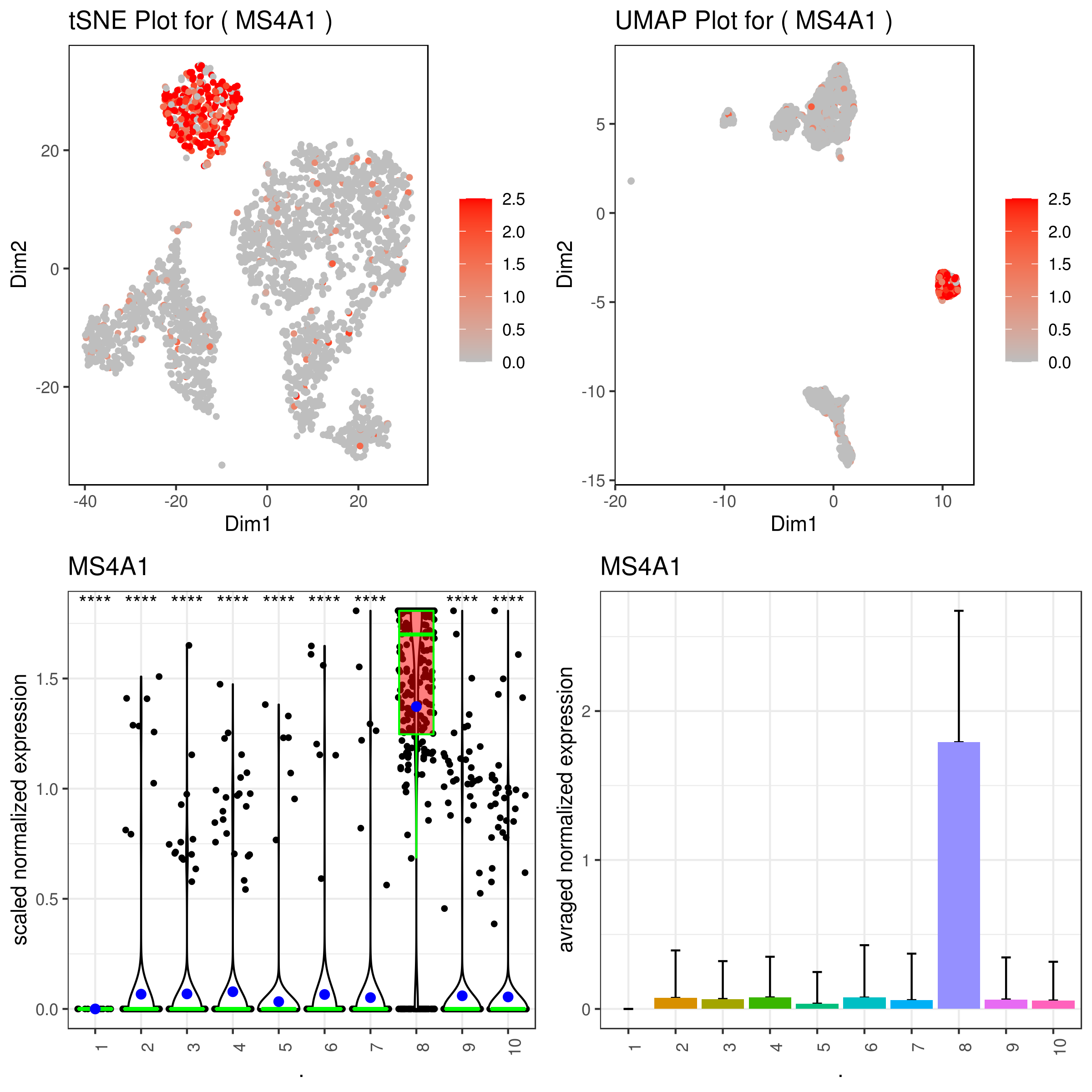
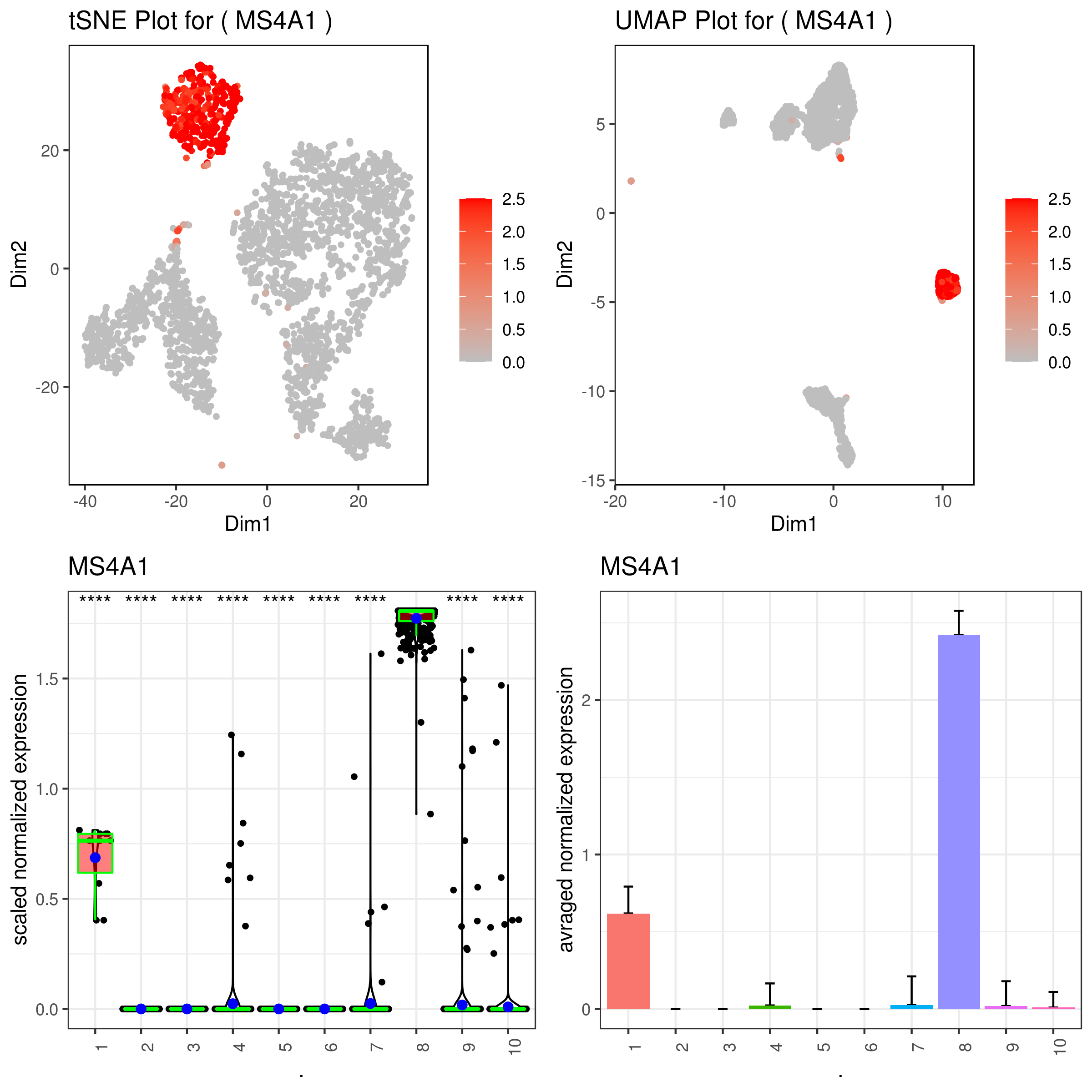
- Plot genes
```r A <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "scatterplot", interactive = F, out.name = "scatter_plot")
PCA 2D
B <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "scatterplot", interactive = F, out.name = "scatter_plot", plot.data.type = "umap")
Box Plot
C <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", box.to.test = 0, box.pval = "sig.signs", col.by = "clusters", plot.type = "boxplot", interactive = F, out.name = "box_plot")
Bar plot (to visualize fold changes)
D <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", col.by = "clusters", plot.type = "barplot", interactive = F, out.name = "bar_plot")
library(gridExtra)
png('gene.plots.png', width = 8, height = 8, units = 'in', res = 300)
grid.arrange(A,B,C,D)
dev.off()
same on imputed data
A <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "scatterplot", interactive = F, data.type = "imputed", out.name = "scatter_plot")
PCA 2D
B <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "scatterplot", interactive = F, out.name = "scatter_plot", data.type = "imputed", plot.data.type = "umap")
Box Plot
C <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", box.to.test = 0, box.pval = "sig.signs", col.by = "clusters", plot.type = "boxplot", interactive = F, data.type = "imputed", out.name = "box_plot")
Bar plot (to visualize fold changes)
D <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", col.by = "clusters", plot.type = "barplot", interactive = F, data.type = "imputed", out.name = "bar_plot")
library(gridExtra)
png('gene.plots_imputed.png', width = 8, height = 8, units = 'in', res = 300)
grid.arrange(A,B,C,D)
dev.off()
```
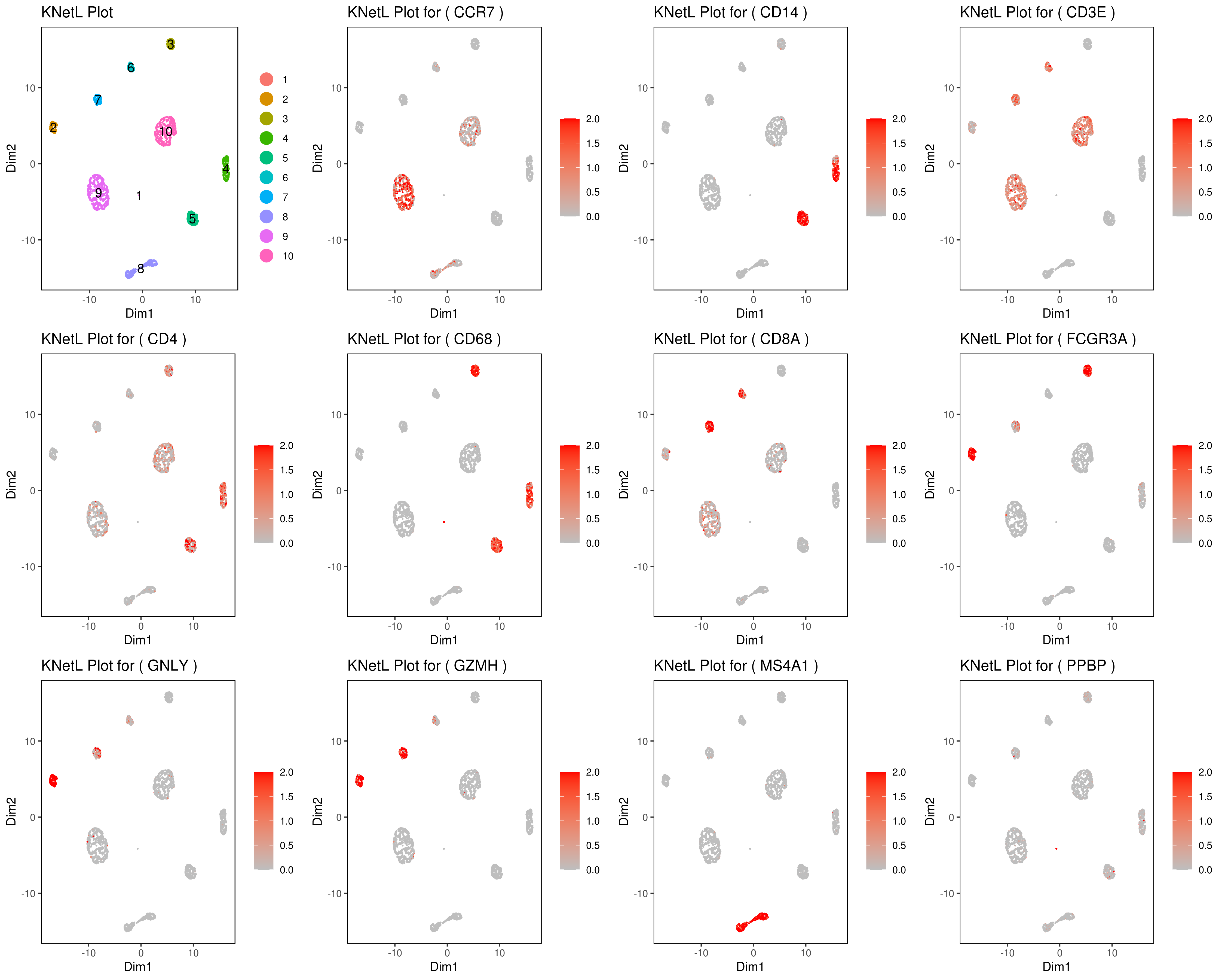
- Multiple plots
Change the section in between #### signs for different plots (e.g. boxplot, bar, ...).
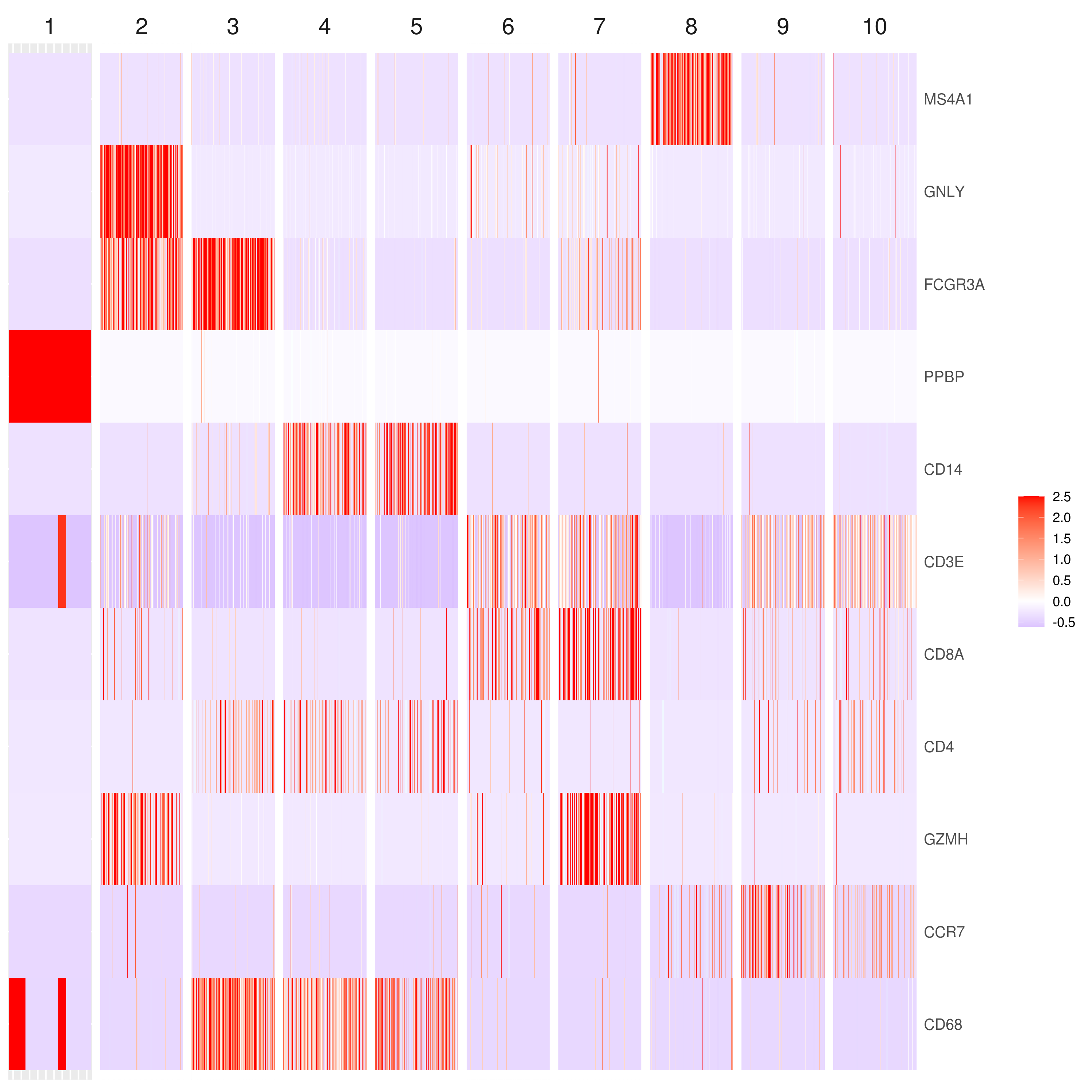
```r genelist = c("MS4A1","GNLY","FCGR3A","NKG7","CD14","CD3E","CD8A","CD4","GZMH","CCR7","CD68")
rm(list = ls(pattern="PL_")) for(i in genelist){
MyPlot <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = i,
interactive = F,
cell.size = 0.1,
plot.data.type = "knetl",
data.type = "main",
scaleValue = T,
min.scale = 0,max.scale = 2.0,
cell.transparency = 1)
NameCol=paste("PL",i,sep="_")
eval(call("<-", as.name(NameCol), MyPlot))
}
library(cowplot) filenames <- ls(pattern="PL_")
B <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.1,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) filenames <- c("B",filenames)
png('genesKNetL.png',width = 15, height = 12, units = 'in', res = 300) plotgrid(plotlist=mget(filenames)) dev.off()
or heatmap
heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = genelist, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters")
```
- Make your own customized plots
```r
You can export the data using this command (one or multiple genes):
gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", write.data = T, scaleValue = F, data.type = "main")
This would create a text file called "MS4A1.tsv".
head(read.table("MS4A1.tsv"))
V1 V2 Expression Clusters Conditions
WT_AAACATACAACCAC.1 12.499481 -11.436633 0.000000 9 WT
WT_AAACATTGAGCTAC.1 -8.783793 24.417999 1.942233 8 WT
WT_AAACATTGATCAGC.1 -2.650761 10.932273 0.000000 10 WT
WT_AAACCGTGCTTCCG.1 -28.916702 -5.542731 0.000000 4 WT
WT_AAACCGTGTATGCG.1 21.211557 -31.626822 0.000000 2 WT
WT_AAACGCACTGGTAC.1 5.225419 -5.141192 0.000000 10 WT
you use this to make your own plots in ggplot2 or other visualization packages.
```
- Annotating clusters
```r ###### Labeling the clusters
CD3E: only in T Cells
FCGR3A (CD16): in CD16+ monocytes and some expression NK cells
GNLY: NK cells
MS4A1: B cells
GZMH: in GZMH+ T8 cells and some expression NK cells
CD8A: in T8 cells
CD4: in T4 and some myeloid cells
CCR7: expressed more in memory cells
CD14: in CD14+ monocytes
CD68: in monocytes/MF
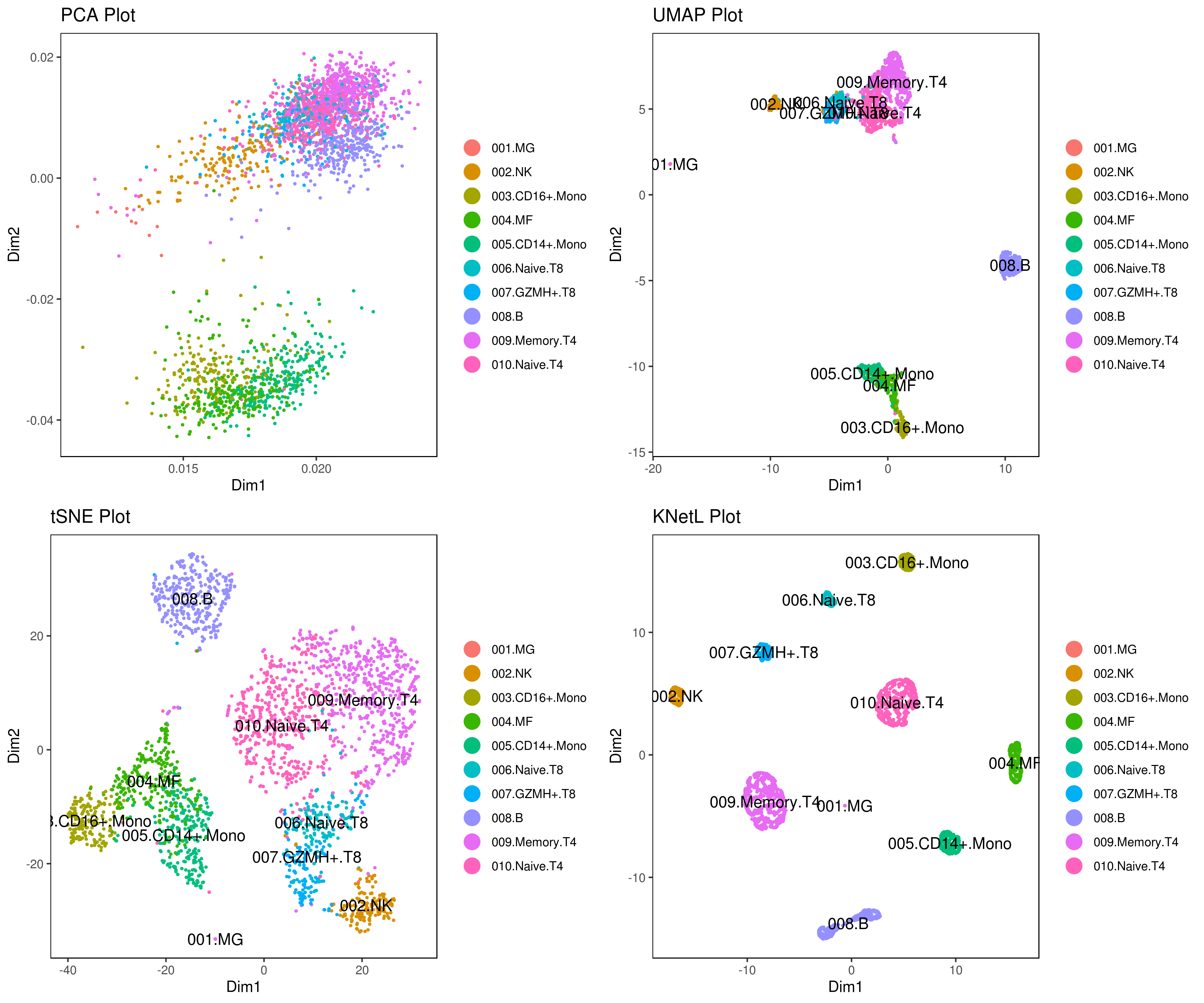
my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 1, to.clust = "001.MG") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 2, to.clust = "002.NK") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 3, to.clust = "003.CD16+.Mono") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 4, to.clust = "004.MF") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 5, to.clust = "005.CD14+.Mono") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 6, to.clust = "006.Naive.T8") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 7, to.clust = "007.GZMH+.T8") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 8, to.clust = "008.B") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 9, to.clust = "009.Memory.T4") my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 10, to.clust = "010.Naive.T4")
A= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) D= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T)
grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) ```

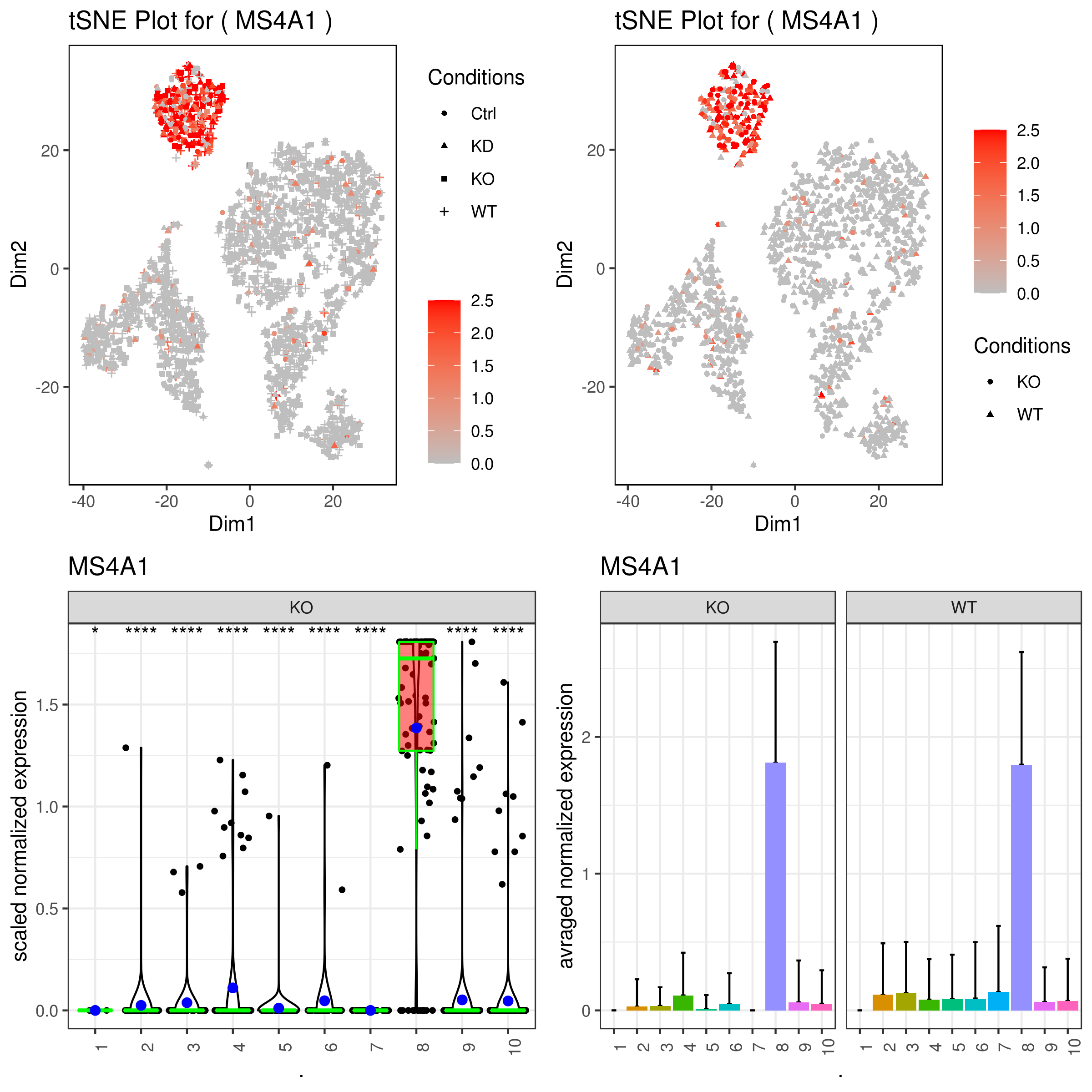
- Plotting conditions and clusters for genes
```r A <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "scatterplot", interactive = F, cell.transparency = 1, scaleValue = TRUE, min.scale = 0, max.scale = 2.5, back.col = "white", cond.shape = TRUE) B <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "scatterplot", interactive = F, cell.transparency = 1, scaleValue = TRUE, min.scale = 0, max.scale = 2.5, back.col = "white", cond.shape = TRUE, conds.to.plot = c("KO","WT"))
C <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "boxplot", interactive = F, back.col = "white", cond.shape = TRUE, conds.to.plot = c("KO"))
D <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "MS4A1", plot.type = "barplot", interactive = F, cell.transparency = 1, back.col = "white", cond.shape = TRUE, conds.to.plot = c("KO","WT"))
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) ```
- Some example 2D and 3D plots and plotting clusters and conditions at the same time
```r
example
cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 1, plot.type = "umap", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", col.by = "clusters", cell.transparency = 0.5, clust.dim = 2, cond.shape = T, interactive = T, out.name = "2dUMAPclusters_conds")
2D
cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 1, plot.type = "tsne", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", col.by = "clusters", cell.transparency = 0.5, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F)
interactive 2D
cluster.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "tsne", col.by = "clusters", clust.dim = 2, interactive = T, out.name = "tSNE2Dclusters")
interactive 3D
cluster.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "tsne", col.by = "clusters", clust.dim = 3, interactive = T, out.name = "tSNE3Dclusters")
Density plot for clusters
cluster.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "pca", col.by = "clusters", interactive = F, density=T)
Density plot for conditions
cluster.plot(my.obj, plot.type = "pca", col.by = "conditions", interactive = F, density=T)
cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 1, plot.type = "diffusion", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", col.by = "clusters", cell.transparency = 0.5, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F)
cluster.plot(my.obj,
cell.size = 1,
plot.type = "diffusion",
cell.color = "black",
back.col = "white",
col.by = "clusters",
cell.transparency = 0.5,
clust.dim = 3,
interactive = F)
```
To see the above made interactive plots click on these links: 2Dplot and 3Dplot







- Differential Expression Analysis
The differential expression (DE) analysis function in iCellR allows the users to choose from any combinations of clusters and conditions. For example, a user with two samples (say WT and KO) has four different possible ways of comparisons:
a-Comparing a cluster/clusters with different cluster/clusters (e.g. cluster 1 and 2 vs. 4)
b-Comparing a cluster/clusters with different cluster/clusters only in one/more condition/conditions (e.g. cluster 1 vs cluster 2 but only the WT sample)
c-Comparing a condition/conditions with different condition/conditions (e.g. WT vs KO)
d-Comparing a condition/conditions with different condition/conditions only in one/more cluster/clusters (e.g. cluster 1 WT vs cluster 1 KO)
```r diff.res <- run.diff.exp(my.obj, de.by = "clusters", cond.1 = c(1,4), cond.2 = c(2)) diff.res1 <- as.data.frame(diff.res) diff.res1 <- subset(diff.res1, padj < 0.05) head(diff.res1)
baseMean 1_4 2 foldChange log2FoldChange pval
AAK1 0.19554589 0.26338228 0.041792762 0.15867719 -2.655833 8.497012e-33
ABHD14A 0.09645732 0.12708519 0.027038379 0.21275791 -2.232715 1.151865e-11
ABHD14B 0.19132829 0.23177944 0.099644572 0.42991118 -1.217889 3.163623e-09
ABLIM1 0.06901900 0.08749258 0.027148089 0.31029018 -1.688310 1.076382e-06
AC013264.2 0.07383608 0.10584821 0.001279649 0.01208947 -6.370105 1.291674e-19
AC092580.4 0.03730859 0.05112053 0.006003441 0.11743700 -3.090041 5.048838e-07
padj
AAK1 1.294690e-28
ABHD14A 1.708446e-07
ABHD14B 4.636290e-05
ABLIM1 1.540087e-02
AC013264.2 1.950557e-15
AC092580.4 7.254675e-03
more examples
Comparing a condition/conditions with different condition/conditions (e.g. WT vs KO)
diff.res <- run.diff.exp(my.obj, de.by = "conditions", cond.1 = c("WT"), cond.2 = c("KO"))
Comparing a cluster/clusters with different cluster/clusters (e.g. cluster 1 and 2 vs. 4)
diff.res <- run.diff.exp(my.obj, de.by = "clusters", cond.1 = c(1,4), cond.2 = c(2))
Comparing a condition/conditions with different condition/conditions only in one/more cluster/clusters (e.g. cluster 1 WT vs cluster 1 KO)
diff.res <- run.diff.exp(my.obj, de.by = "clustBase.condComp", cond.1 = c("WT"), cond.2 = c("KO"), base.cond = 1)
Comparing a cluster/clusters with different cluster/clusters only in one/more condition/conditions (e.g. cluster 1 vs cluster 2 but only the WT sample)
diff.res <- run.diff.exp(my.obj, de.by = "condBase.clustComp", cond.1 = c(1), cond.2 = c(2), base.cond = "WT") ```
- Volcano and MA plots
```r
Volcano Plot
volcano.ma.plot(diff.res, sig.value = "pval", sig.line = 0.05, plot.type = "volcano", interactive = F)
MA Plot
volcano.ma.plot(diff.res, sig.value = "pval", sig.line = 0.05, plot.type = "ma", interactive = F) ```


- Merging, resetting, renaming and removing clusters
```r
let's say you want to merge cluster 3 and 2.
my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 3, to.clust = 2)
to reset to the original clusters run this.
my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, clust.reset = T)
you can also re-name the cluster numbers to cell types. Remember to reset after this so you can ran other analysis.
my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 7, to.clust = "B Cell")
Let's say for what ever reason you want to remove acluster, to do so run this.
my.obj <- clust.rm(my.obj, clust.to.rm = 1)
Remember that this would perminantly remove the data from all the slots in the object except frrom raw.data slot in the object. If you want to reset you need to start from the filtering cells step in the biginging of the analysis (using cell.filter function).
To re-position the cells run tSNE again
my.obj <- run.tsne(my.obj, clust.method = "gene.model", gene.list = "mymodelgenes.txt")
Use this for plotting as you make the changes
cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 1, plot.type = "tsne", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", col.by = "clusters", cell.transparency = 0.5, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F) ```






- Cell gating
```r my.plot <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "GNLY", plot.type = "scatterplot", clust.dim = 2, interactive = F)
cell.gating(my.obj, my.plot = my.plot, plot.type = "tsne")
or
my.plot <- cluster.plot(my.obj,
cell.size = 1,
cell.transparency = 0.5,
clust.dim = 2,
interactive = F)
```


After downloading the cell ids, use the following command to rename their cluster.
r
my.obj <- gate.to.clust(my.obj, my.gate = "cellGating.txt", to.clust = 10)
Batch correction (sample alignment) methods:
1- CPCA (iCellR)** recommended (faster than CCCA)
2- CCCA (iCellR)* recommended
3- MNN (scran wraper) optional
4- MultiCCA (Seurat wraper) optional
5- CPCA + ![]() KNetL based clustering (iCellR)*** recommended for best results!
KNetL based clustering (iCellR)*** recommended for best results!
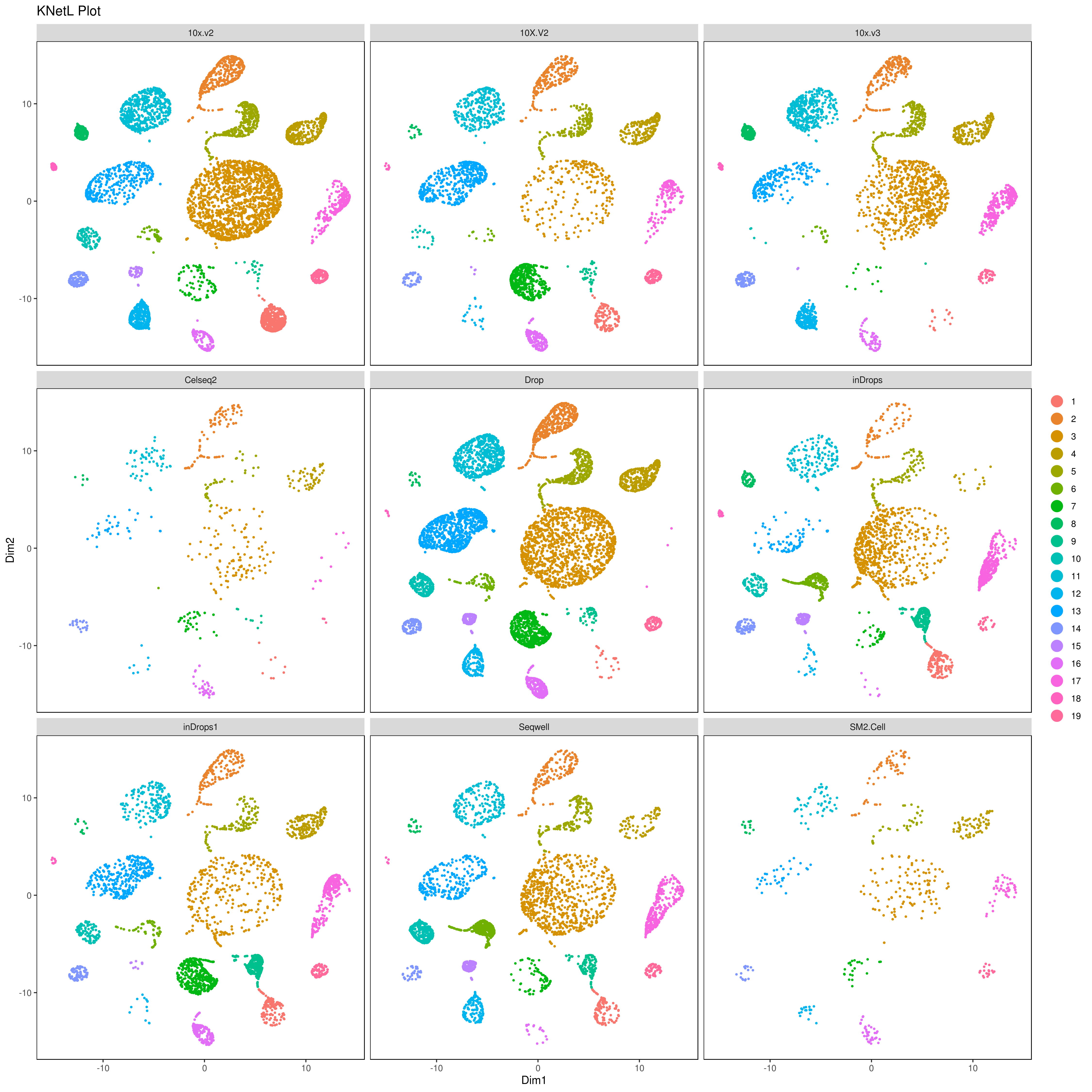
1- How to perform Combined Principal Component Alignment (CPCA)
We analyzed nine PBMC sample datasets provided by the Broad Institute to detect batch differences. These datasets were generated using varying technologies, including 10x Chromium v2 (3 samples), 10x Chromium v3, CEL-Seq2, Drop-seq, inDrop, Seq-Well and SMART-Seq. For more info read: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.31.019109v1.full
```r
download an object of 9 PBMC samples
sample.file.url = "https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/data/pbmc_data/my.obj.Robj"
download the file
download.file(url = sample.file.url, destfile = "my.obj.Robj", method = "auto")
load iCellR and the object
library(iCellR) load("my.obj.Robj")
run PCA on top 2000 genes
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj, top.rank = 2000)
find best genes for second round PCA or batch alignment
my.obj <- find.dim.genes(my.obj, dims = 1:30,top.pos = 20, top.neg = 20) length(my.obj@gene.model)
##### Batch alignment (CPCA method)
my.obj <- iba(my.obj,dims = 1:30, k = 10,ba.method = "CPCA", method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model)
impute data
my.obj <- run.impute(my.obj,dims = 1:10,data.type = "pca", nn = 10)
tSNE and UMAP
my.obj <- run.pc.tsne(my.obj, dims = 1:10) my.obj <- run.umap(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
save object
save(my.obj, file = "my.obj.Robj")
plot
library(gridExtra) A= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.1) B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.1) C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",col.by = "conditions",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.1) D=cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",col.by = "conditions",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.1)
png('AllClusts.png', width = 12, height = 12, units = 'in', res = 300) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) dev.off()
png('AllConds_clusts.png', width = 15, height = 15, units = 'in', res = 300) cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 0.5, plot.type = "umap", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", cell.transparency = 1, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F,cond.facet = T) dev.off()
genelist = c("PPBP","LYZ","MS4A1","GNLY","FCGR3A","NKG7","CD14","S100A9","CD3E","CD8A","CD4","CD19","IL7R","FOXP3","EPCAM")
for(i in genelist){ MyPlot <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = i, interactive = F, conds.to.plot = NULL, cell.size = 0.1, data.type = "main", plot.data.type = "umap", scaleValue = T, min.scale = -2.5,max.scale = 2.0, cell.transparency = 1) NameCol=paste("PL",i,sep="_") eval(call("<-", as.name(NameCol), MyPlot)) }
UMAP = cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.1, anno.size=5) library(cowplot) filenames <- ls(pattern="PL_") filenames <- c("UMAP", filenames)
png('genes.png',width = 18, height = 15, units = 'in', res = 300) plot_grid(plotlist=mget(filenames)) dev.off()
```



2- How to perform Combined Coverage Correction Alignment (CCCA)
```r
same as above only change the option to CCCA
my.obj <- iba(my.obj,dims = 1:30, k = 10,ba.method = "CCCA", method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model) ```

3- How to perform mutual nearest neighbor (MNN) sample alignment
```r
same as above only use run.mnn function instead of iba.
Run MNN
This would automatically run all the samples in your experiment
library(scran) my.obj <- run.mnn(my.obj, k=20, d=50, method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model)
detach the scran pacakge after MNN as it masks some of the functions
detach("package:scran", unload=TRUE) ```

4- How to perform Seurat's MultiCCA sample alignment
```r
same as above only use run.anchor function instead of iba.
Run Anchor
This would automatically run all the samples in your experiment
library(Seurat) my.obj <- run.anchor(my.obj, normalization.method = "SCT", scale.factor = 10000, selection.method = "vst", nfeatures = 2000, dims = 1:20) ```

5- How to perform CPCA + KNetL based clustering for sample alignment/integration
```r
download an object of 9 PBMC samples
sample.file.url = "https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/example2/my.obj.Robj"
download the file
download.file(url = sample.file.url, destfile = "my.obj.Robj", method = "auto")
load iCellR and the object
library(iCellR) load("my.obj.Robj")
run PCA on top 2000 genes
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj, top.rank = 2000)
find best genes for second round PCA or batch alignment
my.obj <- find.dim.genes(my.obj, dims = 1:30,top.pos = 20, top.neg = 20) length(my.obj@gene.model)
##### Batch alignment (CPCA method)
my.obj <- iba(my.obj,dims = 1:30, k = 10,ba.method = "CPCA", method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model)
impute data
my.obj <- run.impute(my.obj,dims = 1:10,data.type = "pca", nn = 10)
tSNE and UMAP
my.obj <- run.pc.tsne(my.obj, dims = 1:10) my.obj <- run.umap(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
run KNetL
my.obj <- run.knetl(my.obj, dims = 1:20, k = 400)
cluster based on KNetL coordinates
The object is already clustered but here is an example:
my.obj <- iclust(my.obj, k = 300, data.type = "knetl")
save object
save(my.obj, file = "my.obj.Robj")
plot 1
A= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=F) B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=F) C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=F) D= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=F)
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D)
plot 2
cluster.plot(my.obj, cell.size = 0.5, plot.type = "knetl", cell.color = "black", back.col = "white", cell.transparency = 1, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F,cond.facet = T)
plot 3
genelist = c("LYZ","MS4A1","GNLY","FCGR3A","NKG7","CD14","S100A9","CD3E","CD8A","CD4","CD19","KLRB1","LTB","IL7R","GZMH","CD68","CCR7","CD68","CD69","CXCR4","IFITM3","IL32","JCHAIN","VCAN","PPBP")
rm(list = ls(pattern="PL")) for(i in genelist){ MyPlot <- gene.plot(my.obj, gene = i, interactive = F, cell.size = 0.1, plot.data.type = "knetl", data.type = "main", scaleValue = T, min.scale = -2.5,max.scale = 2.0, cell.transparency = 1) NameCol=paste("PL",i,sep="") eval(call("<-", as.name(NameCol), MyPlot)) }
library(cowplot) filenames <- ls(pattern="PL_")
B <- cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.1,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=T) filenames <- c("B",filenames)
plot_grid(plotlist=mget(filenames))
```
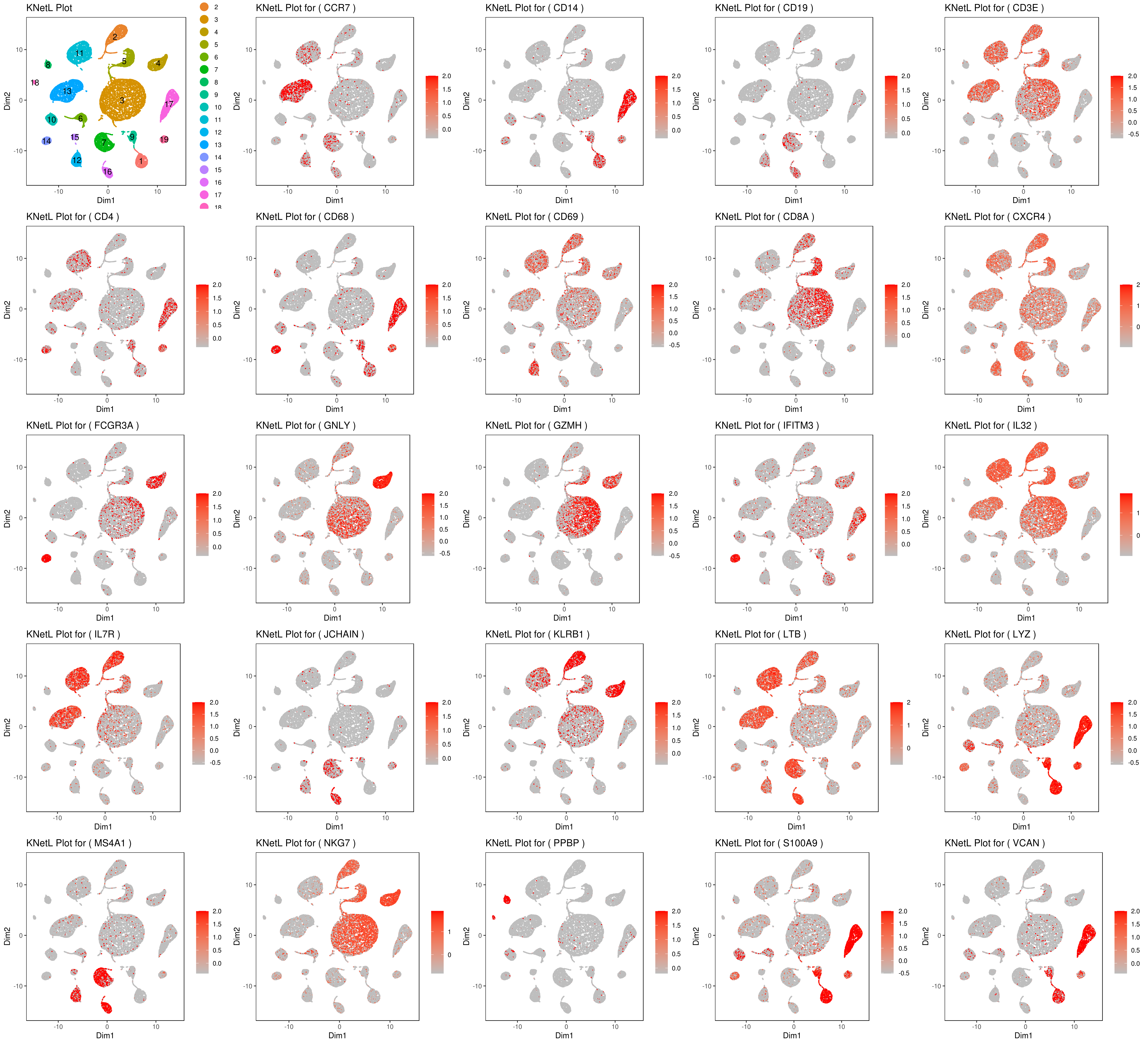
- Pseudotime analysis
```r MyGenes <- top.markers(marker.genes, topde = 50, min.base.mean = 0.2) MyGenes <- unique(MyGenes)
pseudotime.tree(my.obj, marker.genes = MyGenes, type = "unrooted", clust.method = "complete")
or
pseudotime.tree(my.obj, marker.genes = MyGenes, type = "classic", clust.method = "complete")
pseudotime.tree(my.obj, marker.genes = MyGenes, type = "jitter", clust.method = "complete")
```





- Pseudotime analysis using monocle
```r library(monocle)
MyMTX <- my.obj@main.data GeneAnno <- as.data.frame(row.names(MyMTX)) colnames(GeneAnno) <- "geneshortname" row.names(GeneAnno) <- GeneAnno$geneshortname cell.cluster <- (my.obj@best.clust) Ha <- data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(row.names(cell.cluster)),'_',fixed=TRUE)))[1] clusts <- paste("cl.",as.character(cell.cluster$clusters),sep="") cell.cluster <- cbind(cell.cluster,Ha,clusts) colnames(cell.cluster) <- c("Clusts","iCellR.Conds","iCellR.Clusts") Samp <- new("AnnotatedDataFrame", data = cell.cluster) Anno <- new("AnnotatedDataFrame", data = GeneAnno) my.monoc.obj <- newCellDataSet(as.matrix(MyMTX),phenoData = Samp, featureData = Anno)
find disperesedgenes
my.monoc.obj <- estimateSizeFactors(my.monoc.obj) my.monoc.obj <- estimateDispersions(my.monoc.obj) disp_table <- dispersionTable(my.monoc.obj)
unsupclusteringgenes <- subset(disptable, meanexpression >= 0.1) my.monoc.obj <- setOrderingFilter(my.monoc.obj, unsupclusteringgenes$gene_id)
tSNE
my.monoc.obj <- reduceDimension(my.monoc.obj, maxcomponents = 2, numdim = 10,reduction_method = 'tSNE', verbose = T)
cluster
my.monoc.obj <- clusterCells(my.monoc.obj, num_clusters = 10)
plot conditions and clusters based on iCellR analysis
A <- plotcellclusters(my.monoc.obj, 1, 2, color = "iCellR.Conds") B <- plotcellclusters(my.monoc.obj, 1, 2, color = "iCellR.Clusts")
plot clusters based monocle analysis
C <- plotcellclusters(my.monoc.obj, 1, 2, color = "Cluster")
get marker genes from iCellR analysis
MyGenes <- top.markers(marker.genes, topde = 30, min.base.mean = 0.2) my.monoc.obj <- setOrderingFilter(my.monoc.obj, MyGenes)
my.monoc.obj <- reduceDimension(my.monoc.obj, max_components = 2,method = 'DDRTree')
order cells
my.monoc.obj <- orderCells(my.monoc.obj)
plot based on iCellR analysis and marker genes from iCellR
D <- plotcelltrajectory(my.monoc.obj, color_by = "iCellR.Clusts")
heatmap genes from iCellR
plotpseudotimeheatmap(my.monoc.obj[MyGenes,], cores = 1, clusterrows = F, usegeneshortname = T, show_rownames = T) ```


How to demultiplex with hashtag oligos (HTOs)
```r
Read an example file
my.hto <- read.table(file = system.file('extdata', 'dense_umis.tsv', package = 'iCellR'), as.is = TRUE)
or
my.data <- load10x("filteredfeaturebc_matrix",gene.name = 2)
Your HTOs are usually in the end of all the gene names
tail(row.names(my.data),5)
[1] "TotalSeq.C0254anti.humanHashtag4Antibody"
[2] "TotalSeq.C0255anti.humanHashtag5Antibody"
[3] "TotalSeq.C0256anti.humanHashtag6Antibody"
[4] "TotalSeq.C0257anti.humanHashtag7Antibody"
[5] "TotalSeq.C0258anti.humanHashtag8Antibody"
your HTOs are usually in the matrix and have names that are different than gene names
Your HTO names
HTOs <- grep("^TotalSeq",row.names(my.data),value=T)
your gene names
RNAs <- subset(row.names(my.data), !(row.names(my.data) %in% HTOs))
MyHTOs <- subset(my.data, row.names(my.data) %in% HTOs) MyRNAs <- subset(my.data, row.names(my.data) %in% RNAs)
dim(MyHTOs) dim(MyRNAs)
run annotation
data <- hto.anno(hto.data = MyHTOs, cov.thr = 3, assignment.thr = 80) data <- (cbind(ID = rownames(data),data)) write.table((data),"HTOsannotatedHSThigh.tsv",sep="\t", row.names =F)
head(data)
Hashtag1-GTCAACTCTTTAGCG Hashtag2-TGATGGCCTATTGGG
TGACAACAGGGCTCTC 3 18
AAGGAGCGTCATTAGC 7 24
AGTGAGGAGACTGTAA 7 1761
ATCCACCCATGTTCCC 753 20
AAACGGGCAGGACCCT 728 24
ATGTGTGAGTCTTGCA 4 25
Hashtag3-TTCCGCCTCTCTTTG Hashtag4-AGTAAGTTCAGCGTA
TGACAACAGGGCTCTC 7 0
AAGGAGCGTCATTAGC 8 0
AGTGAGGAGACTGTAA 5 0
ATCCACCCATGTTCCC 3 0
AAACGGGCAGGACCCT 3 0
ATGTGTGAGTCTTGCA 370 0
Hashtag5-AAGTATCGTTTCGCA Hashtag7-TGTCTTTCCTGCCAG unmapped
TGACAACAGGGCTCTC 890 5 17
AAGGAGCGTCATTAGC 2 3 3
AGTGAGGAGACTGTAA 11 3 87
ATCCACCCATGTTCCC 5 6 18
AAACGGGCAGGACCCT 9 3 16
ATGTGTGAGTCTTGCA 9 1011 25
assignment.annotation percent.match coverage low.cov
TGACAACAGGGCTCTC Hashtag5-AAGTATCGTTTCGCA 94.68085 940 FALSE
AAGGAGCGTCATTAGC Hashtag2-TGATGGCCTATTGGG 51.06383 47 TRUE
AGTGAGGAGACTGTAA Hashtag2-TGATGGCCTATTGGG 93.97012 1874 FALSE
ATCCACCCATGTTCCC Hashtag1-GTCAACTCTTTAGCG 93.54037 805 FALSE
AAACGGGCAGGACCCT Hashtag1-GTCAACTCTTTAGCG 92.97573 783 FALSE
ATGTGTGAGTCTTGCA Hashtag7-TGTCTTTCCTGCCAG 70.01385 1444 FALSE
assignment.threshold
TGACAACAGGGCTCTC good.assignment
AAGGAGCGTCATTAGC unsure
AGTGAGGAGACTGTAA good.assignment
ATCCACCCATGTTCCC good.assignment
AAACGGGCAGGACCCT good.assignment
ATGTGTGAGTCTTGCA unsure
plot
A = ggplot(data, aes(assignment.annotation,percent.match)) + geomjitter(alpha = 0.25, color = "blue") + geomboxplot(alpha = 0.5) + themebw() + theme(axis.text.x=elementtext(angle=90))
B = ggplot(data, aes(low.cov,percent.match)) + geomjitter(alpha = 0.25, color = "blue") + geomboxplot(alpha = 0.5) + themebw() + theme(axis.text.x=elementtext(angle=90))
library(gridExtra) Name="HTO_stats.png" png(Name, width = 8, height = 8, units = 'in', res = 300) grid.arrange(A,B,ncol=2) dev.off() ```

- Filtering HTOs and merging the samples
```r
let's see how many cells are there
dim(data)
let's say you want to have the cells that are above 80 % likelihood of belonging to an HTO
data <- subset(data, percent.match > 80)
let's see how many cells are left
dim(data)
# Take the HTO IDs that passed filtering bestHTOs <- as.character(unique(data$assignment.annotation))
create new files (matrices) for each HTO (with number of cells added to the folder names)
library(Matrix) for(i in bestHTOs){ sample <- row.names(subset(data,data$assignment.annotation == i)) message(paste(" getting sample",i,"...")) sample <- MyRNAs[ , which(names(MyRNAs) %in% sample)] message(paste(" number of cells",dim(sample)[2])) Name=paste("RNAs",i,dim(sample)[2],sep="_") message(paste(" writing sample",i,"...")) dir.create(Name) COLs <- colnames(sample) ROWs <- row.names(sample) colnames(sample) <- NULL row.names(sample) <- NULL sparse.gbm <- Matrix(as.matrix.data.frame(sample), sparse = T ) Name1=paste(Name,"matrix.mtx",sep="/") writeMM(obj = sparse.gbm, file=Name1) Name1=paste(Name,"barcodes.tsv.gz",sep="/") write.table((COLs),gzfile(Name1), row.names =FALSE, quote = FALSE, col.names = FALSE) MY.ROWs <- cbind(ROWs,ROWs) Name1=paste(Name,"genes.tsv.gz",sep="/") write.table((MY.ROWs),gzfile(Name1),sep="\t", row.names =F, quote = FALSE, col.names = FALSE) }
example data aggregation for 2 samples/HTOs
my.data <- data.aggregation(samples = c("HTO1","HTO2"), condition.names = c("HTO1","HTO2"))
make iCellR object
my.obj <- make.obj(my.data)
The rest is as above :)
```
How to use i.score to rank/score the cells:
This data is from this publication (GEO number: GSE156246 and PMID: 34911733)
This is a how to guide to run i.score function in iCellR and to reproduce the above published data for G0 and non G0 cells.
Download the sample iCellR objects (used in the publication) from here: https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/i.score/ (my.obj@raw.data in these objects are log normalized)
Download sample gene signatures from here: https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/i.score/gene_signatures.tar.gz (gene signatures used in the publication are in the supplementary data of the paper)
```r
load sample gene signature that are in iCellR
(these cell cycle signatures are from here: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-019-1884-x)
library(iCellR) G0 <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'G0.txt', package = 'iCellR')) G1S <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'G1S.txt', package = 'iCellR')) G2M <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'G2M.txt', package = 'iCellR')) M <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'M.txt', package = 'iCellR')) MG1 <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'MG1.txt', package = 'iCellR')) S <- readLines(system.file('extdata', 'S.txt', package = 'iCellR'))
load all the gene signatures
Melnick10GILMORECORENFKBPATHWAY.txt <- readLines("10GILMORECORENFKBPATHWAY.txt") Melnick11HALLMARKMYCTARGETSV1.txt <- readLines("11HALLMARKMYCTARGETSV1.txt") Melnick12GOBETACATENINBINDING.txt <- readLines("12GOBETACATENINBINDING.txt") Melnick13PIDBETACATENINNUCPATHWAY.txt <- readLines("13PIDBETACATENINNUCPATHWAY.txt") Melnick14PIDWNTSIGNALINGPATHWAY.txt <- readLines("14PIDWNTSIGNALINGPATHWAY.txt") Melnick15PIDWNTCANONICALPATHWAY.txt <- readLines("15PIDWNTCANONICALPATHWAY.txt") Melnick16PribludaSENESCENCEINFLAMMATORYGENES.txt <- readLines("16PribludaSENESCENCEINFLAMMATORYGENES.txt") Melnick17FRIDMANSENESCENCEDN.txt <- readLines("17FRIDMANSENESCENCEDN.txt") Melnick18FRIDMANSENESCENCEUP.txt <- readLines("18FRIDMANSENESCENCEUP.txt") Melnick19DeJONGELSCTOP50genes.txt <- readLines("19DeJONGELSCTOP50genes.txt") Melnick1AML1566AraCUP.txt <- readLines("1AML1566AraCUP.txt") Melnick20GALLEUKEMICSTEMCELLUP.txt <- readLines("20GALLEUKEMICSTEMCELLUP.txt") Melnick21GALLEUKEMICSTEMCELLDN.txt <- readLines("21GALLEUKEMICSTEMCELLDN.txt") Melnick22EPPERTCEHSCLSC.txt <- readLines("22EPPERTCEHSCLSC.txt") Melnick23JAATINENHEMATOPOIETICSTEMCELLUP.txt <- readLines("23JAATINENHEMATOPOIETICSTEMCELLUP.txt") Melnick24JAATINENHEMATOPOIETICSTEMCELLDN.txt <- readLines("24JAATINENHEMATOPOIETICSTEMCELLDN.txt") Melnick25INFLAMMATORYRESPONSE.txt <- readLines("25INFLAMMATORYRESPONSE.txt") Melnick26RAMALHOSTEMNESSDN.txt <- readLines("26RAMALHOSTEMNESSDN.txt") Melnick27RAMALHOSTEMNESSUP.txt <- readLines("27RAMALHOSTEMNESSUP.txt") Melnick28REACTOMEREGULATIONOFMITOTICCELLCYCLE.txt <- readLines("28REACTOMEREGULATIONOFMITOTICCELLCYCLE.txt") Melnick2AML1566AraCDN.txt <- readLines("2AML1566AraCDN.txt") Melnick3DUYCISGUP.txt <- readLines("3DUYCISGUP.txt") Melnick4DUYCISGDN.txt <- readLines("4DUYCISGDN.txt") Melnick5DIAPAUSEUPBOROVIAK.txt <- readLines("5DIAPAUSEUPBOROVIAK.txt") Melnick6BOROVIAKDIAPAUSEDN.txt <- readLines("6BOROVIAKDIAPAUSEDN.txt") Melnick7SASPCOPPE.txt <- readLines("7SASPCOPPE.txt") Melnick8SALDIVARATRSUPPRESSEDTARGETS.txt <- readLines("8SALDIVARATRSUPPRESSEDTARGETS.txt") Melnick9BIOCARTANFKBPATHWAY.txt <- readLines("9BIOCARTANFKBPATHWAY.txt") diapauseneg.txt <- readLines("diapauseneg.txt") diapauseposandneg.txt <- readLines("diapauseposandneg.txt") diapausepos.txt <- readLines("diapausepos.txt") DTPsig150Down.txt <- readLines("DTPsig150Down.txt") DTPsig150up.txt <- readLines("DTPsig150up.txt") Lumuniqdown.txt <- readLines("Lumuniqdown.txt") Lumuniqup.txt <- readLines("Lumuniqup.txt") Mesuniqdown.txt <- readLines("Mesuniqdown.txt") Mesuniqup.txt <- readLines("Mesuniqup.txt") panDTPDN.txt <- readLines("newpanDTPDN.txt") panDTPup.txt <- readLines("newpanDTPup.txt") mesDTPincludedDEGDN.txt <- readLines("newmesDTPincludedDEGDN.txt") mesDTPincludedDEGUP.txt <- readLines("newmesDTPincludedDEGUP.txt") lumDTPincludedDEGDN.txt <- readLines("newlumDTPincludedDEGDN.txt") lumDTPincludedDEGUP.txt <- readLines("newlumDTPincludedDEGUP.txt") lumDTPspecificUPnoCC.txt <- readLines("newlumDTPspecificUPnoCC.txt") mesDTPspecificUPnoCC.txt <- readLines("newmesDTPspecificUPnoCC.txt") ```
Group all the signatures in one character object:
r
All <- c("Melnick_10_GILMORE_CORE_NFKB_PATHWAY.txt","Melnick_11_HALLMARK_MYC_TARGETS_V1.txt","Melnick_12_GO_BETA_CATENIN_BINDING.txt","Melnick_13_PID_BETA_CATENIN_NUC_PATHWAY.txt","Melnick_14_PID_WNT_SIGNALING_PATHWAY.txt","Melnick_15_PID_WNT_CANONICAL_PATHWAY.txt","Melnick_16_Pribluda_SENESCENCE_INFLAMMATORY_GENES.txt","Melnick_17_FRIDMAN_SENESCENCE_DN.txt","Melnick_18_FRIDMAN_SENESCENCE_UP.txt","Melnick_19_DeJONGE_LSC_TOP50_genes.txt","Melnick_1_AML1566_AraC_UP.txt","Melnick_20_GAL_LEUKEMIC_STEM_CELL_UP.txt","Melnick_21_GAL_LEUKEMIC_STEM_CELL_DN.txt","Melnick_22_EPPERT_CE_HSC_LSC.txt","Melnick_23_JAATINEN_HEMATOPOIETIC_STEM_CELL_UP.txt","Melnick_24_JAATINEN_HEMATOPOIETIC_STEM_CELL_DN.txt","Melnick_25_INFLAMMATORY_RESPONSE.txt","Melnick_26_RAMALHO_STEMNESS_DN.txt","Melnick_27_RAMALHO_STEMNESS_UP.txt","Melnick_28_REACTOME_REGULATION_OF_MITOTIC_CELL_CYCLE.txt","Melnick_2_AML1566_AraC_DN.txt","Melnick_3_DUY_CISG_UP.txt","Melnick_4_DUY_CISG_DN.txt","Melnick_5_DIAPAUSE_UP_BOROVIAK.txt","Melnick_6_BOROVIAK_DIAPAUSE_DN.txt","Melnick_7_SASP_COPPE.txt","Melnick_8_SALDIVAR_ATR_SUPPRESSED_TARGETS.txt","Melnick_9_BIOCARTA_NFKB_PATHWAY.txt","diapause_neg.txt","diapause_pos_and_neg.txt","diapause_pos.txt","DTP_sig_150_Down.txt","DTP_sig_150_up.txt","Lum_uniq_down.txt","Lum_uniq_up.txt","Mes_uniq_down.txt","Mes_uniq_up.txt","G0","G1S","G2M","M","MG1","S","panDTP_DN.txt","panDTP_up.txt","mes_DTP_included_DEG_DN.txt","mes_DTP_included_DEG_UP.txt","lum_DTP_included_DEG_DN.txt","lum_DTP_included_DEG_UP.txt","lum_DTP_specific_UP_noCC.txt","mes_DTP_specific_UP_noCC.txt")
Load your sample iCellR object
r
load("BT474_DTP.Robj")
Score for cell cycle gene signatures with any of the following scoring methods: tirosh, mean, sum, gsva, ssgsea, zscore and plage. (tirosh and zscore methods are recommended to perform best)
r
dat1 <- i.score(my.obj, scoring.List = c("G0","G1S","G2M","M","MG1","S") ,scoring.method = "tirosh",return.stats = TRUE, data.type = "raw.data")
write.table(dat1,"tirosh_G0.tsv",sep="\t")
Score for all the other signatures (tirosh, mean, sum, gsva, ssgsea, zscore and plage)
r
dat2 <- i.score(my.obj, scoring.List = All ,scoring.method = "tirosh",return.stats = TRUE, data.type = "raw.data")
write.table(dat2,"tirosh_all.tsv",sep="\t")
Prepare data to plot (marge dat1 and dat2)
```r dir.create("boxplotstirosh") setwd("boxplotstirosh")
data <- read.table("../tiroshall.tsv",sep="\t",header=T) dataCC <- read.table("../tiroshG0.tsv",sep="\t",header=T)
df = as.character(dataCC$assignment.annotation) == "G0" df[ df == "TRUE" ] <- "GO" df[ df == "FALSE" ] <- "nonGO"
data <- cbind(cond = rep("sample",length(df)), ID = rownames(data), assignment.annotation = dataCC$assignment.annotation, GO_nonGO = df, data)
write.table((data),file="data.xls",sep="\t", row.names =F) ```
Plot all the signatures individually:
```r data <- read.table("data.xls",sep="\t",header=T)
g <- head(data)[5:55] g <- colnames(g)
library(ggpubr)
for(i in g){ name <- paste("boxplot",i,".png",sep="") png(name,width = 6, height = 4, units = 'in', res = 300) print(ggplot(data, aes(x= GOnonGO,y=data[, i],fill = GOnonGO, alpha = 0.5)) + geomjitter(size = 0.2, color="black") + geomviolin(trim=FALSE, col = "black", alpha = 0.5) + geomboxplot(outlier.color = NA) + themebw() + xlab("Condition") + ylab("Signature Score") + scaleycontinuous(trans = "log1p") + statcomparemeans(aes(group = GOnonGO), label = "p.signif", label.x = 1.5) + theme(axis.text.x = element_blank())) dev.off() } ```
Example for "lumDTPincludedDEGDN.txt"
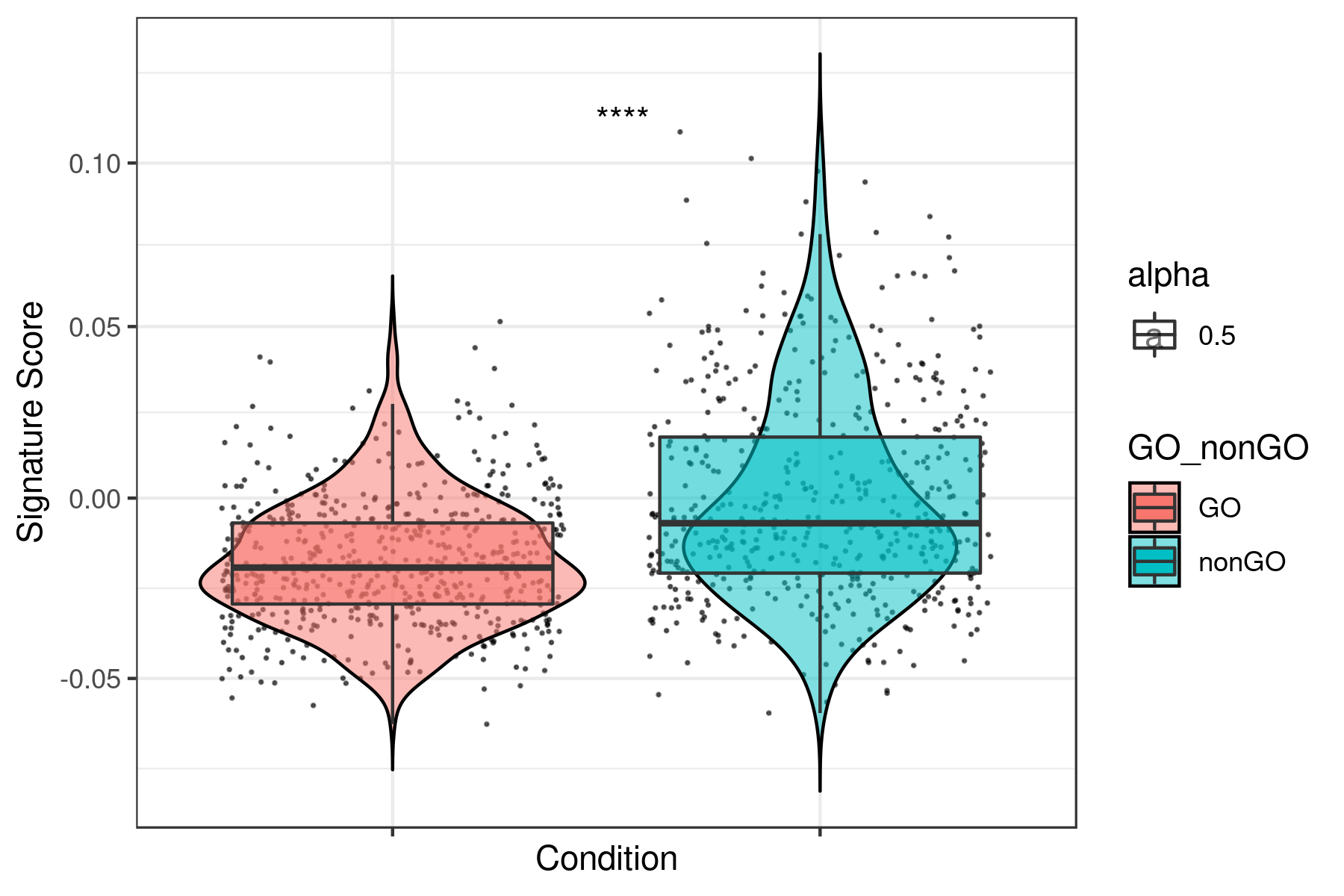
To see all the plots made as above go to this link: https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/i.score/test/boxplots_tirosh/
How to analyze CITE-seq data using iCellR
- Download test samples
```r sample.file.url = "https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/data/CITE-SeqsampleRNA.tsv.gz"
download RNA file
download.file(url = sample.file.url, destfile = "CITE-SeqsampleRNA.tsv.gz", method = "auto")
sample.file.url = "https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/data/CITE-SeqsampleADT.tsv.gz"
download ADT file
download.file(url = sample.file.url,
destfile = "CITE-SeqsampleADT.tsv.gz",
method = "auto")
```
- Read the files and make your object
```r # Read RNA file rna.data <- read.delim("CITE-SeqsampleRNA.tsv.gz",header=TRUE)
# see the head head(rna.data)[1:3]
CTGTTTACACCGCTAG CTCTACGGTGTGGCTC AGCAGCCAGGCTCATT
A1BG 0 0 0
A1BG-AS1 0 0 0
A1CF 0 0 0
A2M 0 0 0
A2M-AS1 0 0 0
A2ML1 0 0 0
# Read ADT file adt.data <- read.delim("CITE-SeqsampleADT.tsv.gz",header=TRUE)
# see the head head(adt.data)[1:3]
CTGTTTACACCGCTAG CTCTACGGTGTGGCTC AGCAGCCAGGCTCATT
CD3 60 52 89
CD4 72 49 112
CD8 76 59 61
CD45RA 575 3943 682
CD56 64 68 87
CD16 161 107 117
if you had multiple sample use the data.aggregation function for both RNA and ADT data.
make iCellR object
my.obj <- make.obj(rna.data)
check object
my.obj
,--. ,-----. ,--.,--.,------.
--'' .--./ ,---. | || || .--. '
,--.| | | .-. :| || || '--'.'
| |' '--'\ --. | || || |
--' -----'----'--'--'`--' '--'
An object of class iCellR version: 1.1.4 Raw/original data dimentions (rows,columns): 20501,8617 Data conditions: no conditions/single sample Row names: A1BG,A1BG-AS1,A1CF ... Columns names: CTGTTTACACCGCTAG,CTCTACGGTGTGGCTC,AGCAGCCAGGCTCATT ...
QC stats performed:FALSE, PCA performed:FALSE, CCA performed:FALSE Clustering performed:FALSE, Number of clusters:0 tSNE performed:FALSE, UMAP performed:FALSE, DiffMap performed:FALSE Main data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0 Normalization factors:,... Imputed data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## scVDJ-Seq
VDJ data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## CITE-Seq
ADT raw data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT main data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT columns names:... ADT row names:...
##### iCellR object
```
- add ADT data
```r my.obj <- add.adt(my.obj, adt.data = adt.data)
check too see
my.obj
,--. ,-----. ,--.,--.,------.
--'' .--./ ,---. | || || .--. '
,--.| | | .-. :| || || '--'.'
| |' '--'\ --. | || || |
--' -----'----'--'--'`--' '--'
An object of class iCellR version: 1.1.4 Raw/original data dimentions (rows,columns): 20501,8617 Data conditions: no conditions/single sample Row names: A1BG,A1BG-AS1,A1CF ... Columns names: CTGTTTACACCGCTAG,CTCTACGGTGTGGCTC,AGCAGCCAGGCTCATT ...
QC stats performed:FALSE, PCA performed:FALSE, CCA performed:FALSE Clustering performed:FALSE, Number of clusters:0 tSNE performed:FALSE, UMAP performed:FALSE, DiffMap performed:FALSE Main data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0 Normalization factors:,... Imputed data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## scVDJ-Seq
VDJ data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## CITE-Seq
- ADT raw data dimentions (rows,columns):10,8617 ADT main data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT columns names:... ADT row names:... ########### iCellR object ########## ```
- QC, filter, normalize, merge ADT and RNA data, run PCA and UMAP
```r
QC
my.obj <- qc.stats(my.obj, s.phase.genes = s.phase, g2m.phase.genes = g2m.phase)
plot as mentioned above
filter
my.obj <- cell.filter(my.obj, min.mito = 0, max.mito = 0.07 , min.genes = 500, max.genes = 4000, min.umis = 0, max.umis = Inf)
normalize RNA
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "ranked.glsf", top.rank = 500)
normalize ADT
my.obj <- norm.adt(my.obj)
gene stats
my.obj <- gene.stats(my.obj, which.data = "main.data")
find genes for PCA
my.obj <- make.gene.model(my.obj, my.out.put = "data", dispersion.limit = 1.5, base.mean.rank = 500, no.mito.model = T, mark.mito = T, interactive = F, no.cell.cycle = T, out.name = "gene.model")
merge RNA and ADT data
my.obj <- adt.rna.merge(my.obj, adt.data = "main")
run PCA and the rest is as above
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj, method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model,data.type = "main")
2 pass PCA
my.obj <- find.dim.genes(my.obj, dims = 1:20,top.pos = 20, top.neg = 20)
second round PC
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj, method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model,data.type = "main")
my.obj <- run.umap(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
check your object
my.obj
,--. ,-----. ,--.,--.,------.
--'' .--./ ,---. | || || .--. '
,--.| | | .-. :| || || '--'.'
| |' '--'\ --. | || || |
--' -----'----'--'--'`--' '--'
An object of class iCellR version: 1.1.4 Raw/original data dimentions (rows,columns): 20501,8617 Data conditions: no conditions/single sample Row names: A1BG,A1BG-AS1,A1CF ... Columns names: CTGTTTACACCGCTAG,CTCTACGGTGTGGCTC,AGCAGCCAGGCTCATT ...
QC stats performed:TRUE, PCA performed:TRUE, CCA performed:FALSE Clustering performed:TRUE, Number of clusters:14 tSNE performed:FALSE, UMAP performed:TRUE, DiffMap performed:FALSE Main data dimentions (rows,columns):20511,8305 Normalization factors:8.448547776071,... Imputed data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## scVDJ-Seq
VDJ data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## CITE-Seq
ADT raw data dimentions (rows,columns):10,8617 ADT main data dimentions (rows,columns):10,8617 ADT columns names:CTGTTTACACCGCTAG... ADT row names:ADT_CD3...
##### iCellR object
```
- plot
```r
find ADT gene names
grep("^ADT_", rownames(my.obj@main.data),value=T)
[1] "ADTCD3" "ADTCD4" "ADTCD8" "ADTCD45RA" "ADT_CD56"
[6] "ADTCD16" "ADTCD11c" "ADTCD14" "ADTCD19" "ADT_CD34"
A = gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "ADT_CD3", plot.data.type = "umap", interactive = F, cell.transparency = 0.5)
B = gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "CD3E", plot.data.type = "umap", interactive = F, cell.transparency = 0.5)
C = gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "ADT_CD16", plot.data.type = "umap", interactive = F, cell.transparency = 0.5)
D = gene.plot(my.obj, gene = "FCGR3A", plot.data.type = "umap", interactive = F, cell.transparency = 0.5)
library(gridExtra) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) ```

How to analyze scVDJ-seq data using iCellR
Here is an example of how to add VDJ data.
```r ###### an example file my.vdj <- read.csv(file = system.file('extdata', 'allcontigannotations.csv', package = 'iCellR'), as.is = TRUE)
head(my.vdj)
barcode iscell contigid high_confidence length
1 AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1 True AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1contig1 True 654
2 AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1 True AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1contig2 True 697
3 AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1 True AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1contig3 False 496
4 AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1 True AAACCTGTCCGAACGC-1contig4 True 539
5 AAACCTGTCGATGAGG-1 True AAACCTGTCGATGAGG-1contig1 True 705
6 AAACCTGTCGATGAGG-1 True AAACCTGTCGATGAGG-1contig2 True 491
chain vgene dgene jgene cgene full_length productive cdr3
1 TRB TRBV4-1 None TRBJ2-7 TRBC2 True True CASSQGVEQYF
2 TRA TRAV8-1 None TRAJ42 TRAC True True CAVKGGSQGNLIF
3 TRB None None TRBJ1-4 TRBC1 False None None
4 Multi None None TRAJ10 TRBC1 False None None
5 TRB TRBV5-5 TRBD1 TRBJ2-7 TRBC1 True True CASSLVSGGNEQYF
6 TRB None None TRBJ1-2 TRBC1 False None None
cdr3nt reads umis rawclonotype_id
1 TGCGCCAGCAGCCAAGGGGTCGAGCAGTACTTC 42610 19 clonotype150
2 TGTGCCGTGAAGGGAGGAAGCCAAGGAAATCTCATCTTT 12297 4 clonotype150
3 None 4314 1 clonotype150
4 None 2212 1 clonotype150
5 TGTGCCAGCAGCTTGGTCTCAGGGGGAAACGAGCAGTACTTC 21148 8 clonotype2
6 None 17717 16 clonotype2
rawconsensusid
1 clonotype150consensus1
2 clonotype150consensus2
3 None
4 None
5 clonotype2consensus1
6 None
Prepare the vdj file
My.VDJ <- prep.vdj(vdj.data = my.vdj, cond.name = "NULL")
head(My.VDJ)
rawclonotypeid barcode iscell contigid
1 clonotype1 ACGCCAGCAAGCGCTC.1 True ACGCCAGCAAGCGCTC-1contig2
2 clonotype1 AACGTTGAGTACGATA.1 True AACGTTGAGTACGATA-1contig2
3 clonotype1 AACTCTTGTCAAAGCG.1 True AACTCTTGTCAAAGCG-1contig1
4 clonotype1 AACGTTGAGTACGATA.1 True AACGTTGAGTACGATA-1contig1
5 clonotype1 ACGCCAGCAAGCGCTC.1 True ACGCCAGCAAGCGCTC-1contig1
6 clonotype1 ACGATGTTCTGGTATG.1 True ACGATGTTCTGGTATG-1contig2
highconfidence length chain vgene dgene jgene cgene fulllength
1 True 571 TRA TRAV27 None TRAJ37 TRAC True
2 True 730 TRA TRAV27 None TRAJ37 TRAC True
3 True 722 TRB TRBV6-3 TRBD2 TRBJ1-1 TRBC1 True
4 True 723 TRB TRBV6-3 TRBD2 TRBJ1-1 TRBC1 True
5 True 722 TRB TRBV6-3 TRBD2 TRBJ1-1 TRBC1 True
6 True 726 TRA TRAV27 None TRAJ37 TRAC True
productive cdr3 cdr3_nt reads
1 True CAGGRSSNTGKLIF TGTGCAGGAGGACGCTCTAGCAACACAGGCAAACTAATCTTT 14241
2 True CAGGRSSNTGKLIF TGTGCAGGAGGACGCTCTAGCAACACAGGCAAACTAATCTTT 27679
3 True CASRTGAGATEAFF TGTGCCAGCAGGACCGGGGCGGGAGCCACTGAAGCTTTCTTT 51844
4 True CASRTGAGATEAFF TGTGCCAGCAGGACCGGGGCGGGAGCCACTGAAGCTTTCTTT 38120
5 True CASRTGAGATEAFF TGTGCCAGCAGGACCGGGGCGGGAGCCACTGAAGCTTTCTTT 24635
6 True CAGGRSSNTGKLIF TGTGCAGGAGGACGCTCTAGCAACACAGGCAAACTAATCTTT 13720
umis rawconsensusid my.rawclonotypeid clonotype.Freq proportion
1 8 clonotype1consensus2 clonotype1 43 0.1572212
2 10 clonotype1consensus2 clonotype1 43 0.1572212
3 24 clonotype1consensus1 clonotype1 43 0.1572212
4 23 clonotype1consensus1 clonotype1 43 0.1572212
5 11 clonotype1consensus1 clonotype1 43 0.1572212
6 7 clonotype1consensus2 clonotype1 43 0.1572212
total.colonotype
1 109
2 109
3 109
4 109
5 109
6 109
png('vdj.stats.png',width = 16, height = 8, units = 'in', res = 300) vdj.stats(My.VDJ) dev.off()
add vdj data to you object
my.obj <- add.vdj(demo.obj, vdj.data = My.VDJ) ```

Another example with multiple files ```r
First read the vdj data
File="allcontigannotations.csv" my.vdj.data <- read.csv(File)
then see the conditions
my.obj
For each condition (WT,KO, ...) subset from the VDJ data
Get="WT"
dat <- colnames(my.obj@main.data) name <- paste(Get,".tsv",sep="") do <- grep(Get,dat, value=T) do <- as.character(as.matrix(data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(do),'_',fixed=TRUE)))[2])) do <- gsub("\.","-",do) do <- subset(my.vdj.data, my.vdj.data$barcode %in% do) write.table((do),file=name,sep="\t", row.names =F)
Get="KO"
dat <- colnames(my.obj@main.data) name <- paste(Get,".tsv",sep="") do <- grep(Get,dat, value=T) do <- as.character(as.matrix(data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(do),'_',fixed=TRUE)))[2])) do <- gsub("\.","-",do) do <- subset(my.vdj.data, my.vdj.data$barcode %in% do) write.table((do),file=name,sep="\t", row.names =F)
read and prep all conditions
Get="WT" name <- paste(Get,".tsv",sep="") do <- read.table(name, header=T) WT <- prep.vdj(vdj.data = do, cond.name = Get)
Get="KO" name <- paste(Get,".tsv",sep="") do <- read.table(name, header=T) KO <- prep.vdj(vdj.data = do, cond.name = Get)
concatenate all the conditions
my.vdj.data <- rbind(WT, KO)
see head of the file
head(my.vdj.data)
rawclonotypeid barcode iscell contigid
1 clonotype1 WTAAACCTGAGCTAACTC-1 True AAACCTGAGCTAACTC-1contig_1
2 clonotype1 WTAAACCTGAGCTAACTC-1 True AAACCTGAGCTAACTC-1contig_2
3 clonotype1 WTAGTTGGTTCTCGCATC-1 True AGTTGGTTCTCGCATC-1contig_3
4 clonotype1 WTTGACAACCAACTGCTA-1 True TGACAACCAACTGCTA-1contig_1
5 clonotype1 WTTGTCCCAGTCAAACTC-1 True TGTCCCAGTCAAACTC-1contig_1
6 clonotype1 WTTGTCCCAGTCAAACTC-1 True TGTCCCAGTCAAACTC-1contig_2
highconfidence length chain vgene dgene jgene cgene fulllength
1 True 693 TRA TRAV8-1 None TRAJ21 TRAC True
2 True 744 TRB TRBV28 TRBD1 TRBJ2-1 TRBC2 True
3 True 647 TRA TRAV8-1 None TRAJ21 TRAC True
4 True 508 TRB TRBV28 TRBD1 TRBJ2-1 TRBC2 True
5 True 660 TRA TRAV8-1 None TRAJ21 TRAC True
6 True 770 TRB TRBV28 TRBD1 TRBJ2-1 TRBC2 True
productive cdr3 cdr3_nt
1 True CAVKDFNKFYF TGTGCCGTGAAAGACTTCAACAAATTTTACTTT
2 True CASSLFSGTGTNEQFF TGTGCCAGCAGTTTATTTTCCGGGACAGGGACGAATGAGCAGTTCTTC
3 True CAVKDFNKFYF TGTGCCGTGAAAGACTTCAACAAATTTTACTTT
4 True CASSLFSGTGTNEQFF TGTGCCAGCAGTTTATTTTCCGGGACAGGGACGAATGAGCAGTTCTTC
5 True CAVKDFNKFYF TGTGCCGTGAAAGACTTCAACAAATTTTACTTT
6 True CASSLFSGTGTNEQFF TGTGCCAGCAGTTTATTTTCCGGGACAGGGACGAATGAGCAGTTCTTC
reads umis rawconsensusid my.rawclonotypeid clonotype.Freq
1 1241 2 clonotype1consensus1 clonotype1 120
2 2400 4 clonotype1consensus2 clonotype1 120
3 1090 2 clonotype1consensus1 clonotype1 120
4 2455 4 clonotype1consensus2 clonotype1 120
5 1346 2 clonotype1consensus1 clonotype1 120
6 3073 8 clonotype1consensus2 clonotype1 120
proportion total.colonotype
1 0.04098361 1292
2 0.04098361 1292
3 0.04098361 1292
4 0.04098361 1292
5 0.04098361 1292
6 0.04098361 1292
add it to iCellR object
my.obj <- add.vdj(my.obj, vdj.data = my.vdj.data) ``` How to plot clonotypes
```r # once you have imported your clonotype data to your iCellR object, in order to plot them you need to have the following parapmeters: # -1 clonotype name (e.g. clono = "clonotype1") # -2 which column number has the clonotype names (e.g. clonotype.column = 2) # -3 which column number has the cell barcode names (e.g. barcode.column = 1)
# In order to plot you need 2 things a- cell barcodes that match the barcodes in UMAP,PCA,tSNE or KNetL data and b- clonotype names.
# to check your clonotype data do this (example):
head(my.obj@vdj.data)
rawclonotypeid_SampleID MyBarcodes V1
1 S5clonotype98 Nor2.AAAACCTGAGACAGACC.1 AAACCTGAGACAGACC.1
2 S5clonotype98 Nor2.AAAACCTGAGACAGACC.1 AAACCTGAGACAGACC.1
3 S4clonotype100 Nor2.BAAACCTGAGAGACTAT.1 AAACCTGAGAGACTAT.1
4 S4clonotype100 Nor2.BAAACCTGAGAGACTAT.1 AAACCTGAGAGACTAT.1
5 S3clonotype3 Nor1.BAAACCTGAGAGTCGGT.1 AAACCTGAGAGTCGGT.1
6 S5clonotype99 Nor2.AAAACCTGAGATATGGT.1 AAACCTGAGATATGGT.1
barcode SampleID rawclonotypeid is_cell
1 S5_AAACCTGAGACAGACC.1 5 clonotype98 True
2 S5_AAACCTGAGACAGACC.1 5 clonotype98 True
3 S4_AAACCTGAGAGACTAT.1 4 clonotype100 True
4 S4_AAACCTGAGAGACTAT.1 4 clonotype100 True
5 S3_AAACCTGAGAGTCGGT.1 3 clonotype3 True
6 S5_AAACCTGAGATATGGT.1 5 clonotype99 True
contigid highconfidence length chain vgene dgene
1 AAACCTGAGACAGACC-1contig2 True 514 TRB TRBV14 None
2 AAACCTGAGACAGACC-1contig1 True 495 TRB TRBV20-1 None
3 AAACCTGAGAGACTAT-1contig2 True 496 TRB TRBV9 None
4 AAACCTGAGAGACTAT-1contig1 True 529 TRA TRAV26-1 None
5 AAACCTGAGAGTCGGT-1contig1 True 512 TRB TRBV6-5 None
6 AAACCTGAGATATGGT-1contig2 True 544 TRA TRAV12-2 None
jgene cgene full_length productive cdr3
1 TRBJ1-5 TRBC1 True True CASSFEGGSTQPQHF
2 TRBJ2-7 TRBC2 True True CSARVRGRSSYEQYF
3 TRBJ2-2 TRBC2 True True CASSVGVNTGELFF
4 TRAJ52 TRAC True True CIVRGAGGTSYGKLTF
5 TRBJ1-1 TRBC1 True True CASSYRPNTEAFF
6 TRAJ33 TRAC True True CAVKRDSNYQLIW
cdr3_nt reads umis
1 TGTGCCAGCAGTTTTGAGGGGGGATCGACTCAGCCCCAGCATTTT 886 1
2 TGCAGTGCTAGAGTAAGGGGACGGAGCTCCTACGAGCAGTACTTC 1912 3
3 TGTGCCAGCAGCGTGGGCGTAAACACCGGGGAGCTGTTTTTT 10804 12
4 TGCATCGTCAGGGGGGCTGGTGGTACTAGCTATGGAAAGCTGACATTT 960 4
5 TGTGCCAGCAGTTACCGCCCGAACACTGAAGCTTTCTTT 4286 6
6 TGTGCCGTGAAAAGGGATAGCAACTATCAGTTAATCTGG 1244 2
rawconsensusid my.rawclonotypeid clonotype.Freq proportion
1 clonotype98consensus1 S5_clonotype98 1 0.0001983930
2 clonotype98consensus2 S5_clonotype98 1 0.0001983930
3 clonotype100consensus2 S4_clonotype100 1 0.0001923817
4 clonotype100consensus1 S4_clonotype100 1 0.0001923817
5 clonotype3consensus1 S3_clonotype3 49 0.0070635721
6 clonotype99consensus1 S5_clonotype99 1 0.0001983930
total.colonotype
1 5096
2 5096
3 5280
4 5280
5 5943
6 5096
In this example column number 1 and 2 have the clonotype and barcode info needed to plot.
Sort clonotype names with highset frequency:
clonotype.frequency <- as.data.frame(sort(table(as.character(as.matrix((my.obj@vdj.data)[1]))),decreasing = TRUE))
head(clonotype.frequency)
Var1 Freq
1 S2_clonotype1 306
2 S1_clonotype1 242
3 S3_clonotype1 232
4 S4_clonotype1 216
5 S5_clonotype1 210
6 S2_clonotype2 113
let's plot S1_clonotype1 which is seen in 242 cells in all the conditions.
if you want to plot only in one condtion or few conditions use this option "conds.to.plot" (e.g. conds.to.plot = c("WT","KO"))
If conds.to.plot = NULL it would plot all of them (all 242 cells).
Plot colonotype 1
clono.plot(my.obj, plot.data.type = "knetl", clonotype.column = 1, barcode.column = 2, clono = "S1_clonotype1", conds.to.plot = NULL, cell.transparency = 1, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F)
plot multiple clonotypes
ordered.clonotypes <- as.character(as.matrix((clonotype.frequency)[1]))
let's plot top 19 clonotypes with highest frequency:
clonolist <- (ordered.clonotypes)[1:19] clonolist
[1] "S2clonotype1" "S1clonotype1" "S3clonotype1" "S4clonotype1"
[5] "S5clonotype1" "S2clonotype2" "S3clonotype2" "S1clonotype2"
[9] "S2clonotype4" "S1clonotype4" "S3clonotype4" "S2clonotype3"
[13] "S4clonotype2" "S1clonotype3" "S4clonotype3" "S5clonotype2"
[17] "S3clonotype3" "S2clonotype9" "S3_clonotype6"
rm(list = ls(pattern="PL")) for(i in clonolist){ MyPlot <- clono.plot(my.obj, plot.data.type = "knetl", clonotype.column = 1, barcode.column = 2, clono = i, conds.to.plot = NULL, cell.transparency = 1, clust.dim = 2, interactive = F) NameCol=paste("PL",i,sep="") eval(call("<-", as.name(NameCol), MyPlot)) }
library(cowplot) filenames <- ls(pattern="PL_")
B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1,anno.clust=TRUE) filenames <- c("B",filenames)
png("19clonotypes.png",width = 20, height = 20, units = 'in', res = 300) plotgrid(plotlist=mget(filenames)) dev.off() ```

How to analyze large bulk RNA-Seq data (TCGA)
In this example the samples are normalized using DESeq2 so no normalization is needed.
```r sample.file.url = "https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/data/TCGAsampleNormalized_data.tsv.gz"
download.file(url = sample.file.url, destfile = "TCGAsampleNormalized_data.tsv.gz", method = "auto")
TCGA.data <- read.table("TCGAsampleNormalized_data.tsv.gz") head(TCGA.data)[1:3]
BasalTCGA.A1.A0SK.txt BasalTCGA.A1.A0SP.txt Basal_TCGA.A2.A04P.txt
TSPAN6 5823.4300 4318.034382 5265.733258
TNMD 0.0000 6.049079 6.763079
DPM1 3248.1536 2528.515113 1183.538813
SCYL3 1059.7135 965.836315 1109.144945
C1orf112 1251.3155 1070.687022 485.589067
FGR 106.2438 933.574559 512.641383
library(iCellR) my.obj <- make.obj(TCGA.data)
my.obj@main.data <- my.obj@raw.data
my.obj
,--. ,-----. ,--.,--.,------.
--'' .--./ ,---. | || || .--. '
,--.| | | .-. :| || || '--'.'
| |' '--'\ --. | || || |
--' -----'----'--'--'`--' '--'
An object of class iCellR version: 1.2.4 Raw/original data dimentions (rows,columns): 69797,882 Data conditions in raw data: Basal,Her2,LumA,LumB,Normal (131,64,404,170,113) Row names: TSPAN6,TNMD,DPM1 ... Columns names: BasalTCGA.A1.A0SK.txt,BasalTCGA.A1.A0SP.txt,Basal_TCGA.A2.A04P.txt ...
QC stats performed:FALSE, PCA performed:FALSE, CCA performed:FALSE Clustering performed:FALSE, Number of clusters:0 tSNE performed:FALSE, UMAP performed:FALSE, DiffMap performed:FALSE Main data dimentions (rows,columns):69797,882 Normalization factors:,... Imputed data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## scVDJ-Seq
VDJ data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## CITE-Seq
ADT raw data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT main data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT columns names:... ADT row names:...
##### iCellR object
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj)
my.obj <- run.clustering(my.obj, clust.method = "kmeans", dist.method = "euclidean", index.method = "silhouette", max.clust =25, min.clust = 2, dims = 1:10)
my.obj <- run.pc.tsne(my.obj, dims = 1:10) my.obj <- run.umap(my.obj, dims = 1:10, method = "umap-learn")
cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",cell.color = "black",col.by = "conditions",cell.transparency = 0.5,interactive = F) cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",cell.color = "black",col.by = "conditions",cell.transparency = 0.5,interactive = F) cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",cell.color = "black",col.by = "conditions",cell.transparency = 0.5,interactive = F) cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",cell.color = "black",cell.transparency = 1,interactive = F) ```

# Cell type prediction using ImmGen, Mouse and Human Cell Atlas
To do this you need to download the following databse files from our iCellR data link (more data to come soon).
```r
download the .rda files from here: https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/data/
Load the .rda files as below
load("Immgen.GSE109125.205.rda") load("Immgen.GSE122108.412.rda") load("Immgen.GSE122597.83.rda") load("Immgen.GSE124829.190.rda") load("Immgen.microarray.GSE15907.653.rda") load("Immgen.microarray.GSE37448.189.rda") load("immgen.rna.rda") load("immgen.uli.rna.rda") load("mouse.cell.atlas.rda") ```
| Key | Source | Samples | Description | Cell Types | | ------------- |:-------------:| :-----:| :----- | -----| | GSE109125 | ImmGen | 205 | 83 populations representing all lineages and several differentiation cascades prepared from unchallenged mice and after LPS, anti-CD3, viral infection cell activation. | B Cells, Stromal Cells, Dendritic Cells, Granulocytes, Innate Lymphocytes, Stem Cells, Macrophages, ab T Cells, gd T Cells | | GSE122108 | ImmGen | 412 | 130 populations comprising progenitors, residents, and stimulated (C.alb, LPS, injury, APAP+ starved overnight and pIC) mononuclear phagocytes for OpenSource MNP Project. | Macrophages, Kupffer Cell/Macrophages, Dendritic Cells, Microglia, Monocytes. | | GSE122597 | ImmGen | 83 | Five highly purified immunocyte populations profiled to unusual depth as multiple replicates (8 to 16). Suitable for exploration of genes expressed at very low levels. | NK Cells, Follicular B, Naive CD4+ abT, gdT cells and peritoneal macrophages. | | GSE124829 | ImmGen | 190 | 11 diverse immunocyte populations from male and female mice of varying ages stimulated with different dose of IFN to understand the immune system's sexual differences. | B Cells, Dendritic Cells, Neutrophils, Macrophages, Natural Killer T Cells, ab T Cells, gd T Cells, Microglia, Regulatory T Cells. | | GSE15907 | ImmGen | 653 | 178 populations compromiing of gene-expression microarray datasets ("version1" labeling) from primary cells from multiple immune lineages are isolated ex-vivo, primarily from 6weeks B6 male mice. | gd T Cells, ab T Cells, Dendritic Cells, Macrophages, Stem Cells, B Cells, Stromal Cells, Neutrophils, Fibroblast, NK Cells, NK T Cells, Monocytes, CD4 Naive T Cell. | | GSE37448 | ImmGen | 189 | 80 populations compromising of gene-expression microarray datasets ("version2" labeling) from primary cells from multiple immune lineages are isolated ex-vivo, primarily from 6weeks B6 male mice. Complements the V1 compendium with additional cells. Unfortunately, the version change in the labeling process, while more efficient, introduced some biases such that the two sections of the data can be compared grossly, but not at fine resolution (we tried...). | gd T Cells, ab T Cells, Dendritic Cells, Macrophages, Stem Cells, B Cells, Stromal Cells, Neutrophils, Fibroblast, NK Cells, NK T Cells, Monocytes, CD4 Naive T Cell. | | rna | ImmGen | 23 | Full depth directional RNA sequencing was performed on the core ImmGen populations to generate reference datasets for the tissues from 5 week-old C57BL/6J (Jackson Laboratory) males and females, double-sorted by flow cytometry, per ImmGen cell preparation SOP. | B, CD4T, CD8T, DC, MQ,NK, NKT, Treg | | uli.rna | ImmGen | 157 | | | | mca | Mouse Cell Atlas | 43 tissues | Constructed as a basic scheme for the Mouse Cell Atlas using Microwell-seq. | Uterus, TrophoblastStemCells, Thymus, Testis, Stomach, Spleen, SmallIntestine, Prostate, Placenta, PeripheralBlood, Pancreas, Ovary, NeontalBrain, NeonatalSkin, NeonatalRib, NeonatalMuscle, NeonatalHeart, NeonatalCalvaria, Muscle, Mouse3T3, MesenchymalStemCellsPrimary, MesenchymalStemCells, MammaryGland.Virgin, MammaryGland.Pregnancy, MammaryGland.Lactation, MammaryGland.Involution, Male.fetal.Gonad, Lung, Liver, Kidney, FetalStomach, FetalLung, FetalLiver, FetalKidney, FetalIntestine, FetalBrain, Female.fetal.Gonad, EmbryonicStemCells, EmbryonicMesenchyme, Brain, BoneMarrowcKit, BoneMarrow, Bladder |
Choose a cluster and take for example top 10 genes for that cluster and then choose one of the databases that is best for you from the above list and predict your cell type. Note that if you have B cells for example and the database of your choice dose not have B cells, it would predict the closest looking cells to B cells. So it's important to use the right database for the right type of data.
```r
Choose top 40 genes for cluster 8 for example
MyGenes <- top.markers(marker.genes, topde = 40, min.base.mean = 0.2, cluster = 8)
# predict
plot
cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "rna", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "point.plot")
cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "uli.rna", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "point.plot", top.cell.types = 50)
cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "rna", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "heatmap")
cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "uli.rna", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "heatmap")
As you can see cluster 8 is most likely to be B-cells.
more examples
cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "GSE109125", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "point.plot", top.cell.types = 50)
cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "GSE37448", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "heatmap", top.cell.types = 50)
for tissue type prediction use this:
cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "mca", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "point.plot")
And finally check the genes in the cells and find the common ones to predict
heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters") ```




You can automate this for all the clusters as below. Add as many plot as you wish.
```r Clusters = sort(unique(my.obj@best.clust$clusters))
for(i in Clusters){ Cluster = i MyGenes <- top.markers(marker.genes, topde = 10, min.base.mean = 0.2, cluster = Cluster)
first plot
Name <- paste("ImmGenCluster",Cluster,"pointPlotRNA.pdf",sep="") pdf(Name, width = 10, height = 10) print(cell.type.pred(immgen.data = "rna", gene = MyGenes, plot.type = "point.plot")) dev.off()
second plot
Name <- paste("ImmGenCluster",Cluster,"_check.pdf",sep="") pdf(Name, width = 10, height = 10) print(heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters")) dev.off() } ```
- Pathway analysis
```r
Pathway
pathways.kegg(my.obj, clust.num = 7)
this function is being improved and soon will be available
```

Spatial Transcriptomics (ST) analysis
In this example, we have downloaded 2 samples from 10X genomics website. You can get the data from these links: Anterior and Posterior. To make it easier you can also use the commands below to download from our server.
```r # download sample data url = "https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/example7SpatialTranscriptomic/V1MouseBrainSagittalAnteriorSection2filteredfeaturebcmatrix.tar.gz"
download the file
download.file(url = url, destfile = "V1MouseBrainSagittalAnteriorSection2filteredfeaturebcmatrix.tar.gz", method = "auto")
url ="https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/example7SpatialTranscriptomic/V1MouseBrainSagittalAnteriorSection2_spatial.tar.gz"
download the file
download.file(url = url, destfile = "V1MouseBrainSagittalAnteriorSection2_spatial.tar.gz", method = "auto")
url ="https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/example7SpatialTranscriptomic/V1MouseBrainSagittalPosteriorSection2filteredfeaturebcmatrix.tar.gz"
download the file
download.file(url = url, destfile = "V1MouseBrainSagittalPosteriorSection2filteredfeaturebcmatrix.tar.gz", method = "auto")
url ="https://genome.med.nyu.edu/results/external/iCellR/example7SpatialTranscriptomic/V1MouseBrainSagittalPosteriorSection2_spatial.tar.gz"
download the file
download.file(url = url, destfile = "V1MouseBrainSagittalPosteriorSection2_spatial.tar.gz", method = "auto")
untar
untar("V1MouseBrainSagittalAnteriorSection2filteredfeaturebcmatrix.tar.gz") untar("V1MouseBrainSagittalAnteriorSection2_spatial.tar.gz")
file.rename("spatial","spatialAnterior2") file.rename("filteredfeaturebcmatrix","filteredfeaturebcmatrixAnterior2")
untar("V1MouseBrainSagittalPosteriorSection2filteredfeaturebcmatrix.tar.gz") untar("V1MouseBrainSagittalPosteriorSection2_spatial.tar.gz")
file.rename("spatial","spatialPosterior2") file.rename("filteredfeaturebcmatrix","filteredfeaturebcmatrixPosterior2") ```
- Load the data
```r library(iCellR)
Anterior2 <- load10x("filteredfeaturebcmatrixAnterior2",gene.name = 2) Posterior2 <- load10x("filteredfeaturebcmatrixPosterior2",gene.name = 2)
if you want to analyze both samples
Samples <- c("Anterior2","Posterior2") my.data <- data.aggregation(samples = Samples, condition.names = Samples)
if you want to analyze 1 sample
my.data <- load10x("filteredfeaturebcmatrixPosterior2",gene.name = 2)
my.obj <- make.obj(my.data)
Anterior2 <- capture.image.10x("spatialAnterior2") Posterior2 <- capture.image.10x("spatialPosterior2")
if you want to analyze both samples
Samples <- c("Anterior2","Posterior2") my.obj <- add.10x.image(my.obj, image.data.list = Samples, condition.names = Samples)
if one sample
My.image <- image.capture.10x("Post2_spatial")
my.obj <- add.10x.image(my.obj, image.data.list = "My.image")
my.obj
,--. ,-----. ,--.,--.,------.
--'' .--./ ,---. | || || .--. '
,--.| | | .-. :| || || '--'.'
| |' '--'\ --. | || || |
--' -----'----'--'--'`--' '--'
An object of class iCellR version: 1.6.0 Raw/original data dimentions (rows,columns): 31053,6118 Data conditions in raw data: Anterior2,Posterior2 (2825,3293) Row names: A030001D20Rik,A030003K21Rik,A030005K14Rik ... Columns names: Anterior2AAACAAGTATCTCCCA.1,Anterior2AAACACCAATAACTGC.1,Anterior2_AAACAGAGCGACTCCT.1 ...
QC stats performed:FALSE, PCA performed:FALSE Clustering performed:FALSE, Number of clusters:0 tSNE performed:FALSE, UMAP performed:FALSE, DiffMap performed:FALSE Main data dimensions (rows,columns): 0,0 Normalization factors:,... Imputed data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0
######## scVDJ-seq
VDJ data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## CITE-seq
ADT raw data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT main data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT columns names:... ADT row names:...
######## scATAC-seq
ATAC raw data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ATAC main data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ATAC columns names:... ATAC row names:...
######## Spatial
Spatial data dimentions (rows,columns):9984,5
##### iCellR object
```
The rest of the analysis is just like regular scRNA-Seq. Filter, normalize, run PCA, tSNE, UMAP, KNetL map and cluster. Then you can start ploting as below:
```r A=spatial.plot(my.obj,col.by = "clusters",conds.to.plot = "Anterior2",interactive= F) B=spatial.plot(my.obj,col.by = "clusters",conds.to.plot = "Posterior2",interactive= F) C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) D= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",col.by = "conditions",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) E=spatial.plot(my.obj,col.by = "gene", gene = c("Cd4"), conds.to.plot = "Anterior2",interactive= F, scaleValue = TRUE) F=spatial.plot(my.obj,col.by = "gene", gene = c("Cd4"), conds.to.plot = "Posterior2",interactive= F, scaleValue = TRUE)
library(gridExtra) png('AllClusts.png', width = 8, height = 8, units = 'in', res = 300) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D,E,F) dev.off() ```

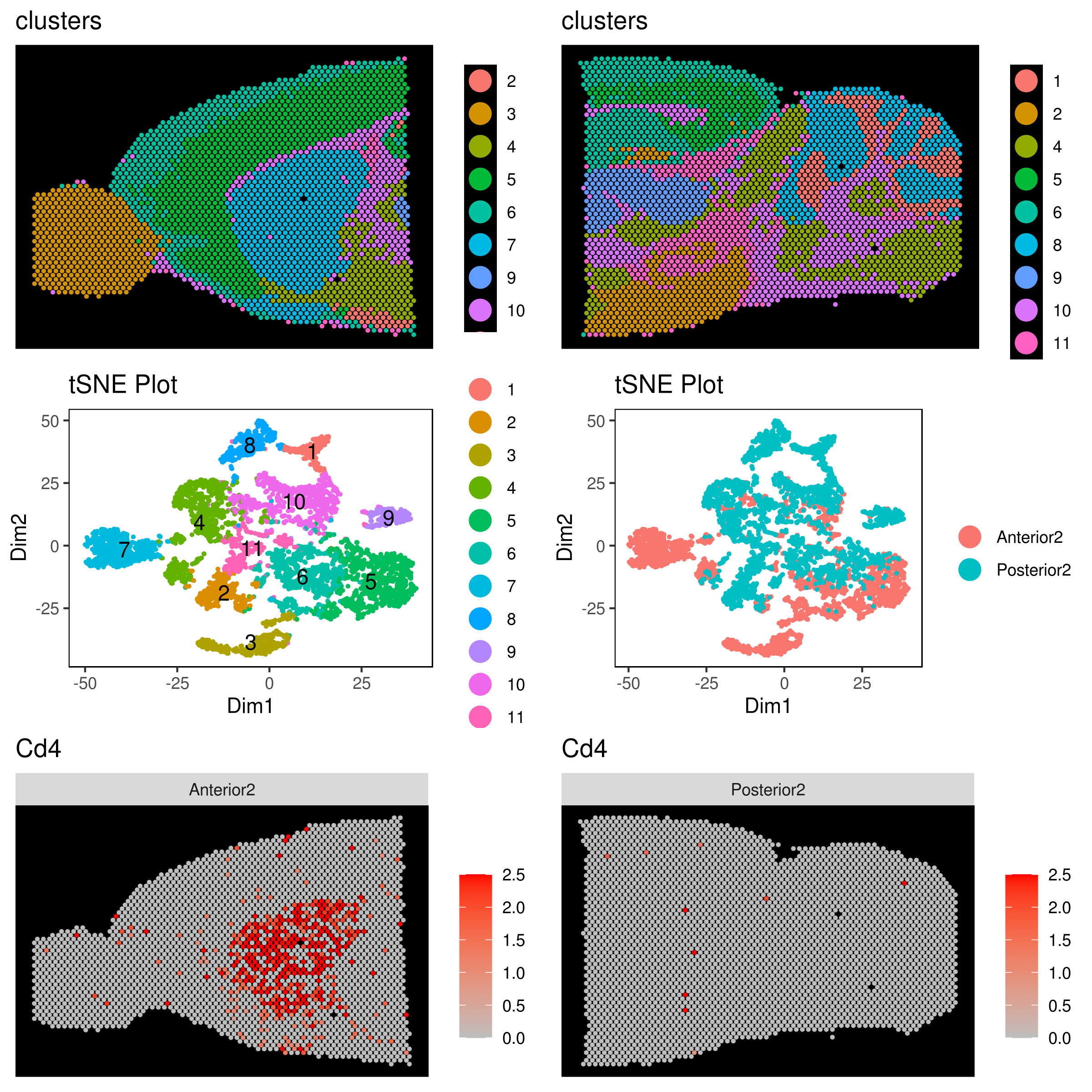
Single cell ATAC sequencing with scRNA-Seq (scATAC-Seq)
```r library("iCellR") my.data <- load10x("filteredgenebc_matrices/")
see the row names
row.names(my.data)
get peak names
ATAC <- grep("^chr",row.names(my.data),value=T)
get scATAC data
MyATAC <- subset(my.data, row.names(my.data) %in% ATAC) head(MyATAC)[1:3]
AAACAGCCAAGTGAAC.1 AAACAGCCACTGACCG.1 AAACAGCCATGATTGT.1
chr1.181218.181695 0 0 1
chr1.191296.191699 0 0 0
chr1.629770.630129 0 0 0
chr1.633806.634251 0 0 0
chr1.778422.779040 0 0 0
chr1.827306.827702 0 0 0
dim(MyATAC)
[1] 21923 6326
get RNA data
MyRNAs <- subset(my.data, !row.names(my.data) %in% ATAC) head(MyRNAs)[1:3]
AAACAGCCAAGTGAAC.1 AAACAGCCACTGACCG.1 AAACAGCCATGATTGT.1
MIR1302.2HG 0 0 0
FAM138A 0 0 0
OR4F5 0 0 0
AL627309.1 0 0 0
AL627309.3 0 0 0
AL627309.2 0 0 0
dim(MyRNAs)
[1] 36633 6326
make iCellR object
my.obj <- make.obj(MyRNAs)
add ATAC-Seq data
my.obj@atac.raw <- MyATAC my.obj@atac.main <- MyATAC
check your object
my.obj
,--. ,-----. ,--.,--.,------.
--'' .--./ ,---. | || || .--. '
,--.| | | .-. :| || || '--'.'
| |' '--'\ --. | || || |
--' -----'----'--'--'`--' '--'
An object of class iCellR version: 1.6.2 Raw/original data dimentions (rows,columns): 24127,6326 Data conditions: no conditions/single sample Row names: MIR1302.2HG,TTLL10.AS1,MRPL20.AS1 ... Columns names: AAACAGCCAAGTGAAC.1,AAACAGCCACTGACCG.1,AAACAGCCATGATTGT.1 ...
QC stats performed:FALSE, PCA performed:FALSE Clustering performed:FALSE, Number of clusters:0 tSNE performed:FALSE, UMAP performed:FALSE, DiffMap performed:FALSE Main data dimensions (rows,columns): 0,0 Normalization factors:,... Imputed data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0
######## scVDJ-seq
VDJ data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
######## CITE-seq
ADT raw data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT main data dimensions (rows,columns):0,0 ADT columns names:... ADT row names:...
######## scATAC-seq
ATAC raw data dimensions (rows,columns):21923,6326 ATAC main data dimensions (rows,columns):21923,6326 ATAC columns names:AAACAGCCAAGTGAAC.1... ATAC row names:chr1.181218.181695...
######## Spatial
Spatial data dimentions (rows,columns):0,0
##### iCellR object
```
From here do the regular scRNA-seq as expleind above. See example below
```r
QC
my.obj <- qc.stats(my.obj, s.phase.genes = s.phase, g2m.phase.genes = g2m.phase)
plot as mentioned above
filter
my.obj <- cell.filter(my.obj, min.mito = 0, max.mito = 0.07 , min.genes = 500, max.genes = 4000, min.umis = 0, max.umis = Inf)
normalize RNA
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "ranked.glsf", top.rank = 500)
normalize ADT
my.obj <- norm.adt(my.obj)
gene stats
my.obj <- gene.stats(my.obj, which.data = "main.data")
find genes for PCA
my.obj <- make.gene.model(my.obj, my.out.put = "data", dispersion.limit = 1.5, base.mean.rank = 500, no.mito.model = T, mark.mito = T, interactive = F, no.cell.cycle = T, out.name = "gene.model")
run PCA and the rest is as above
my.obj <- run.pca(my.obj, method = "gene.model", gene.list = my.obj@gene.model,data.type = "main")
tSNE
my.obj <- run.pc.tsne(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
UMAP
my.obj <- run.umap(my.obj, dims = 1:10)
KNetL
my.obj <- run.knetl(my.obj, dims = 1:20, zoom = 200, dim.redux = "umap")
clustering based on KNetL
my.obj <- iclust(my.obj, sensitivity = 200, data.type = "knetl")
clustering based on PCA
my.obj <- iclust(my.obj, sensitivity = 100, data.type = "pca", dims=1:10)
check clusters and adjust if needed (optinal)
cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T)
my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 3, to.clust = 4)
my.obj <- change.clust(my.obj, change.clust = 3, to.clust = 10)
order clusters
my.obj <- clust.ord(my.obj,top.rank = 500, how.to.order = "distance")
plot
A= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "pca",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) B= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "umap",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) C= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "tsne",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T) D= cluster.plot(my.obj,plot.type = "knetl",interactive = F,cell.size = 0.5,cell.transparency = 1, anno.clust=T)
library(gridExtra) png('AllClusts.png', width = 12, height = 10, units = 'in', res = 300) grid.arrange(A,B,C,D) dev.off()
save object
save(my.obj, file = "my.obj.Robj")
find markers
marker.genes <- findMarkers(my.obj, data.type = "main", fold.change = 2, padjval = 0.1, uniq = F, positive = T)
marker.genes1 <- cbind(row = rownames(marker.genes), marker.genes) write.table((marker.genes1),file="marker.genes.tsv", sep="\t", row.names =F)
MyGenes <- top.markers(marker.genes, topde = 10, min.base.mean = 0.2, filt.ambig = F) MyGenes <- unique(MyGenes)
png('heatmapgggenes.png', width = 10, height = 10, units = 'in', res = 300) heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters",cell.sort = F, conds.to.plot = NULL) dev.off() ```
Work on scATAC data (normalize and find marker peaks for each cluster)
```r
normalize ACAT
my.obj <- norm.data(my.obj, norm.method = "ranked.glsf", top.rank = 500, ATAC.data = TRUE, ATAC.filter = TRUE)
marker.peaks <- findMarkers(my.obj, data.type = "atac", fold.change = 2, padjval = 0.1, uniq = F, positive = T)
marker.peaks1 <- cbind(row = rownames(marker.peaks), marker.peaks) write.table((marker.peaks1),file="marker.peaks.tsv", sep="\t", row.names =F)
head(marker.peaks1)
row baseMean baseSD
chr17.64986035.64986113 chr17.64986035.64986113 0.01217359 0.18257818
chr1.26542287.26542678 chr1.26542287.26542678 0.05828764 0.80077656
chr4.8199063.8199275 chr4.8199063.8199275 0.04280424 0.56205649
chr20.50274929.50275237 chr20.50274929.50275237 0.04684509 0.63361490
chr2.218382038.218382236 chr2.218382038.218382236 0.03122394 0.31153105
chr11.1760469.1760814 chr11.1760469.1760814 0.07050175 0.63322284
AvExpInCluster AvExpInOtherClusters foldChange
chr17.64986035.64986113 0.07868394 0.002346603 33.530999
chr1.26542287.26542678 0.33849093 0.016887273 20.044144
chr4.8199063.8199275 0.24803497 0.012481148 19.872769
chr20.50274929.50275237 0.27007513 0.013862584 19.482308
chr2.218382038.218382236 0.17736269 0.009631770 18.414340
chr11.1760469.1760814 0.39043782 0.023230813 16.806894
log2FoldChange pval padj clusters
chr17.64986035.64986113 5.067424 1.187697e-05 2.875415e-02 1
chr1.26542287.26542678 4.325109 3.653916e-05 8.539202e-02 1
chr4.8199063.8199275 4.312721 6.059691e-06 1.489472e-02 1
chr20.50274929.50275237 4.284093 2.871301e-05 6.779143e-02 1
chr2.218382038.218382236 4.202758 6.359572e-10 1.677019e-06 1
chr11.1760469.1760814 4.070981 6.813447e-11 1.800794e-07 1
gene cluster1 cluster2
chr17.64986035.64986113 chr17.64986035.64986113 0.0786839378 0.000000000
chr1.26542287.26542678 chr1.26542287.26542678 0.3384909326 0.008895062
chr4.8199063.8199275 chr4.8199063.8199275 0.2480349741 0.038672840
chr20.50274929.50275237 chr20.50274929.50275237 0.2700751295 0.028703704
chr2.218382038.218382236 chr2.218382038.218382236 0.1773626943 0.000000000
chr11.1760469.1760814 chr11.1760469.1760814 0.3904378238 0.004537037
cluster3 cluster4 cluster5 cluster6
chr17.64986035.64986113 0.000000000 0.0000000000 0.0006934750 0.0010038760
chr1.26542287.26542678 0.031485714 0.0029244992 0.0052261002 0.0041264535
chr4.8199063.8199275 0.000000000 0.0007226502 0.0027450683 0.0113212209
chr20.50274929.50275237 0.027092857 0.0121741140 0.0041820941 0.0051516473
chr2.218382038.218382236 0.004292857 0.0042095532 0.0006722307 0.0038561047
chr11.1760469.1760814 0.071678571 0.0177288136 0.0141820941 0.0061099806
cluster7 cluster8
chr17.64986035.64986113 0.003099029 0.009080357
chr1.26542287.26542678 0.047110680 0.044484375
chr4.8199063.8199275 0.014819417 0.028651786
chr20.50274929.50275237 0.025499029 0.028765625
chr2.218382038.218382236 0.011988350 0.035508929
chr11.1760469.1760814 0.042093204 0.050708705
MyGenes <- top.markers(marker.peaks, topde = 10, min.base.mean = 0.2, filt.ambig = F) MyGenes <- unique(MyGenes)
png('heatmapggpeaks.png', width = 10, height = 10, units = 'in', res = 300) heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters",cell.sort = F, conds.to.plot = NULL, data.type = "atac") dev.off()
my.obj <- run.impute(my.obj,data.type = "knetl", nn = 10, ATAC.data = FALSE)
png('heatmapggpeaks.png', width = 10, height = 10, units = 'in', res = 300) heatmap.gg.plot(my.obj, gene = MyGenes, interactive = F, cluster.by = "clusters",cell.sort = F, conds.to.plot = NULL, data.type = "atac.imputed") dev.off()
you can also find avarage peak intensity per cluster
my.obj <- clust.avg.exp(my.obj, data.type = "atac") head(my.obj@clust.avg)
gene cluster1 cluster2 ...
chr1.100037799.100038931 0.38238731 0.36750000 ...
chr1.100132733.100133298 0.11195725 1.13593827 ...
chr1.100249637.100250160 0.09851425 0.09511728 ...
chr1.100265992.100266479 0.06768394 0.17707407 ...
chr1.10032488.10033387 0.35273705 0.14885802 ...
chr1.100352150.100352921 0.12006088 0.00000000 ...
find out which cluster has the highest number
dat <- as.data.frame(t((my.obj@clust.avg)[,-1])) dat <- hto.anno(hto.data = dat)
head(dat$assignment.annotatio)
[1] cluster1 cluster2 cluster4 cluster2 cluster3 cluster4
8 Levels: cluster1 cluster2 cluster3 cluster4 cluster5 ... cluster8
```
Peak analysis
```r
make a bed file per cluster from the marker.peaks file you made up here
make.bed(marker.peaks)
load packages
library(ChIPseeker) library(clusterProfiler)
load genome
require(TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg38.knownGene) txdb <- TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg38.knownGene Anno="org.Hs.eg.db"
load bed files
Mylist1 = list.files(pattern=".bed") Mylist1
Mylist <- as.list(Mylist1) NAMES <- gsub('_peaks.bed','',Mylist1) names(Mylist) <- NAMES files <- Mylist files
perform analysis (example)
promoter <- getPromoters(TxDb=txdb, upstream=3000, downstream=3000) tagMatrixList <- lapply(files, getTagMatrix, windows=promoter)
pdf("Plot_ProfileLineAll.pdf") plotAvgProf(tagMatrixList, xlim=c(-3000, 3000)) dev.off()
pdf('Plot_ProfileLine.pdf', width = 8, height = 10) plotAvgProf(tagMatrixList, xlim=c(-3000, 3000), facet="row") dev.off()
pdf("Plot_heatmaps.pdf", width = 50, height = 6) tagHeatmap(tagMatrixList, xlim=c(-3000, 3000), color=NULL) dev.off()
annotate
peakAnnoList <- lapply(files, annotatePeak, TxDb=txdb, tssRegion=c(-3000, 3000), verbose=FALSE)
plot annotatin
pdf("Plot_AnnoBar.pdf") plotAnnoBar(peakAnnoList) dev.off()
######### peak annotation
peakAnnoList <- lapply(files, annotatePeak, TxDb=txdb, tssRegion=c(-3000, 3000), verbose=FALSE, annoDb=Anno)
capture.output(peakAnnoList, file = "peakAnnoList.txt")
genes = lapply(peakAnnoList, function(i) as.data.frame(i))
lapply(1:length(genes), function(i) write.table(genes[[i]], file = paste0(names(genes[i]), ".xls"), row.names = FALSE, sep="\t"))
```
Merging scATAC files with different intervals (as dipicted in bedtools website)
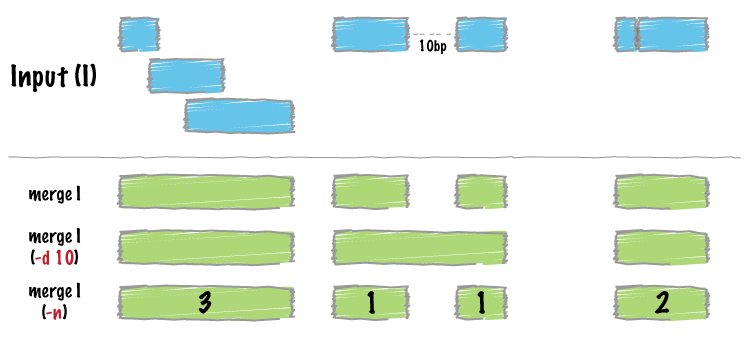
```
Let's say you have 2 files that you need to merege
example file
C <- load10x("count-JJsnCcDNA/",gene.name = 2) M <- load10x("count-JJsnMcDNA/",gene.name = 2)
ATAC.C <- grep("^chr",row.names(C),value=T) ATAC.M <- grep("^chr",row.names(M),value=T)
MyATAC.C <- subset(C, row.names(C) %in% ATAC.C) MyATAC.M <- subset(M, row.names(M) %in% ATAC.M)
head(MyATAC.C)[1:3]
C <- MyATAC.C M <- MyATAC.M
dim(C)
[1] 58678 4211
dim(M)
[1] 57776 4736
f1 <- row.names(C) f2 <- row.names(M)
all.peaks <- c(f1,f2) length(all.peaks)
[1] 116454
make a bed file
chr <- as.character(as.matrix(data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(all.peaks),'.',fixed=TRUE)))[1])) start <- data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(all.peaks),'.',fixed=TRUE)))[2] end <- data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(all.peaks),'.',fixed=TRUE)))[3]
DAT <- as.data.frame(chr) DAT$start <- as.numeric(as.matrix(start)) DAT$end <- as.numeric(as.matrix(end)) head(DAT)
chr start end
1 chr1 181218 181695
2 chr1 191296 191699
3 chr1 629770 630129
4 chr1 633806 634251
5 chr1 778422 779040
6 chr1 827306 827702
make Genomic Ranges
library("GenomicRanges")
all.gr <- GRanges(seqnames=DAT$chr,ranges=IRanges(start=DAT$start,end=DAT$end))
all.gr
GRanges object with ?? ranges and 0 metadata columns:
seqnames ranges strand
[1] chr1 181218-181695 *
[2] chr1 191296-191699 *
[3] chr1 629770-630129 *
[4] chr1 633806-634251 *
[5] chr1 778422-779040 *
... ... ... ...
[52] chr1 1303892-1306216 *
[53] chr1 1307242-1309359 *
[54] chr1 1324425-1325236 *
[55] chr1 1348940-1349958 *
[56] chr1 1372031-1372220 *
-------
seqinfo: 1 sequence from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths
############ sort and merge the peaks
mrg <- reduce(all.gr)
Before merge
length(all.gr)
[1] 116454
after merge
length(mrg)
[1] 71426
#################### choose file and give name
MyFile <- f1 name="f1_new.bed"
#################### copy paste the code here to make a new bed file
#################### the new bed has the old and new intervals (new intervals to be replaced with old)
chr <- as.character(as.matrix(data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(MyFile),'.',fixed=TRUE)))[1])) start <- data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(MyFile),'.',fixed=TRUE)))[2] end <- data.frame(do.call('rbind', strsplit(as.character(MyFile),'.',fixed=TRUE)))[3]
make a bed file
DAT <- as.data.frame(chr) DAT$start <- as.numeric(as.matrix(start)) DAT$end <- as.numeric(as.matrix(end)) MyFile <- DAT
make intrval file to replace to new regions
MyFile.gr <- GRanges(seqnames=MyFile$chr,ranges=IRanges(start=MyFile$start,end=MyFile$end))
OverLap <- findOverlaps(MyFile.gr, mrg)
OLD1 <- (OverLap@from) NEW1 <- (OverLap@to)
OLD = MyFile.gr[OLD1] NEW = mrg[NEW1]
chr <- as.character(OLD@seqnames) DAT <- as.data.frame(chr) DAT$start <- OLD@ranges@start DAT$end <- (OLD@ranges@start + OLD@ranges@width) - 1
DAT$new.chr<- as.character(NEW@seqnames) DAT$new.start <- NEW@ranges@start DAT$new.end <- (NEW@ranges@start + NEW@ranges@width) - 1
head(DAT)
chr start end new.chr new.start new.end
1 chr1 3247563 3248453 chr1 3247563 3248453
2 chr1 3360706 3361554 chr1 3360706 3361554
3 chr1 3552372 3553230 chr1 3552372 3553230
4 chr1 3645171 3646034 chr1 3645093 3646034
5 chr1 3670318 3671081 chr1 3670318 3671090
6 chr1 3671326 3672230 chr1 3671314 3672230
dim(DAT)
58678 6
length(MyFile.gr)
58678
diff
have = mrg[unique(NEW1)] dontHave = mrg[-unique(NEW1)]
ADD <- dontHave L <- length(as.character(ADD@seqnames)) chr <-rep("NA",L) DAT1 <- as.data.frame(chr) DAT1$start <- rep("NA",L) DAT1$end <- rep("NA",L) DAT1$new.chr<- as.character(ADD@seqnames) DAT1$new.start <- ADD@ranges@start DAT1$new.end <- (ADD@ranges@start + ADD@ranges@width) - 1
Final.DAT <- rbind(DAT,DAT1)
Write
write.table(Final.DAT,name,row.names=FALSE,sep="\t", quote = FALSE)
reapeat this process for f2 (M) as well
The first 3 columns are the original peaks and the last 3 are the ones that need to be replaced with original one. The NA peaks would also get the new peak ids but in the matrix the cells will have 0 for expressions. To do this use the iCellR function replace.peak.id.
MyATAC.C <- replace.peak.id(atac.data=MyATAC.C, bed.file = Final.DAT.C) MyATAC.M <- replace.peak.id(atac.data=MyATAC.M, bed.file = Final.DAT.M)
finally aggregate the samples and add to iCellR object
my.atac.data <- data.aggregation(samples = c("MyATAC1","MyATAC2","MyATAC3"), condition.names = c("WT","KO","Ctrl"))
add ATAC-Seq data
my.obj@atac.raw <- my.atac.data my.obj@atac.main <- my.atac.data ```
Owner
- Name: Alireza Khodadadi-Jamayran
- Login: rezakj
- Kind: user
- Location: Applied Bioinformatics Labs, Langone Medical Center, New York University, NY.
- Website: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=author:%22Khodadadi-Jamayran%20A%22
- Repositories: 2
- Profile: https://github.com/rezakj
Assistant Director, Applied Bioinformatics Labs, New York University School of Medicine
GitHub Events
Total
- Issues event: 2
- Watch event: 4
Last Year
- Issues event: 2
- Watch event: 4
Committers
Last synced: over 2 years ago
Top Committers
| Name | Commits | |
|---|---|---|
| Alireza Khodadadi-Jamayran | r****j | 61 |
| Khodadadi-Jamayran | k****1@K****e | 5 |
| Khodadadi-Jamayran | k****1@k****g | 5 |
| Khodadadi-Jamayran | k****1@K****l | 2 |
Committer Domains (Top 20 + Academic)
Issues and Pull Requests
Last synced: 6 months ago
All Time
- Total issues: 36
- Total pull requests: 3
- Average time to close issues: about 1 month
- Average time to close pull requests: about 1 year
- Total issue authors: 27
- Total pull request authors: 1
- Average comments per issue: 2.28
- Average comments per pull request: 0.0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Past Year
- Issues: 2
- Pull requests: 0
- Average time to close issues: N/A
- Average time to close pull requests: N/A
- Issue authors: 1
- Pull request authors: 0
- Average comments per issue: 0.0
- Average comments per pull request: 0
- Merged pull requests: 0
- Bot issues: 0
- Bot pull requests: 0
Top Authors
Issue Authors
- Yale73 (4)
- IkjotSidhu (3)
- YKH810325 (2)
- joybarrett08 (2)
- jajcobyang (2)
- nicholascwho (2)
- MavroLucic (1)
- zehualilab (1)
- bioysu (1)
- france-hub (1)
- lucas-bishop (1)
- gt7901b (1)
- rohitrrj (1)
- honghh2018 (1)
- jsmoon4 (1)
Pull Request Authors
- kant (3)
Top Labels
Issue Labels
Pull Request Labels
Packages
- Total packages: 1
-
Total downloads:
- cran 612 last-month
- Total docker downloads: 20,406
- Total dependent packages: 0
- Total dependent repositories: 0
- Total versions: 24
- Total maintainers: 1
cran.r-project.org: iCellR
Analyzing High-Throughput Single Cell Sequencing Data
- Homepage: https://github.com/rezakj/iCellR
- Documentation: http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/iCellR/iCellR.pdf
- License: GPL-2
-
Latest release: 1.6.7
published about 2 years ago
Rankings
Maintainers (1)
Dependencies
- R >= 3.3.0 depends
- ggplot2 * depends
- plotly * depends
- Hmisc * imports
- Matrix * imports
- NbClust * imports
- RANN * imports
- RColorBrewer * imports
- Rcpp * imports
- Rtsne * imports
- ape * imports
- data.table * imports
- ggdendro * imports
- ggpubr * imports
- ggrepel * imports
- gridExtra * imports
- hdf5r * imports
- htmlwidgets * imports
- igraph * imports
- jsonlite * imports
- knitr * imports
- methods * imports
- pheatmap * imports
- plyr * imports
- png * imports
- progress * imports
- reshape * imports
- scatterplot3d * imports
- shiny * imports
- uwot * imports
